CV 42 - USS Franklin D. Roosevelt
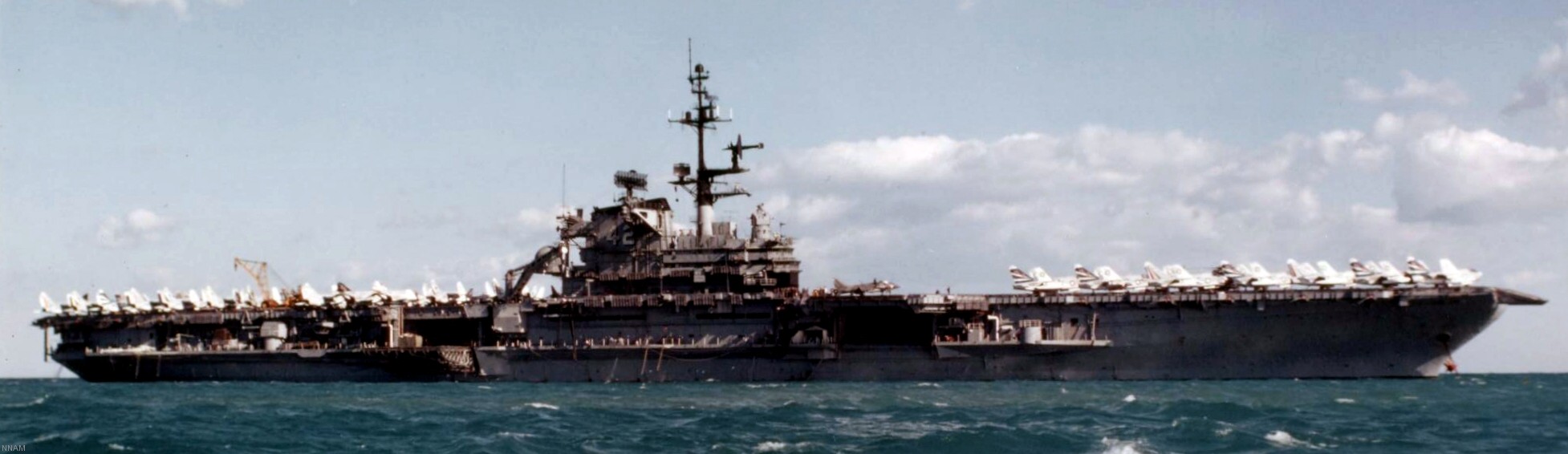 with Carrier Air Wing 19 (CVW-19) embarked - 1976-77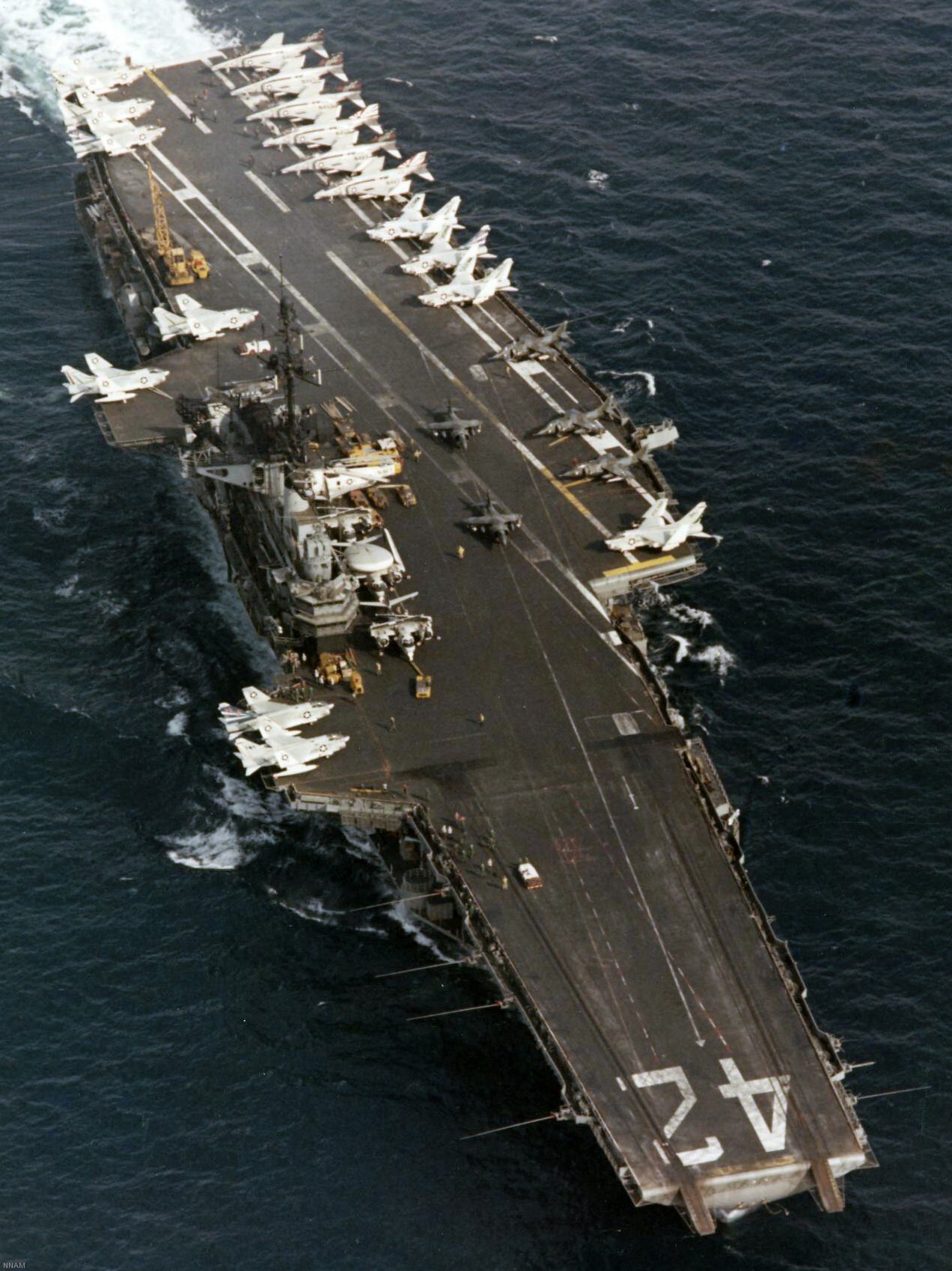  with Carrier Air Wing 19 (CVW-19) embarked - 1976-77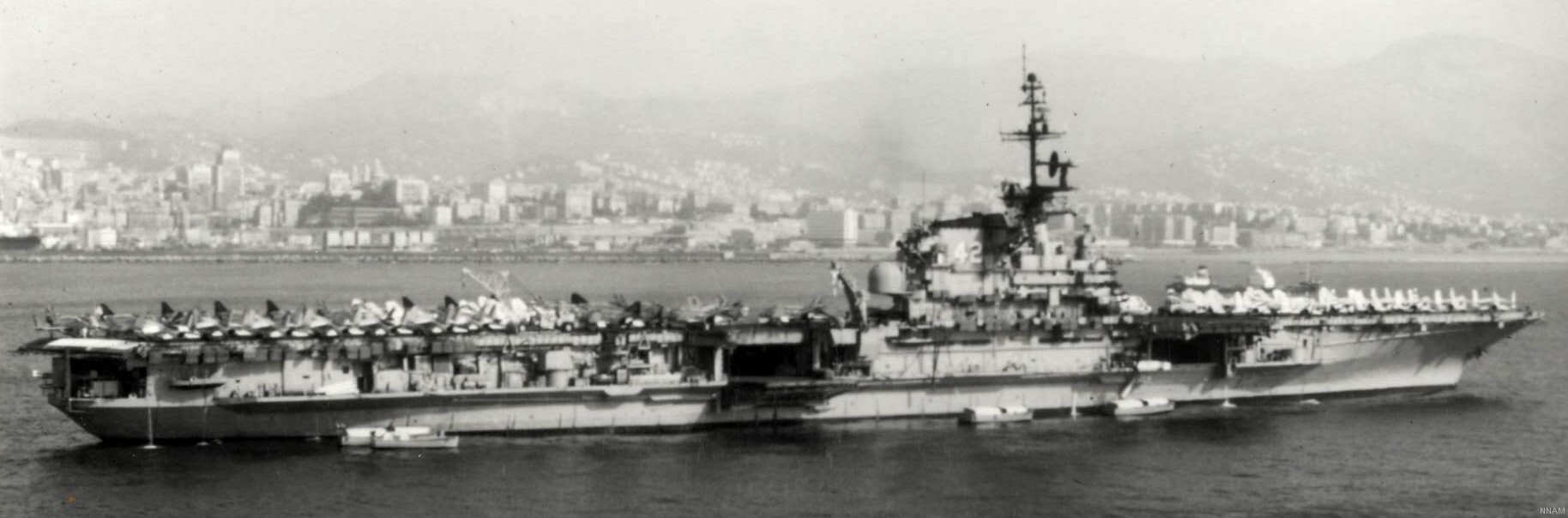  with Carrier Air Wing 19 (CVW-19) embarked - 1976-77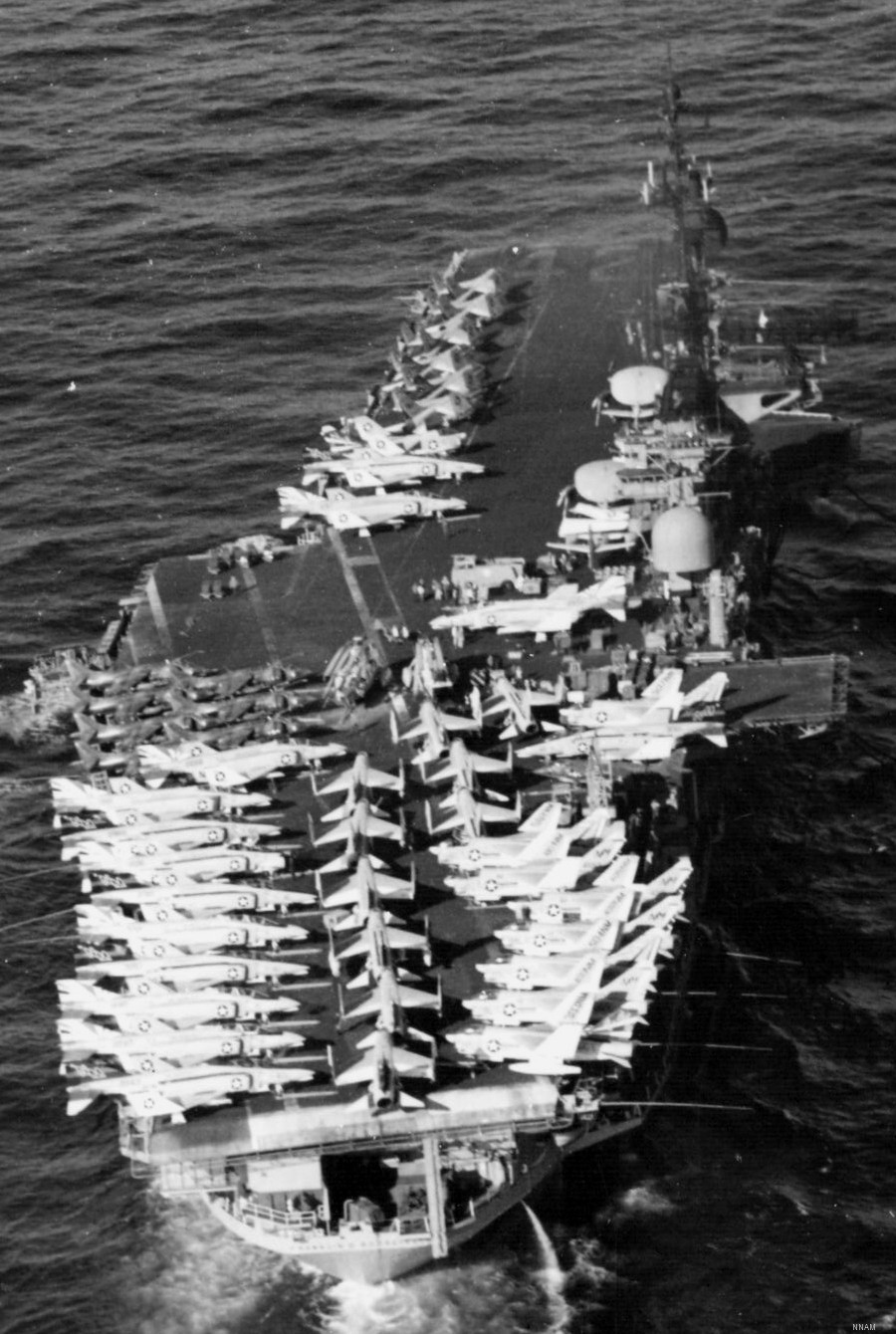  with Carrier Air Wing 19 (CVW-19) embarked - October 1976redesignated CV 42 on June 30, 1975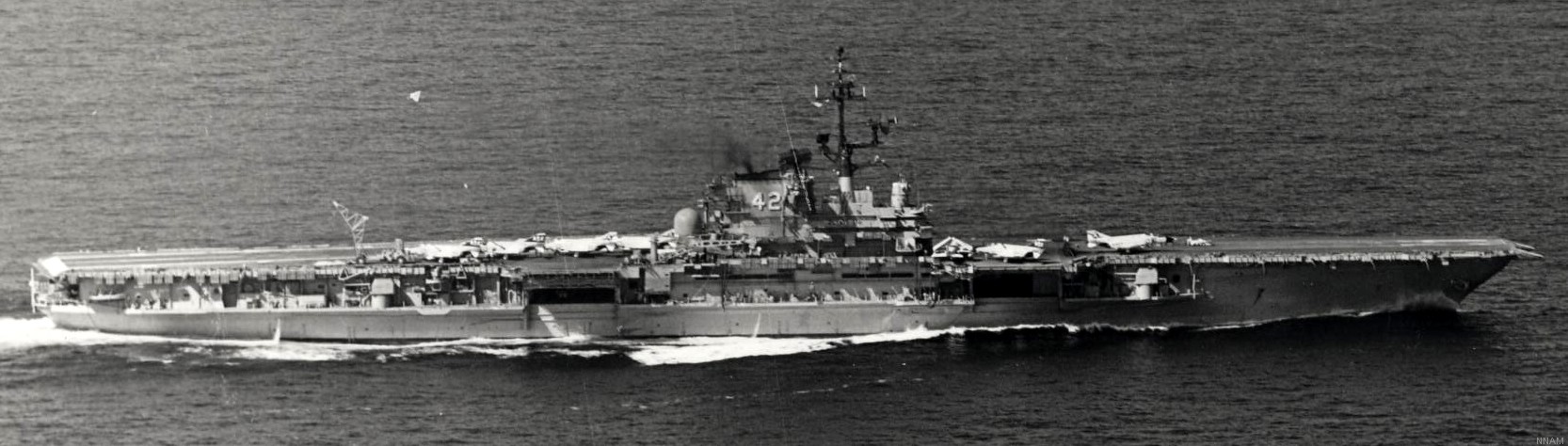  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1975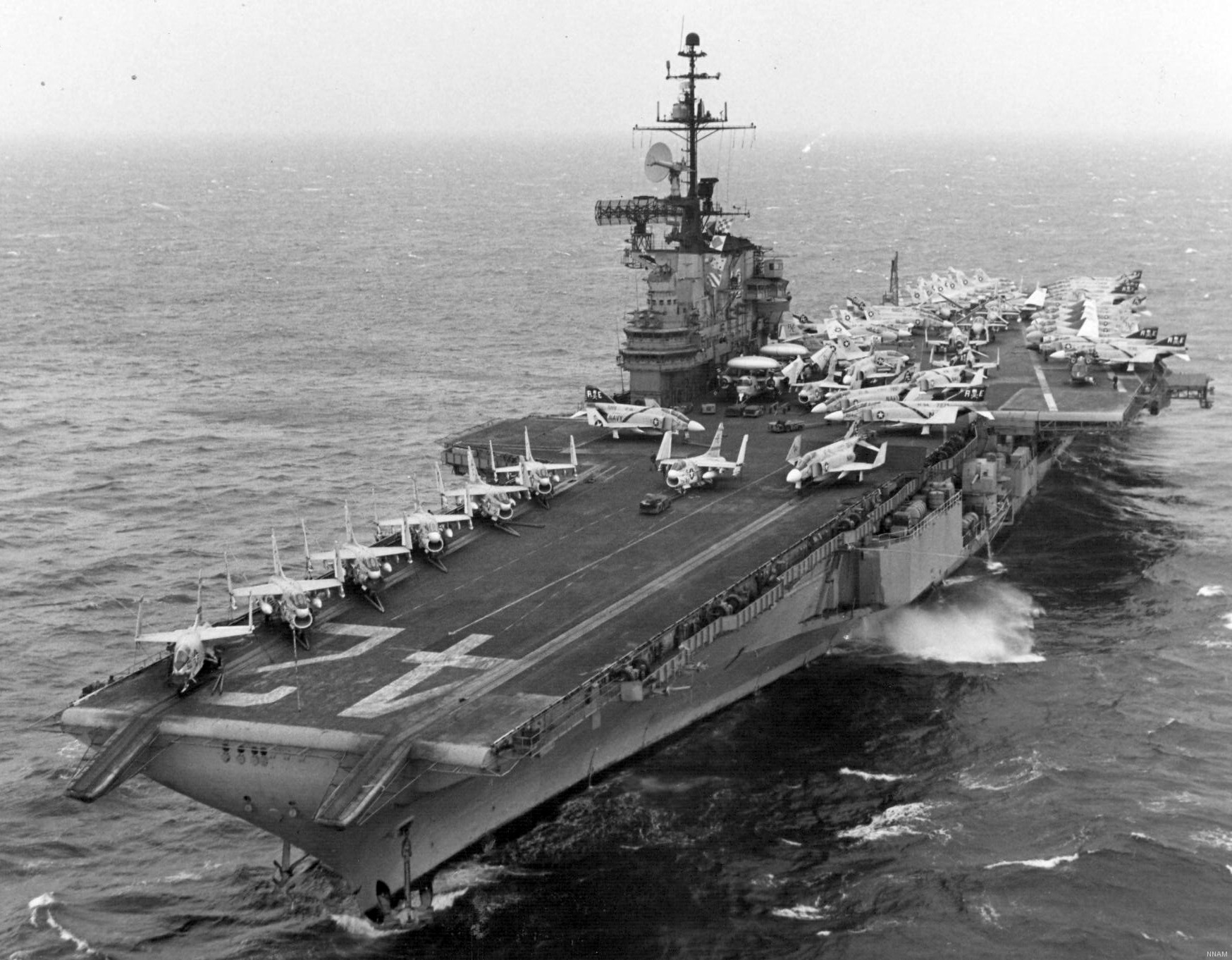  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1973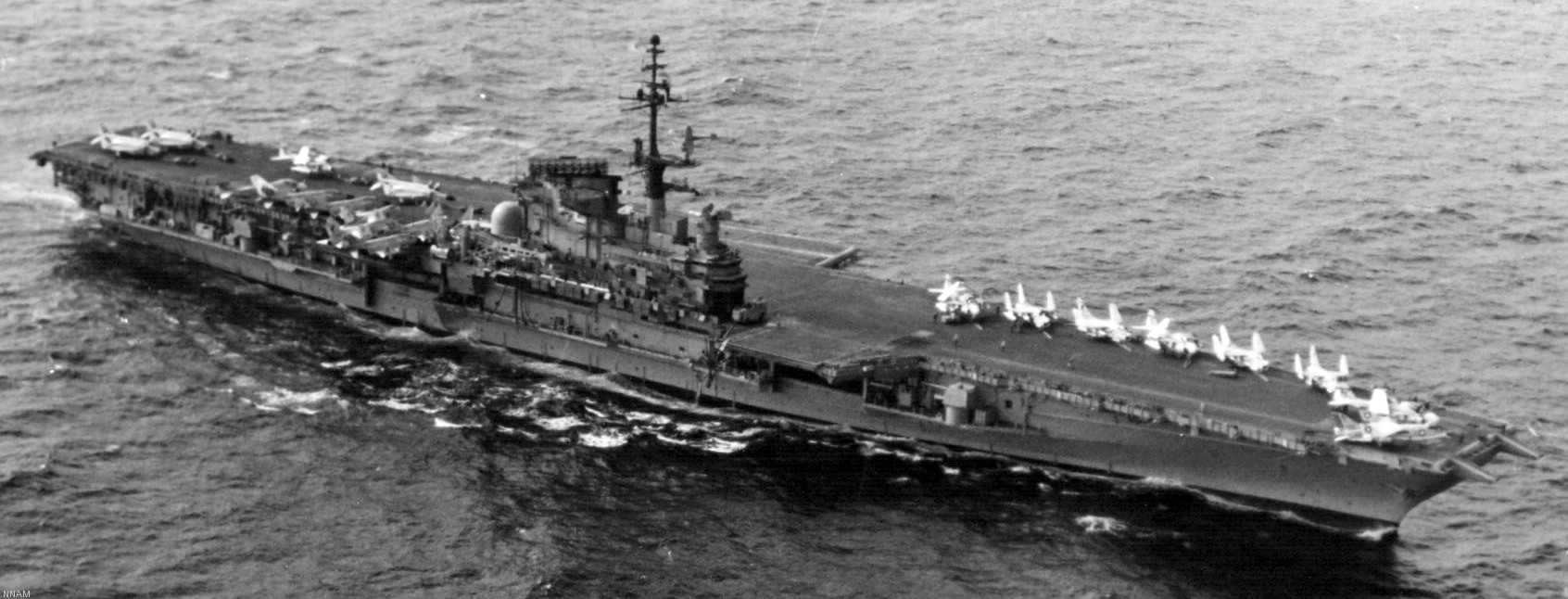  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1973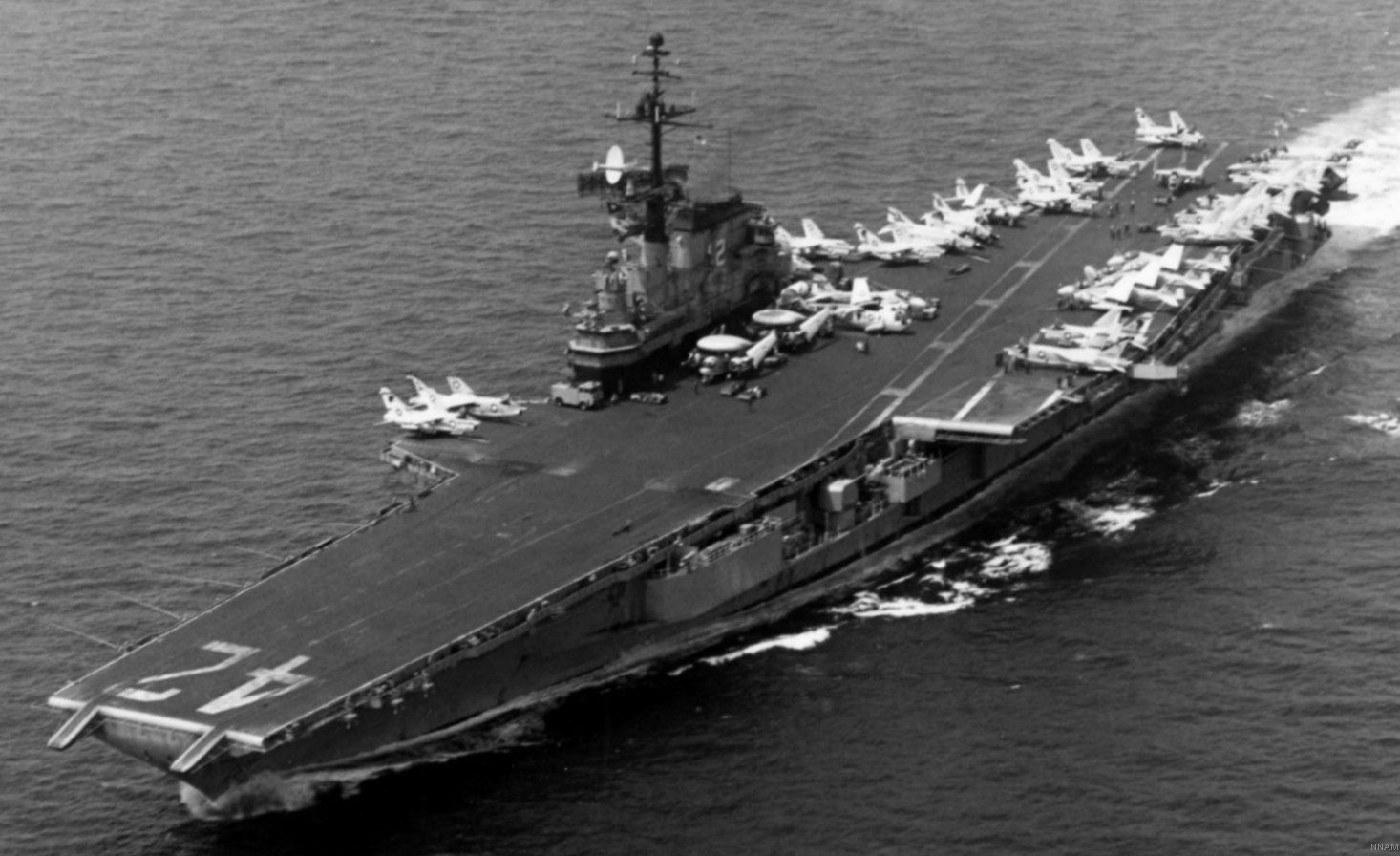  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1973  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1973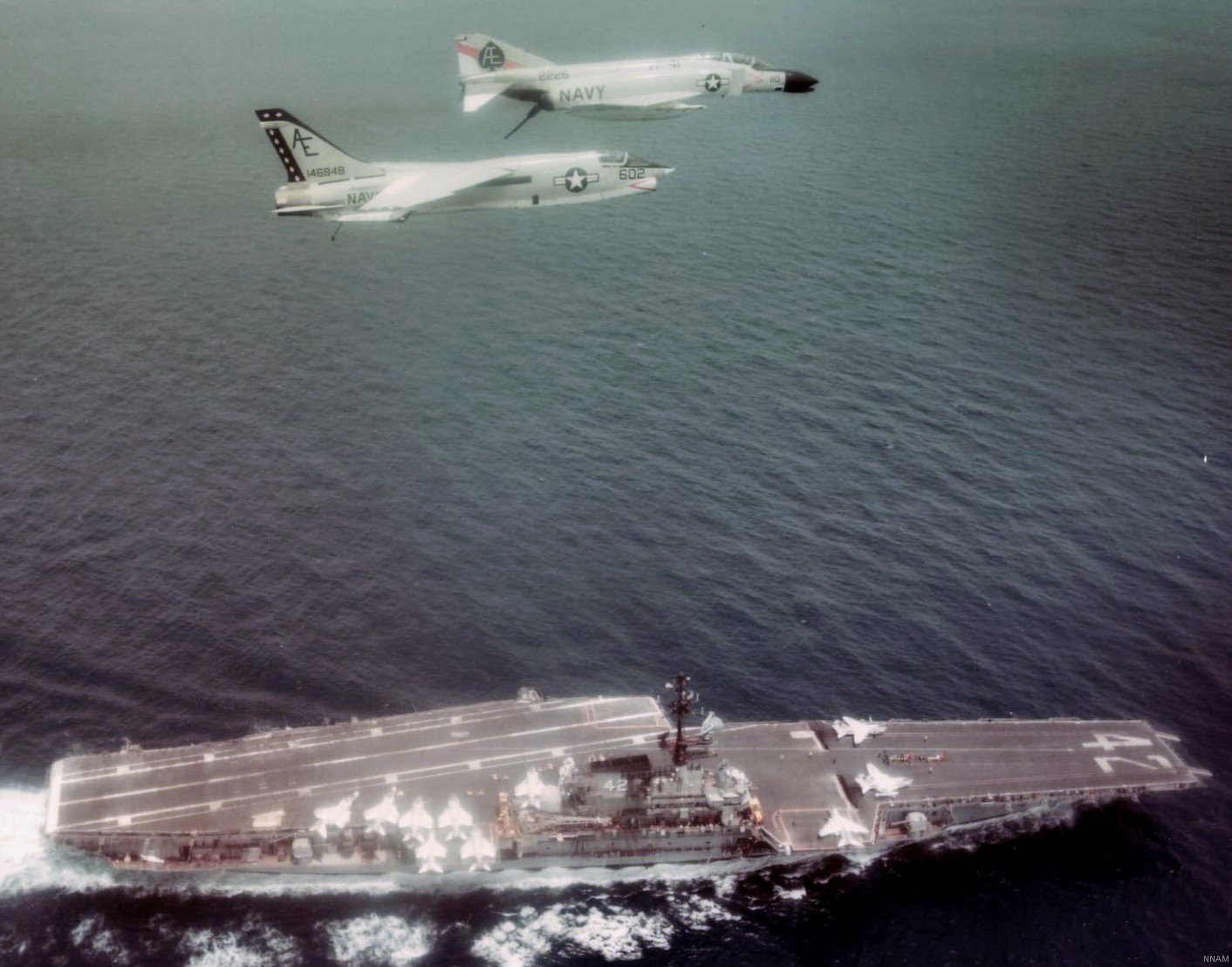  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1973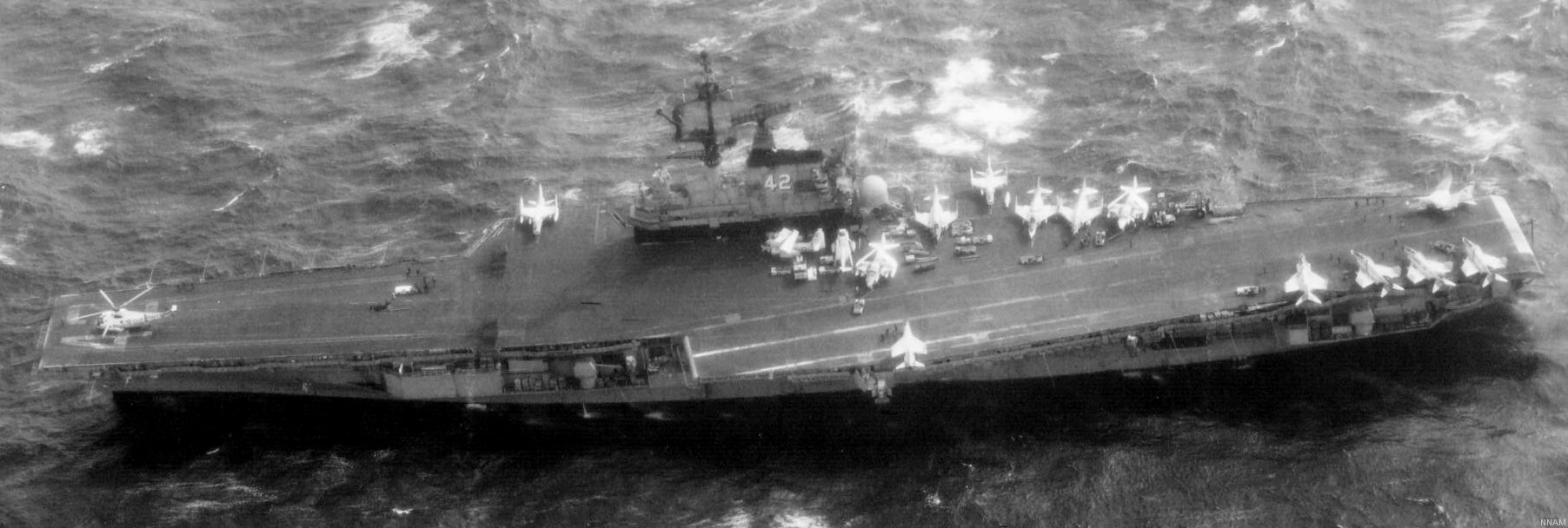  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1972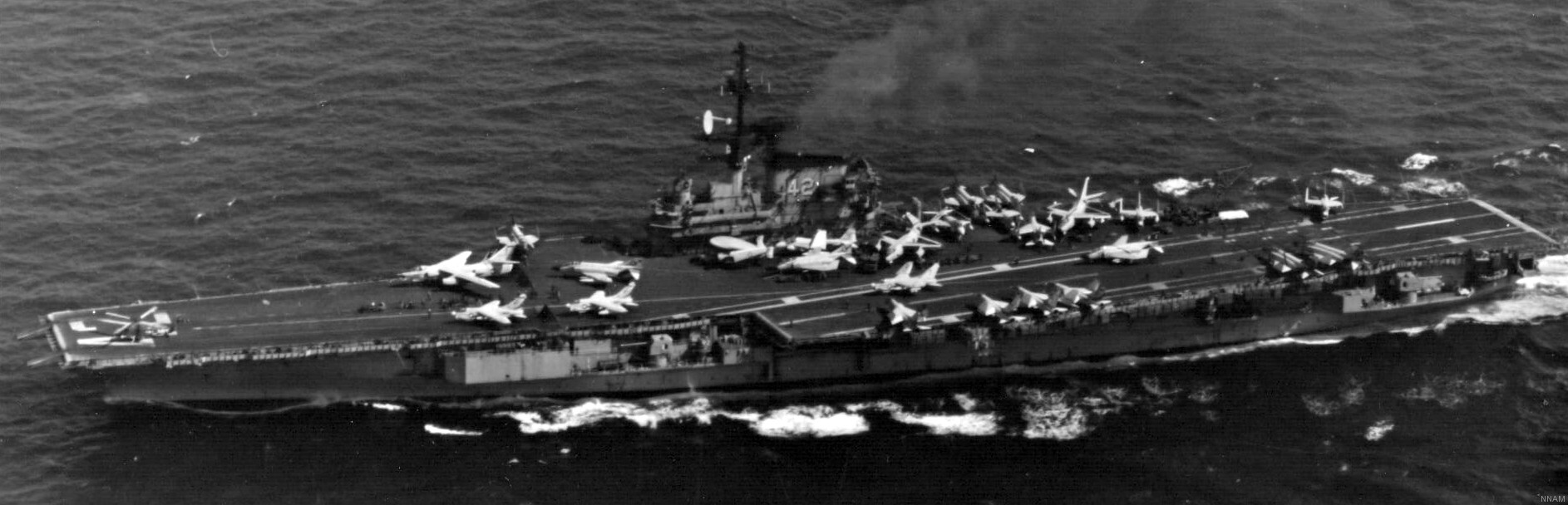  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1970-71  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1970-71  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1970-71  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1970-71  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - circa 1970-71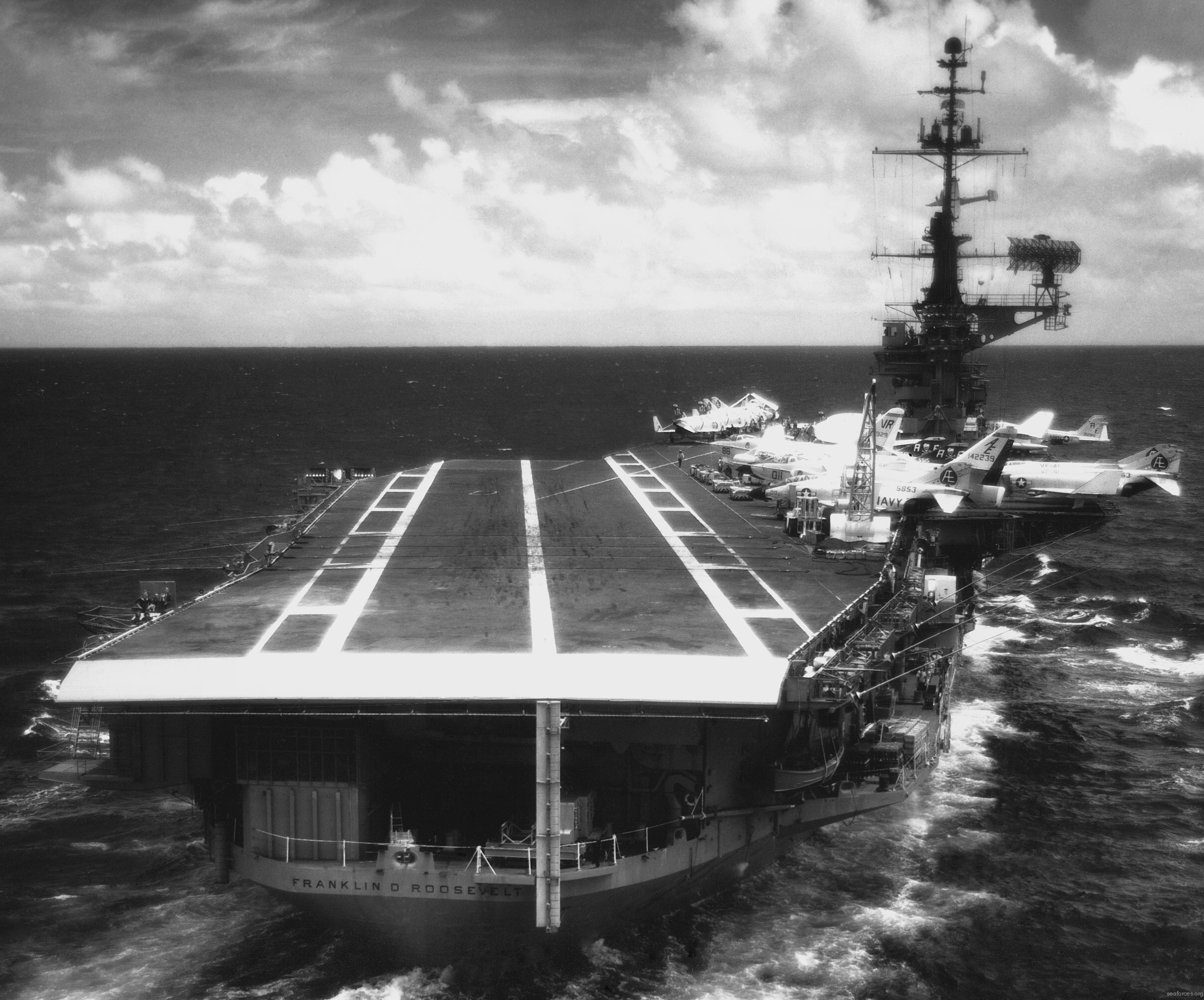  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - 1970's  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - 1970's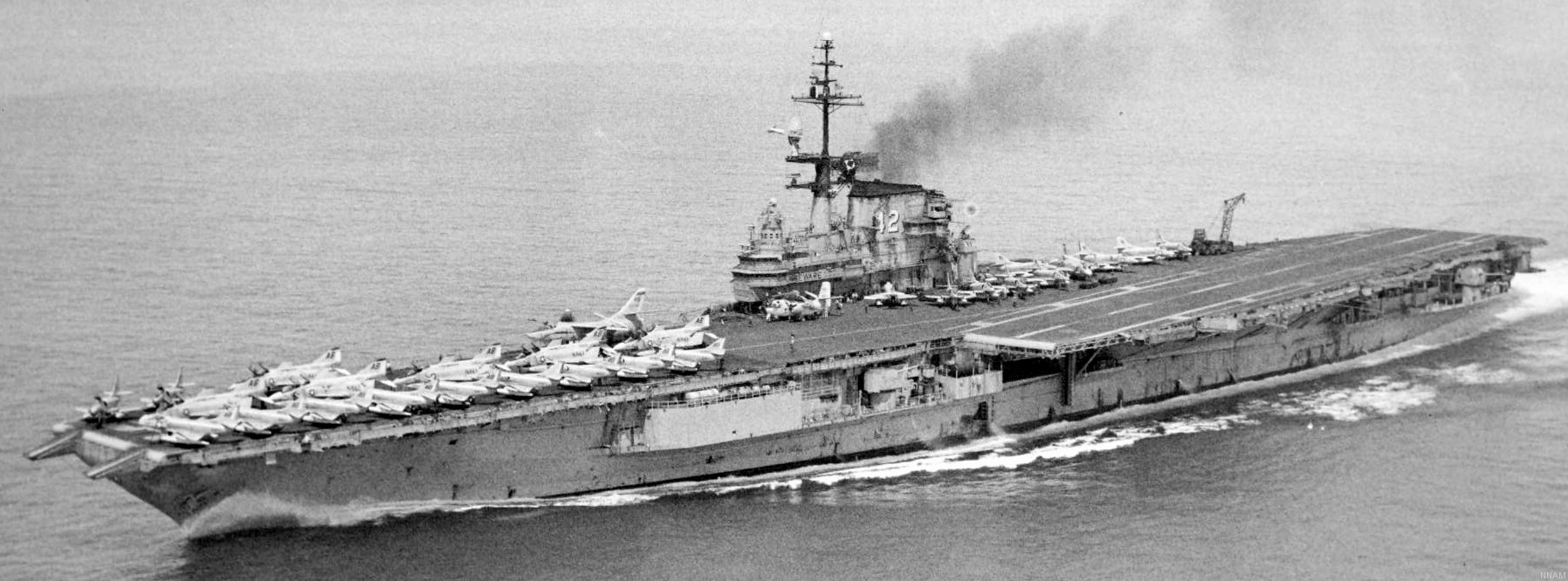  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - 1969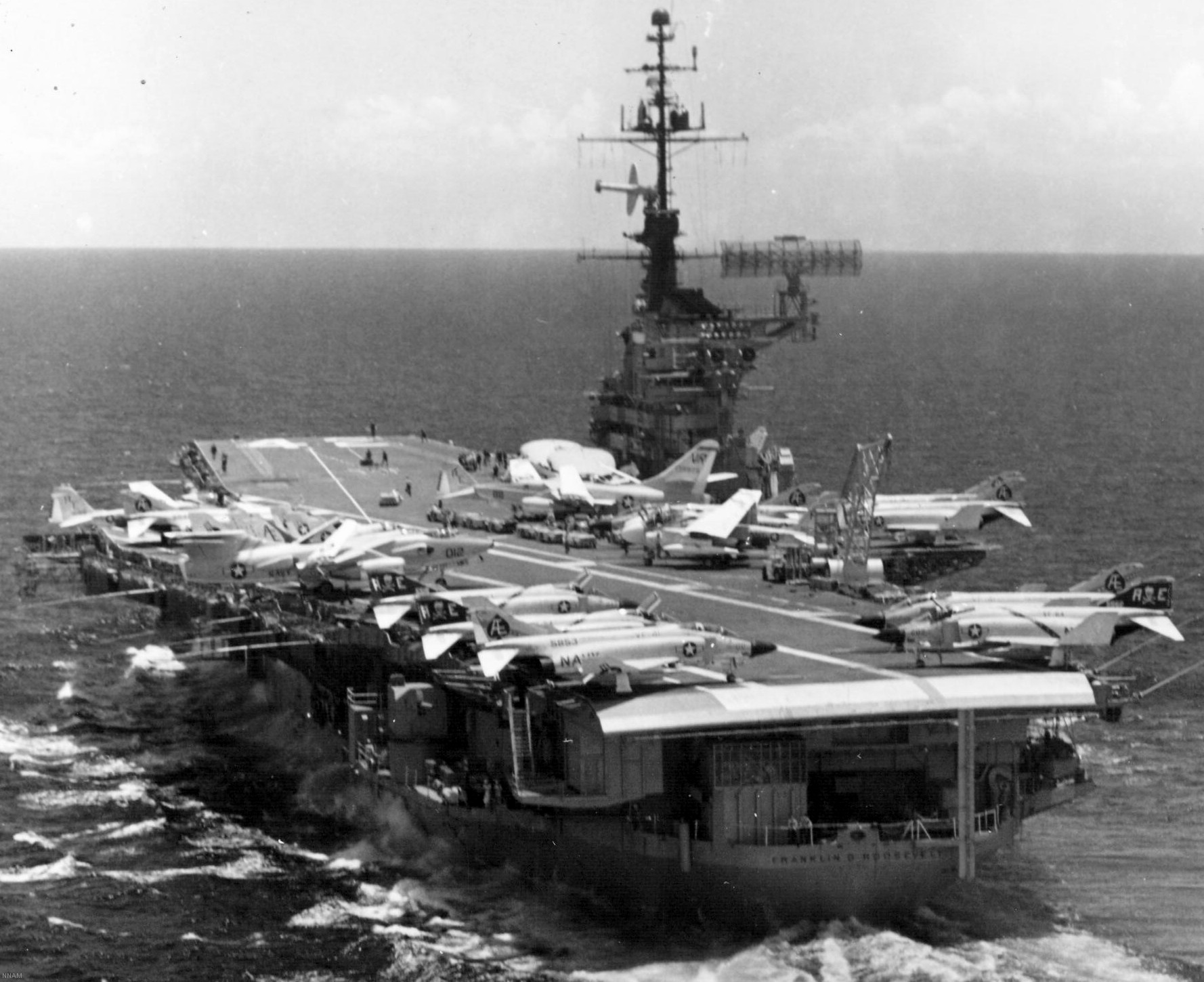  with Carrier Air Wing 6 (CVW-6) embarked - July 1969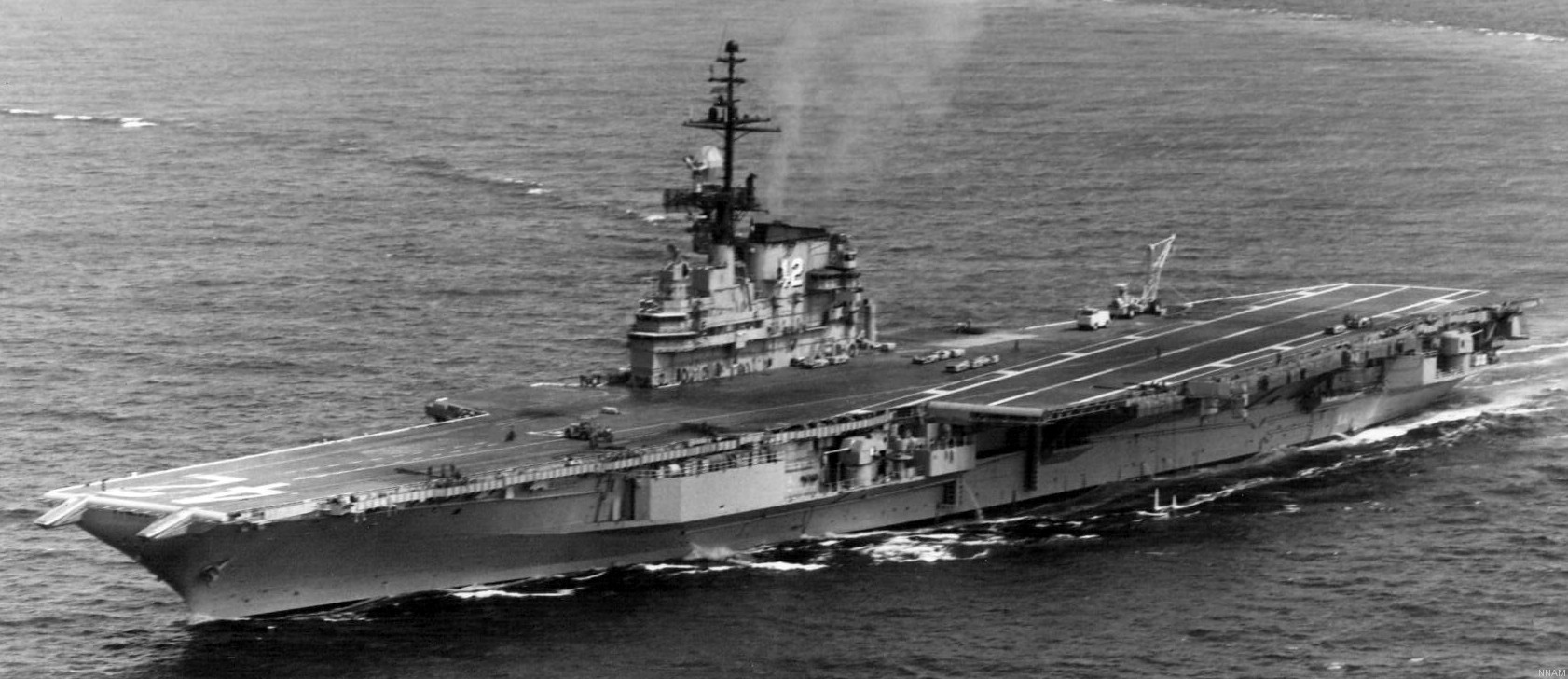  after refit - July 1969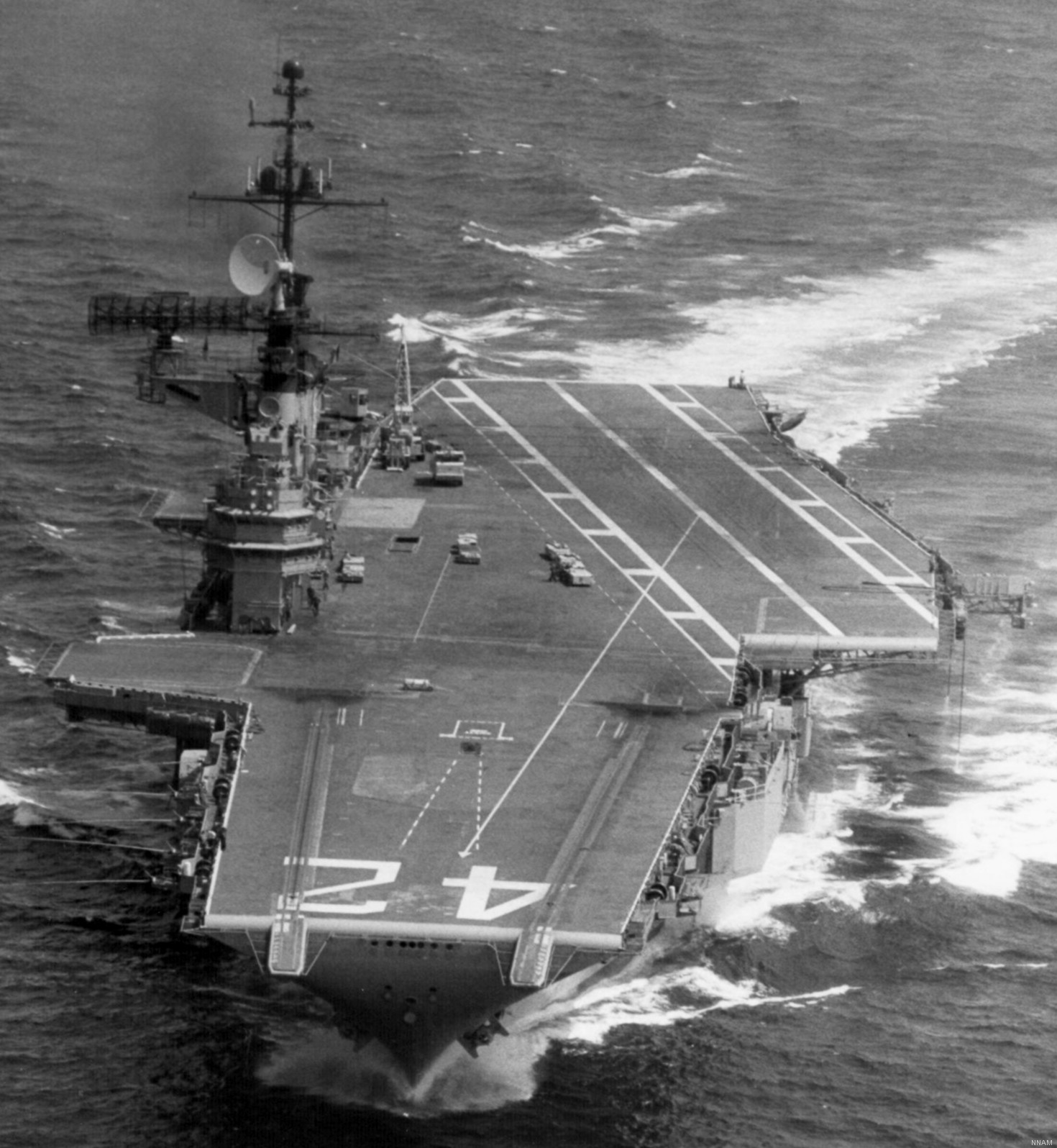  after refit - July 1969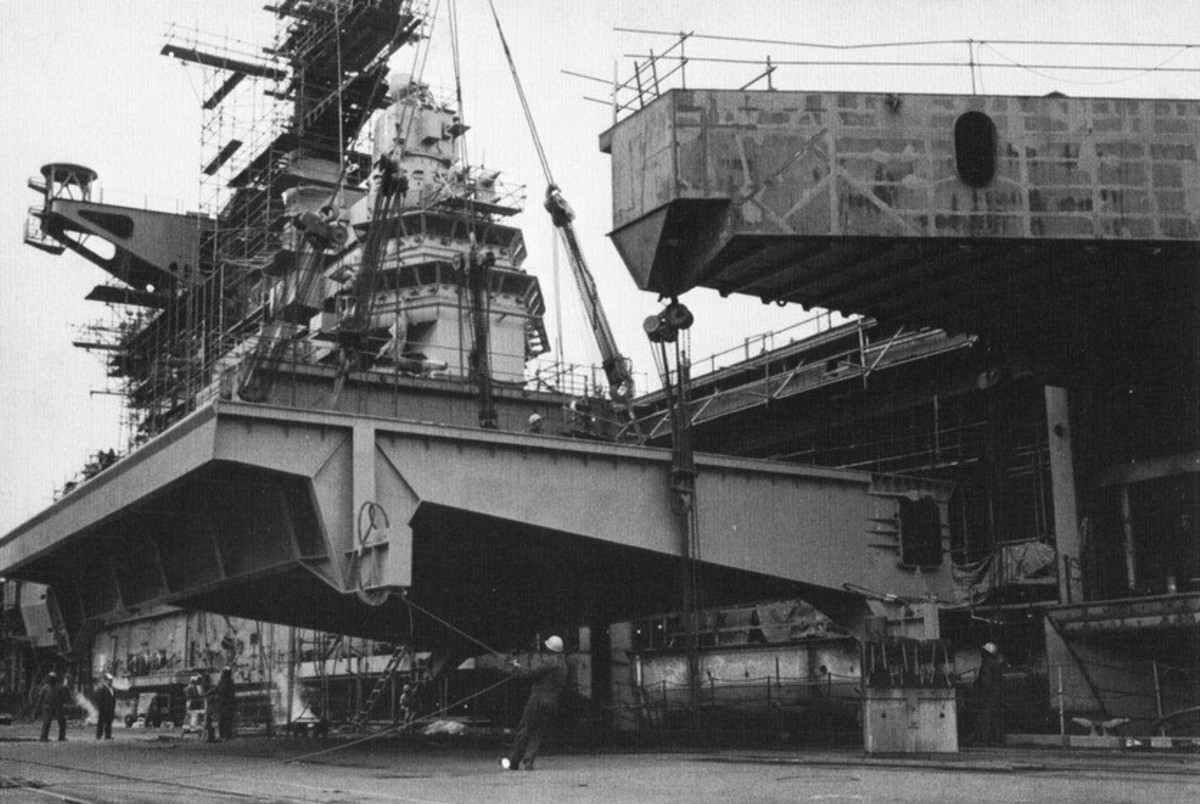  USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVA 42) receiving a new deck-edge elevator at the Norfolk Naval Shipyard, Virginia. Roosevelt was initially slated to undergo an extensive reconstruction (SCB 101.68) similar to that received by USS Midway (CVA 41) from 1966 to 1970. This plan was derailed by massive cost overruns in Midway's reconstruction, which eventually totalled $202 million. Roosevelt was therefore limited to an austere $46 million refit, enabling her to operate the Grumman A-6 Intruder and LTV A-7 Corsair II. In July 1968, Roosevelt entered Norfolk Naval Shipyard for her 11-month modernization program. The forward centerline elevator was relocated to the starboard deck edge forward of the island, the port waist catapult was removed, the crew spaces were refurbished, and two of the four remaining 127 mm anti-aircraft turrets were removed. Roosevelt also received a deck edge spray system using the new seawater compatible fire-fighting chemical, Light Water. She put to sea again on 26 May 1969.overhaul & modernization: December 1968 - June 1969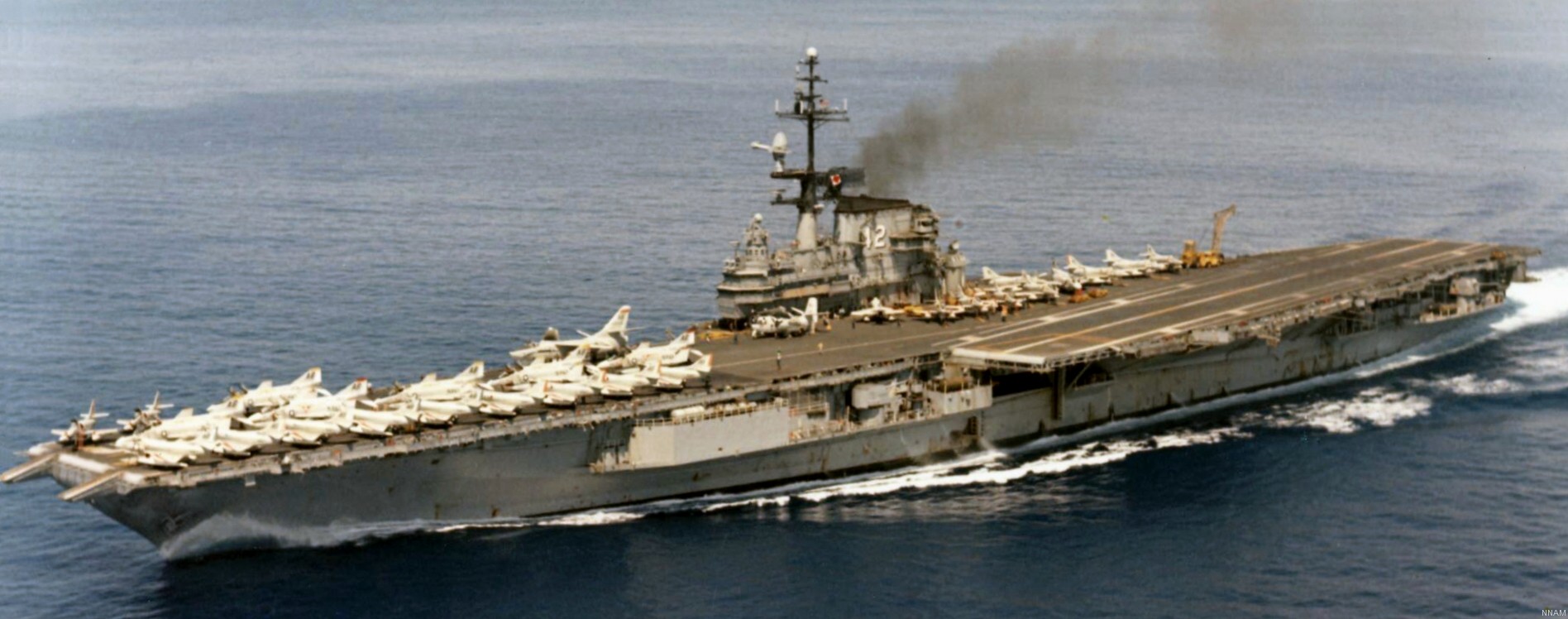  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - 1967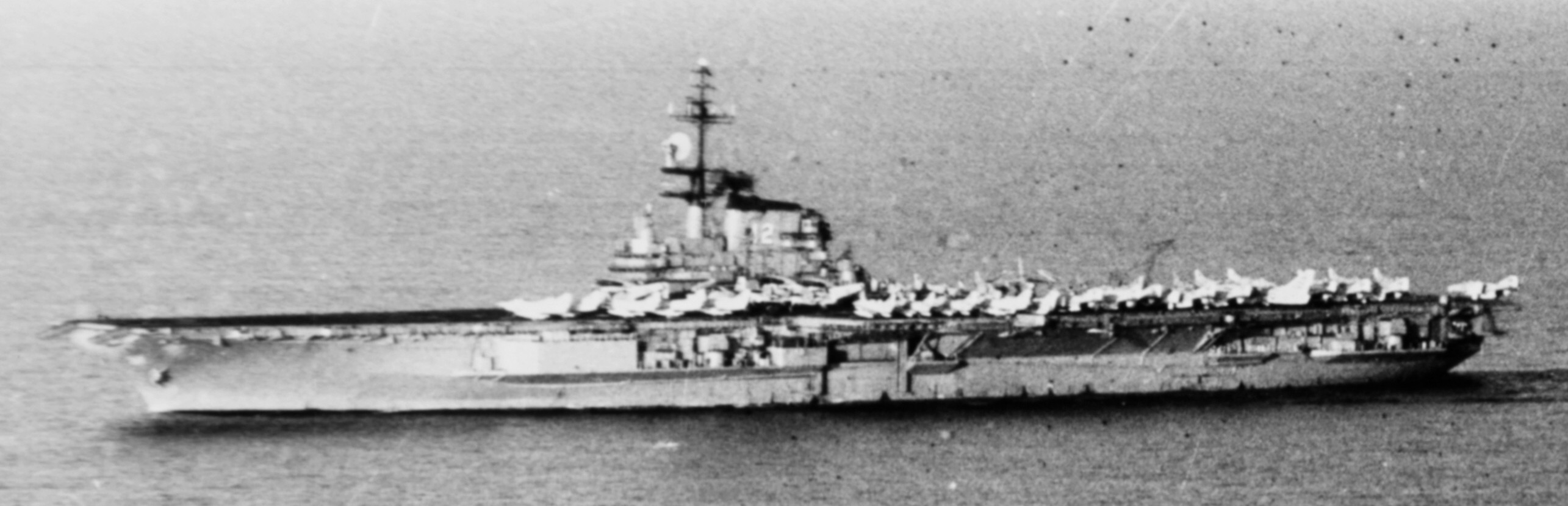  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - 1967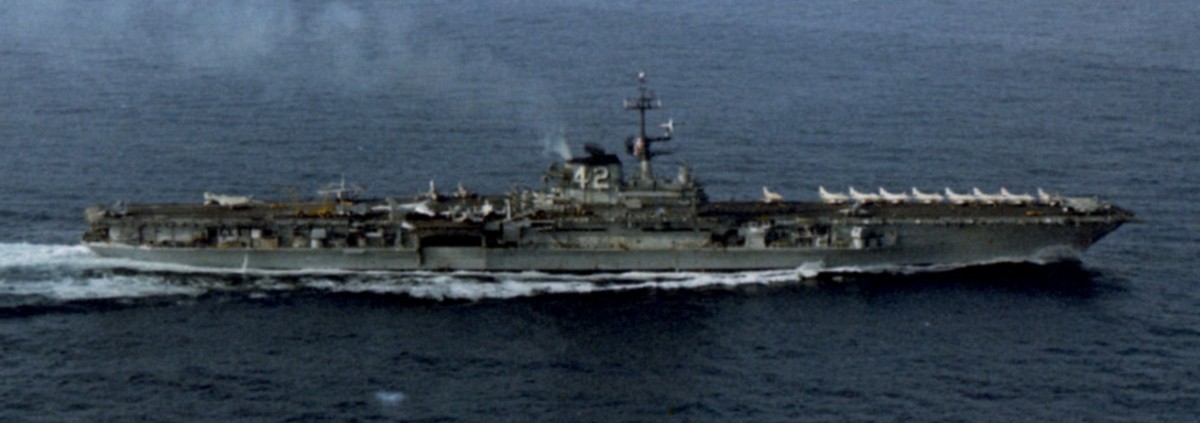  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - 1966-67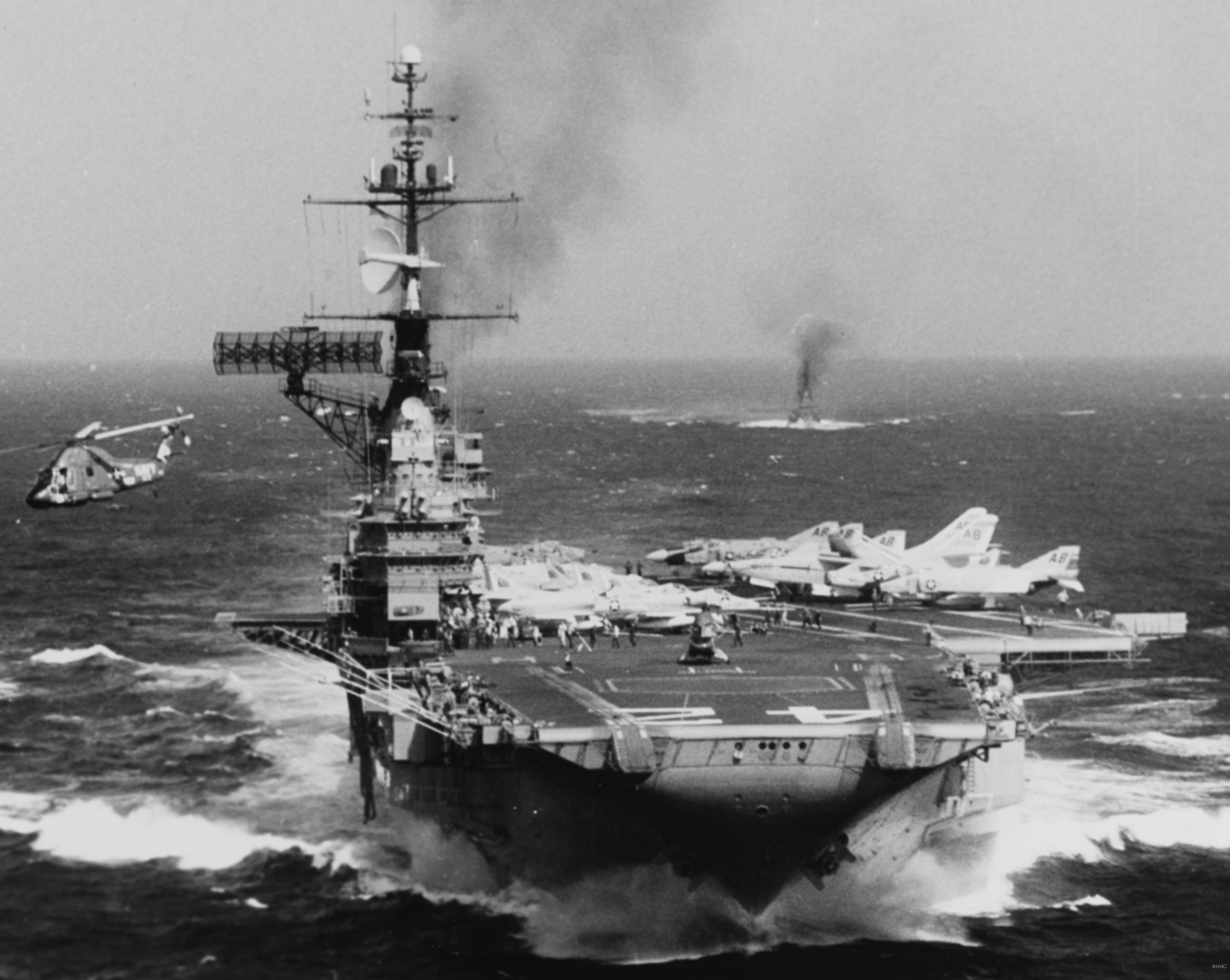  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - October 1966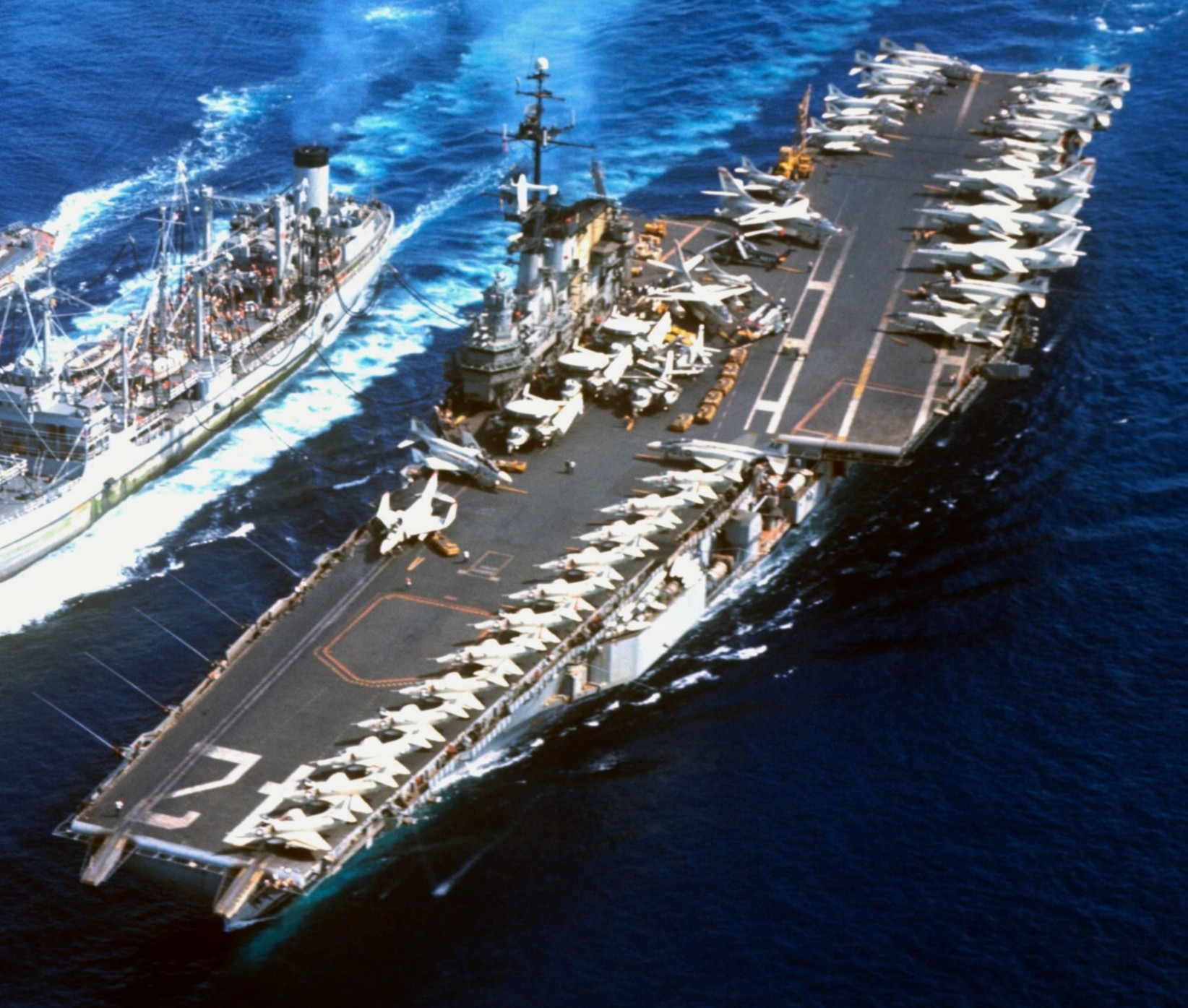  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - Gulf of Tonkin - September 1966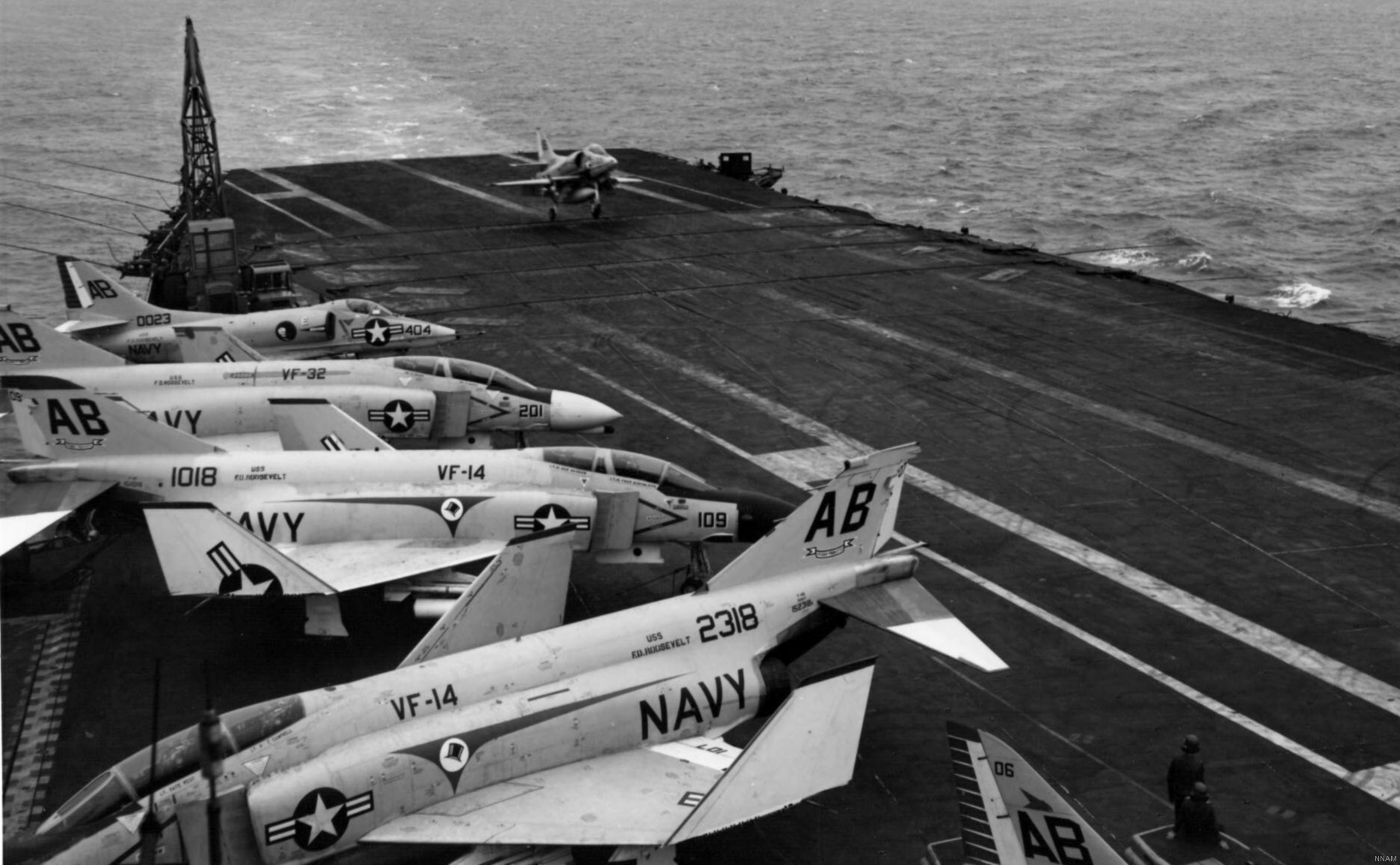  with aircraft of Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - August 1966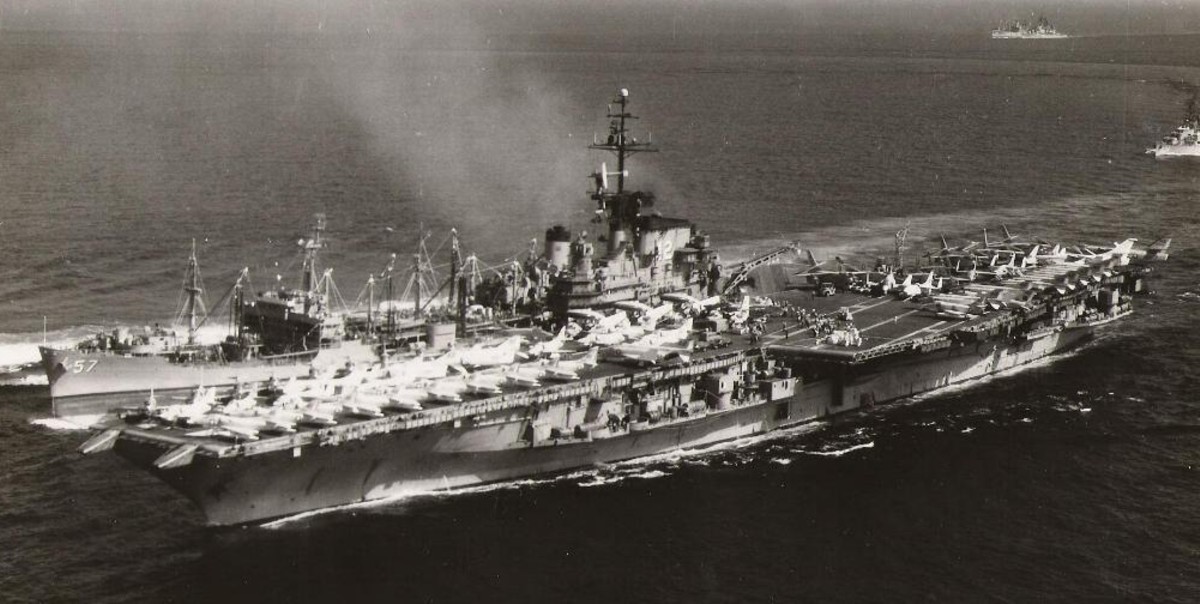  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - January 1966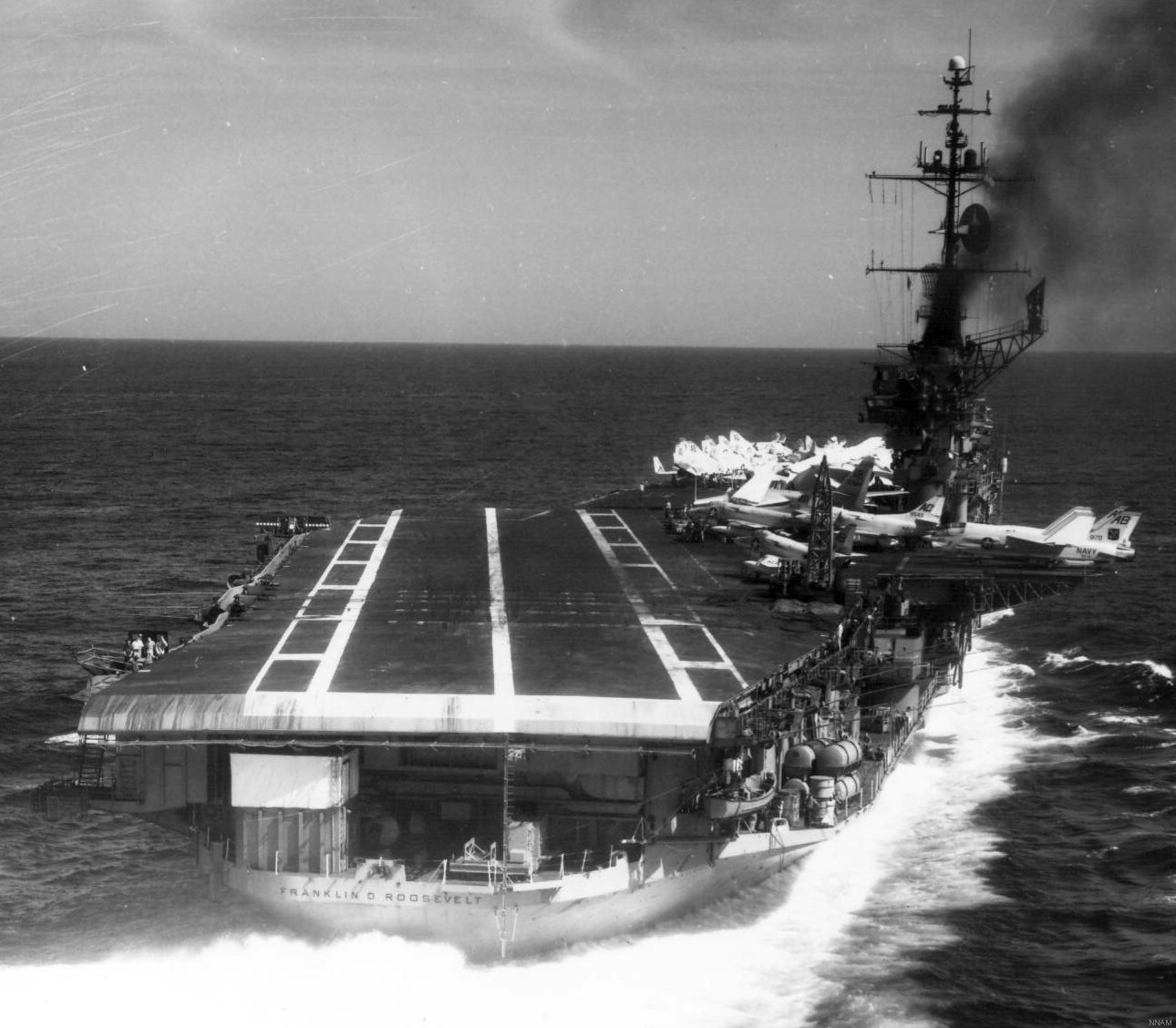  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - September 1965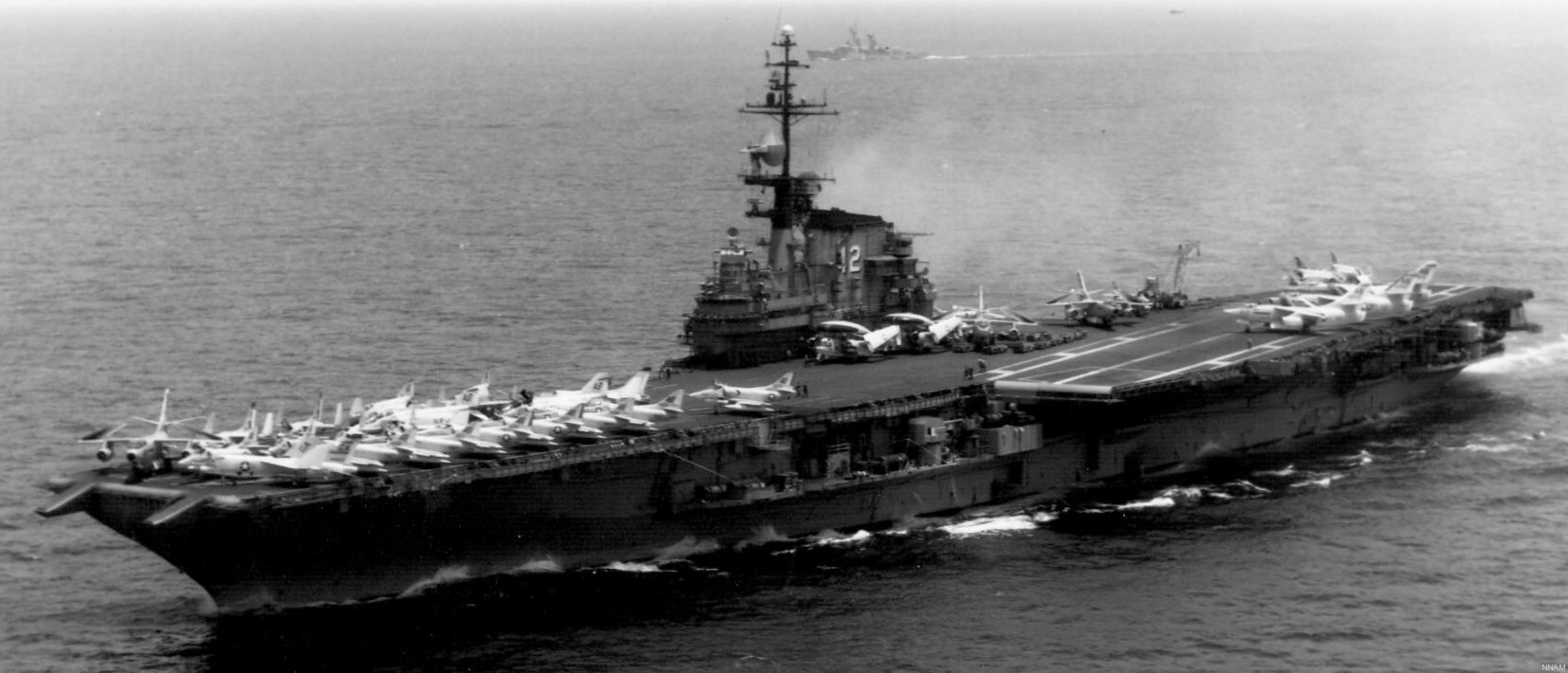  with Carrier Air Wing 1 (CVW-1) embarked - May 1965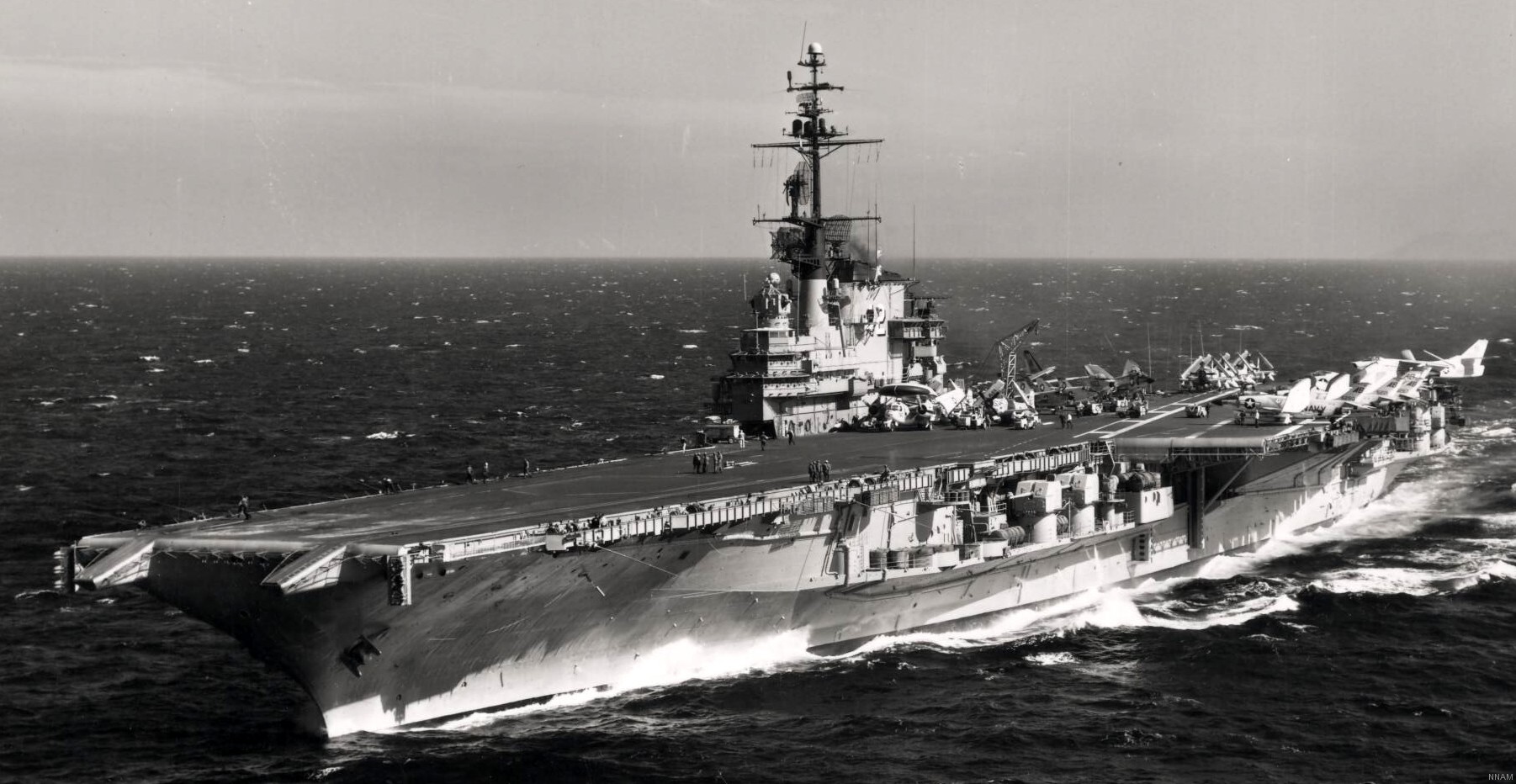  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - March 1963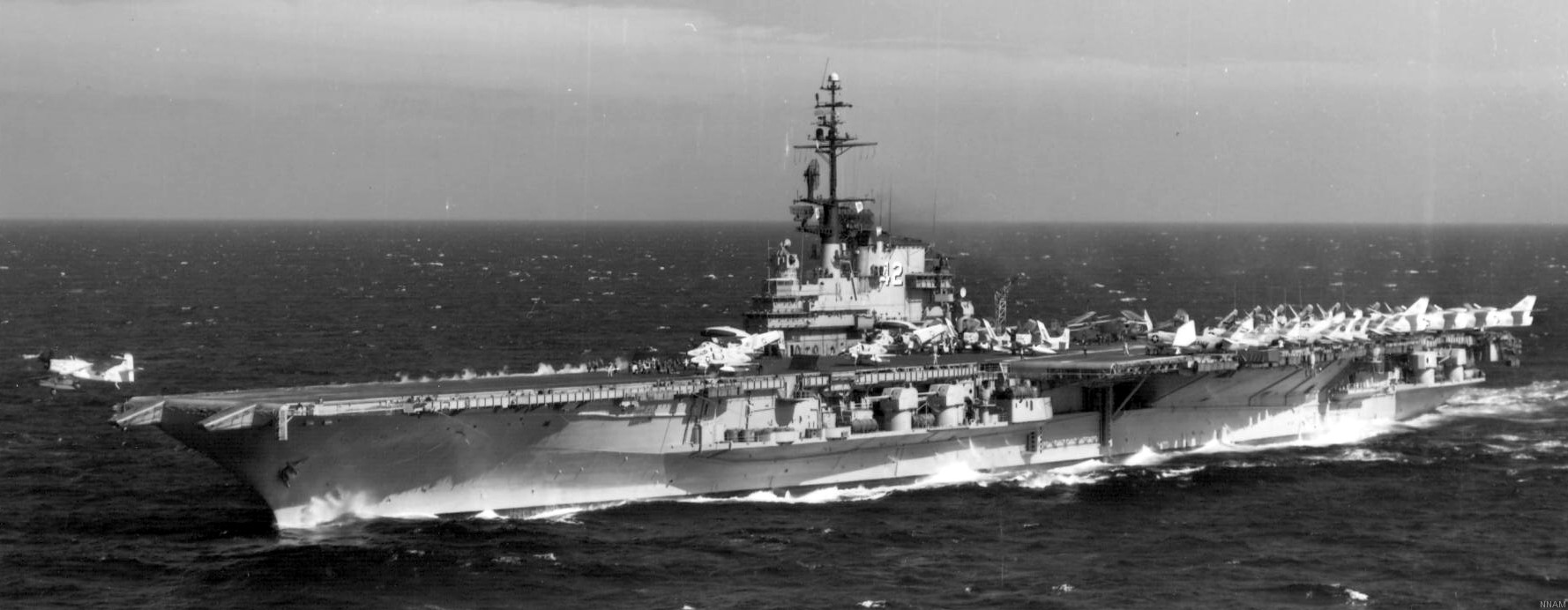  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - March 1963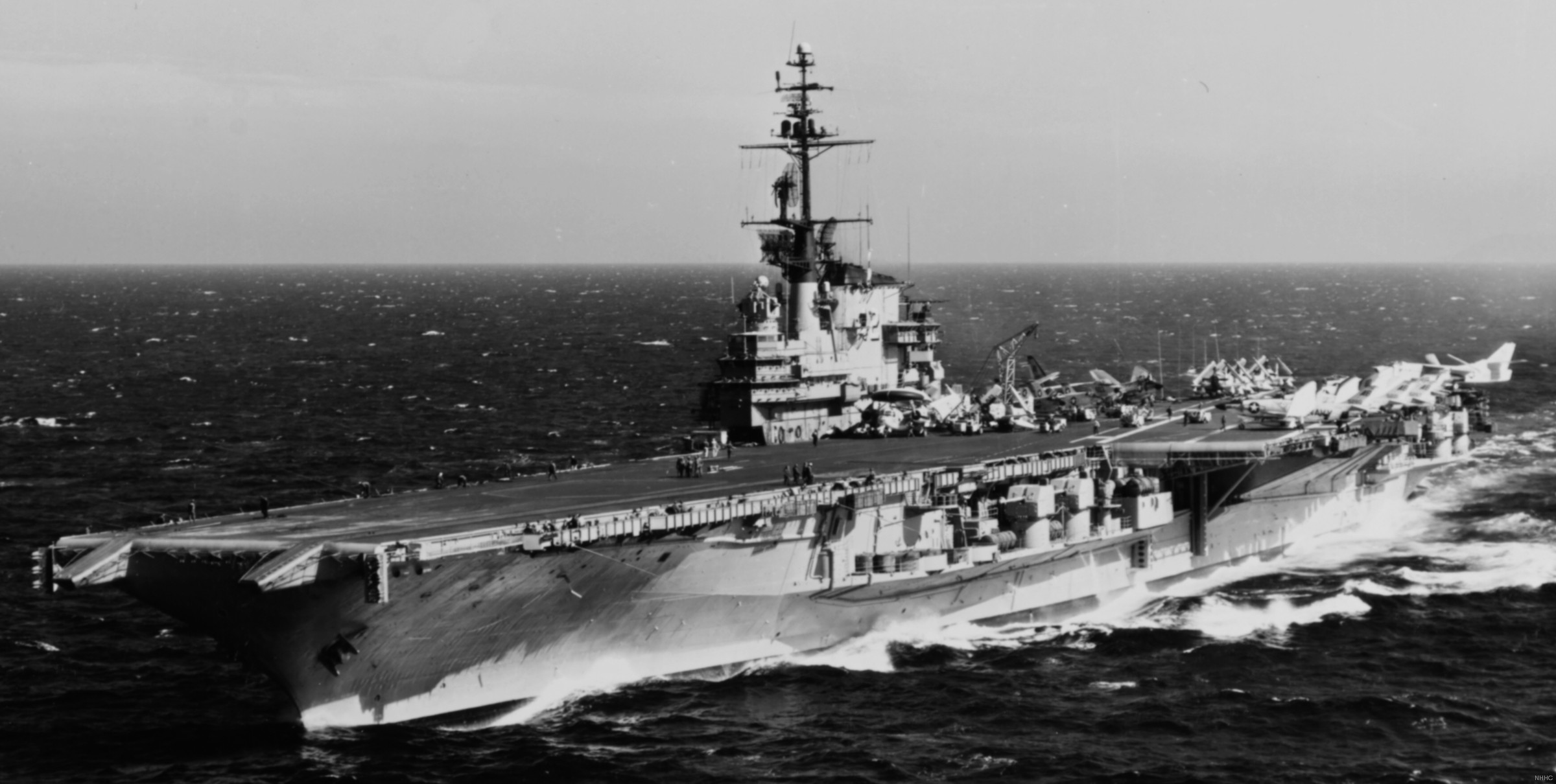  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - March 1963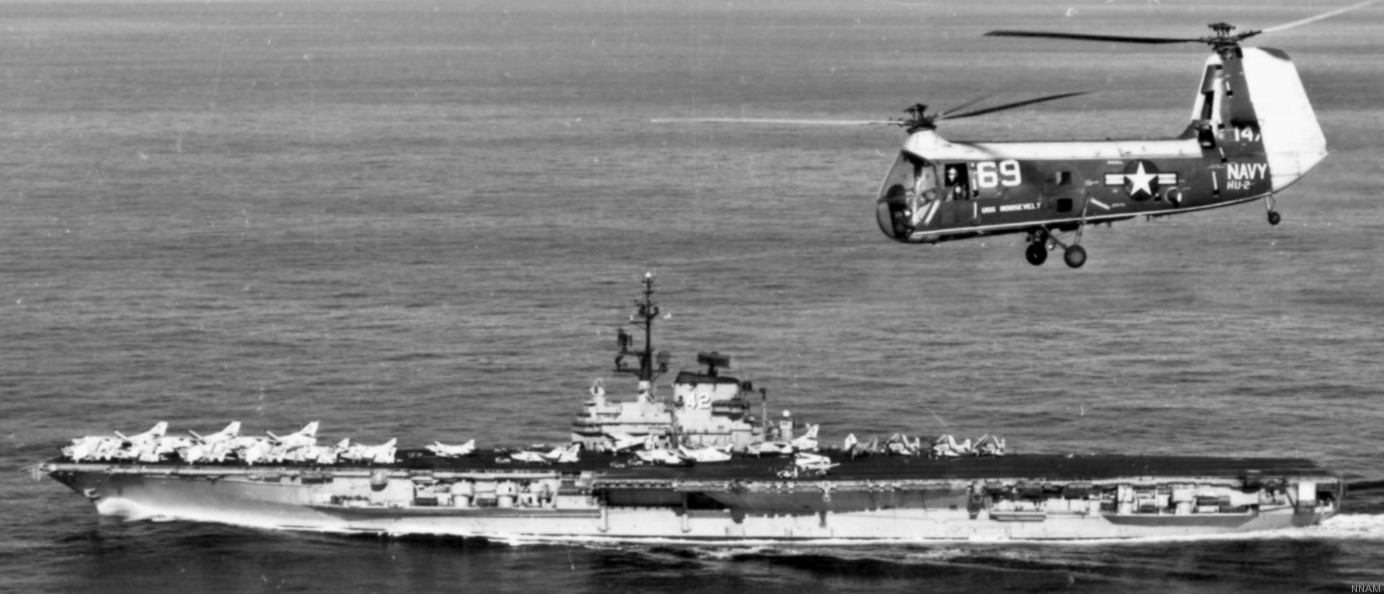  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - January 1963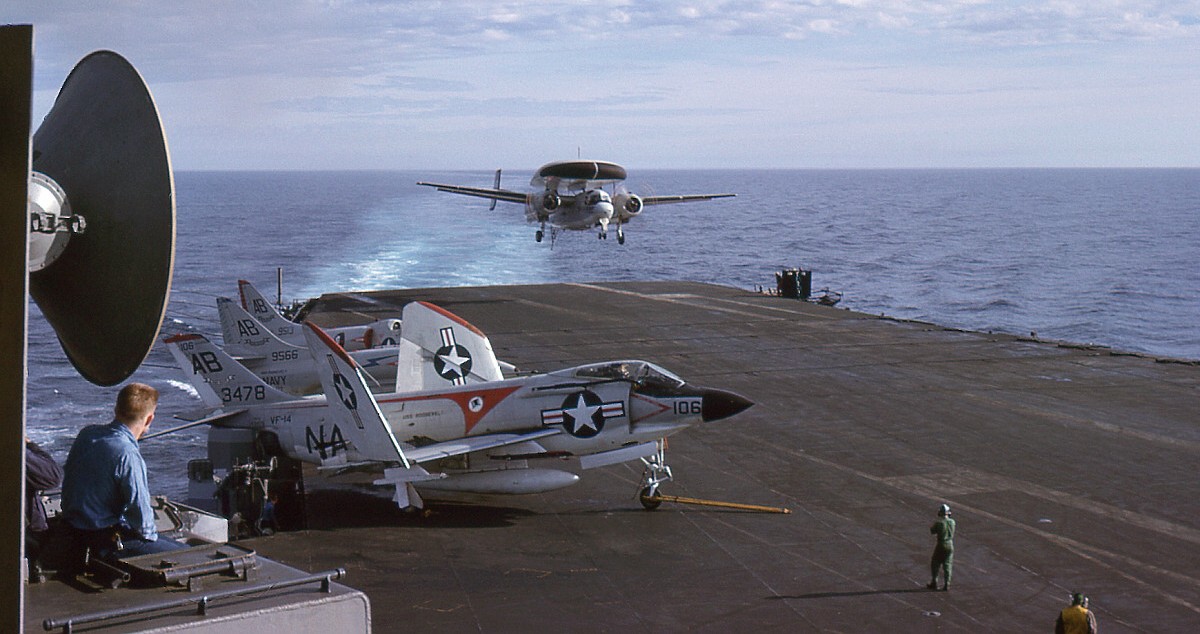  with aircraft of Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - 1962-63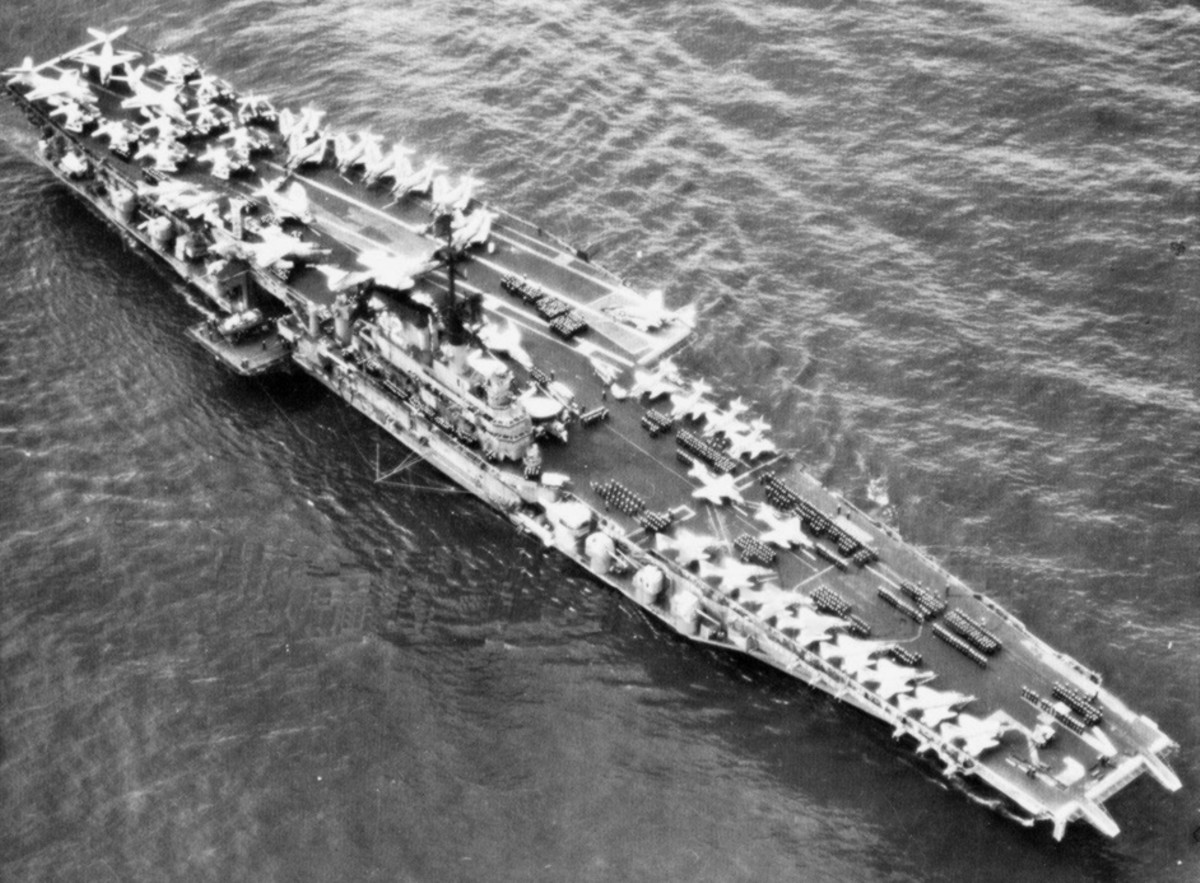  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - 1961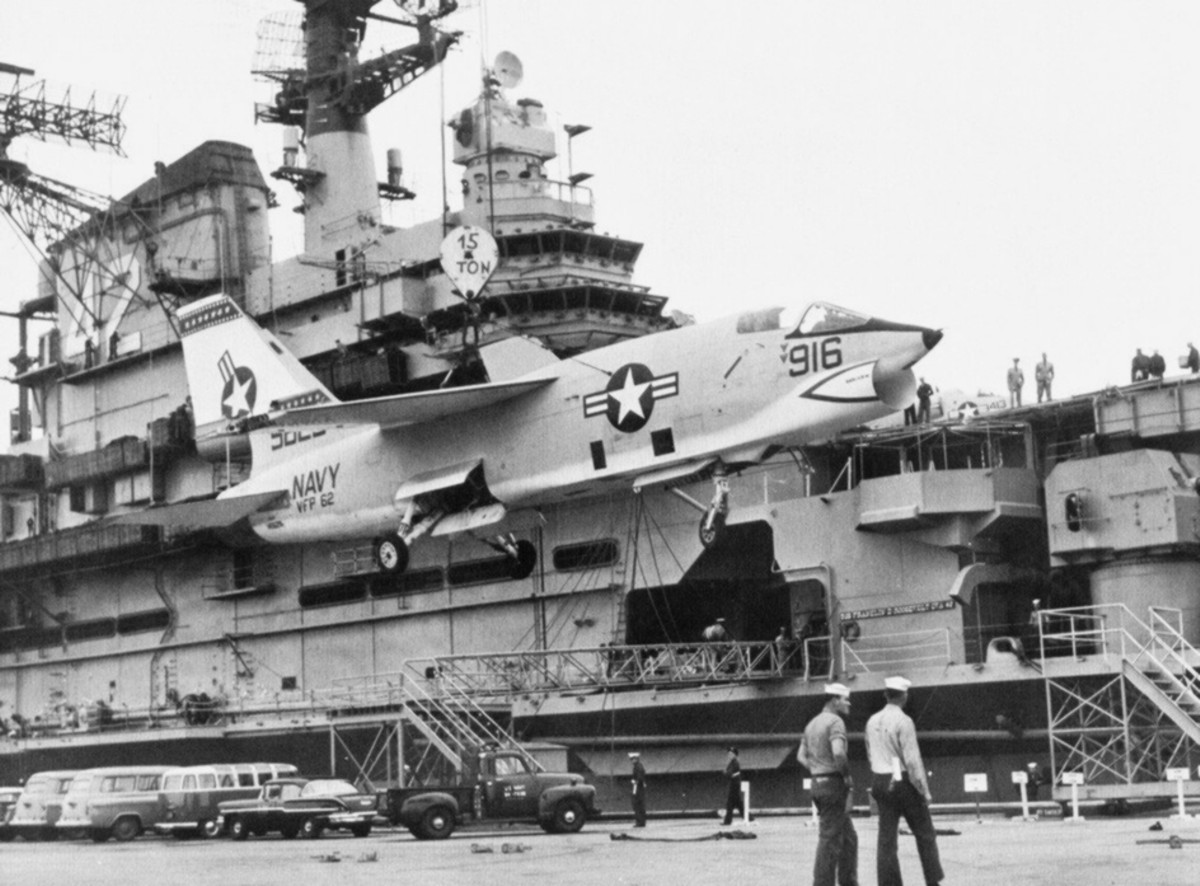  Vought F8U-1P Crusader from Photographic Reconnaissance Squadron VFP-62 Det.37 "Fighting Photos" is hoisted aboard USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVA 42) at Mayport, Florida, in preparation of FDR´s 1961 deployment to the Mediterranean Sea - February 1961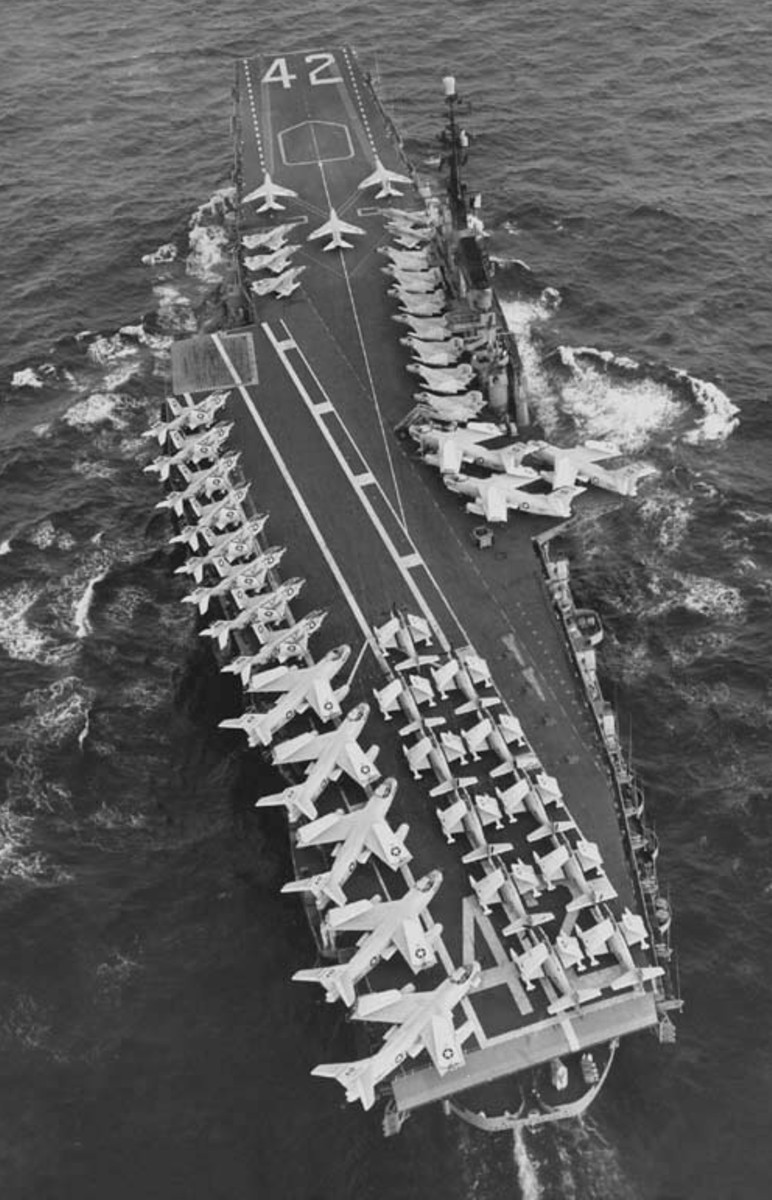  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - 1959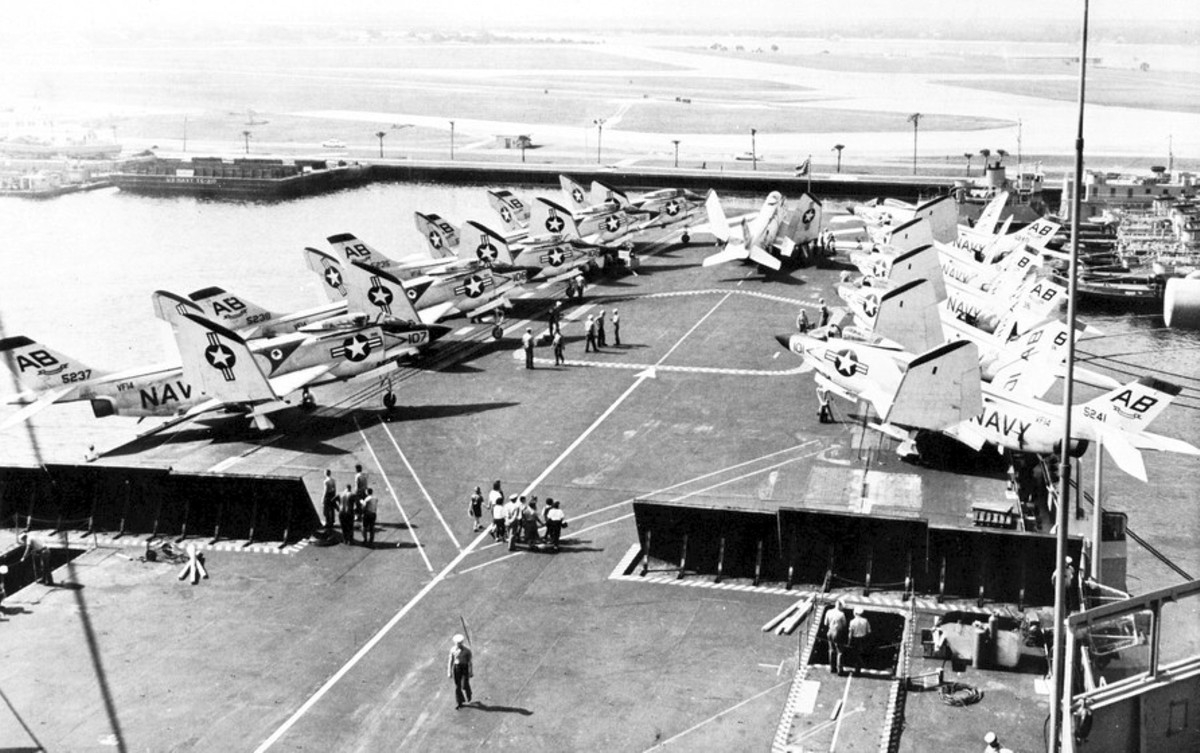  with Carrier Air Group 1 (CVG-1) embarked - 1959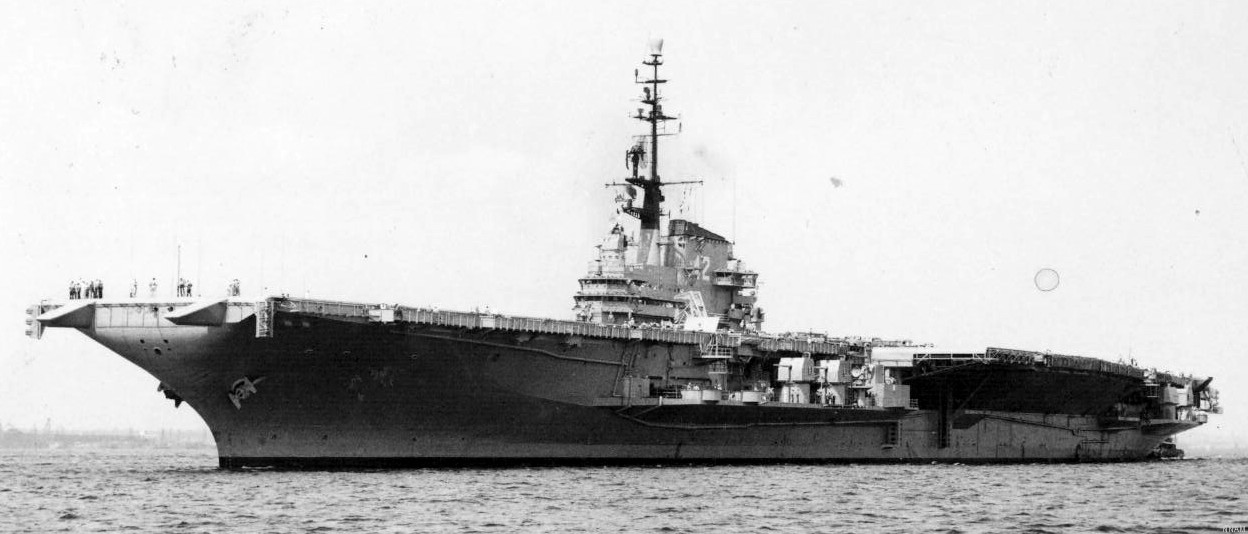  September 1958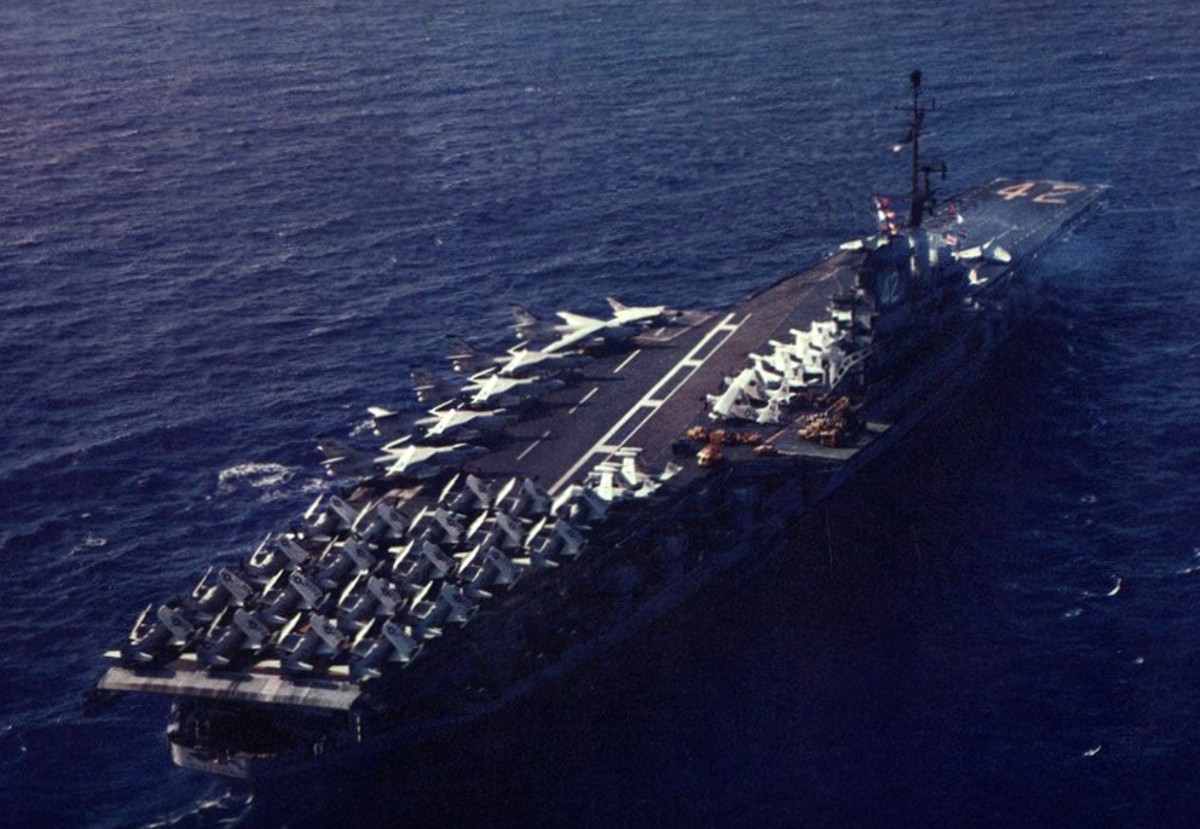  with Carrier Air Group 17 (CVG-17) embarked - circa 1957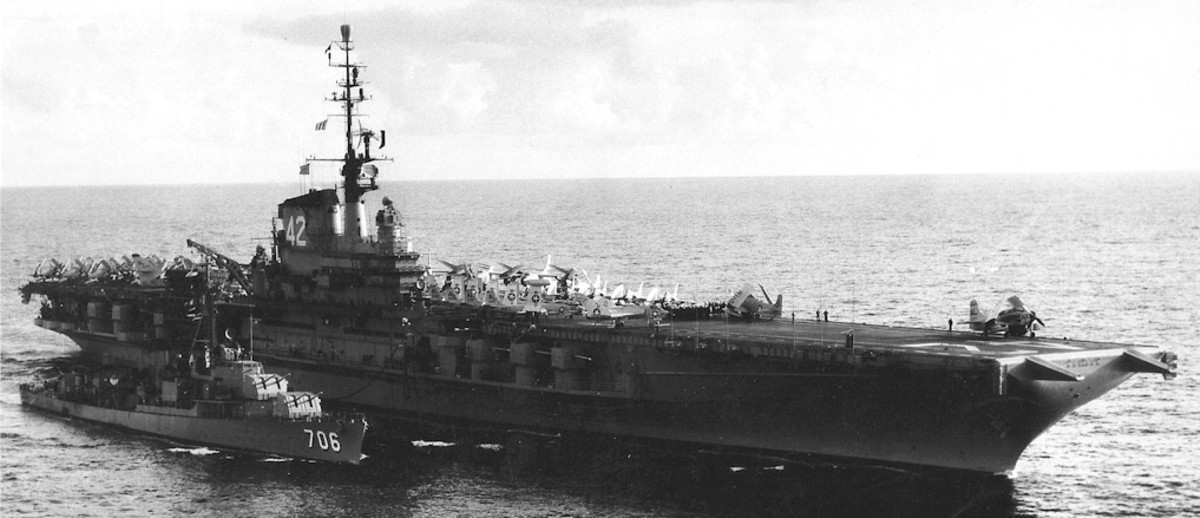  with Carrier Air Group 17 (CVG-17) embarked - circa 1957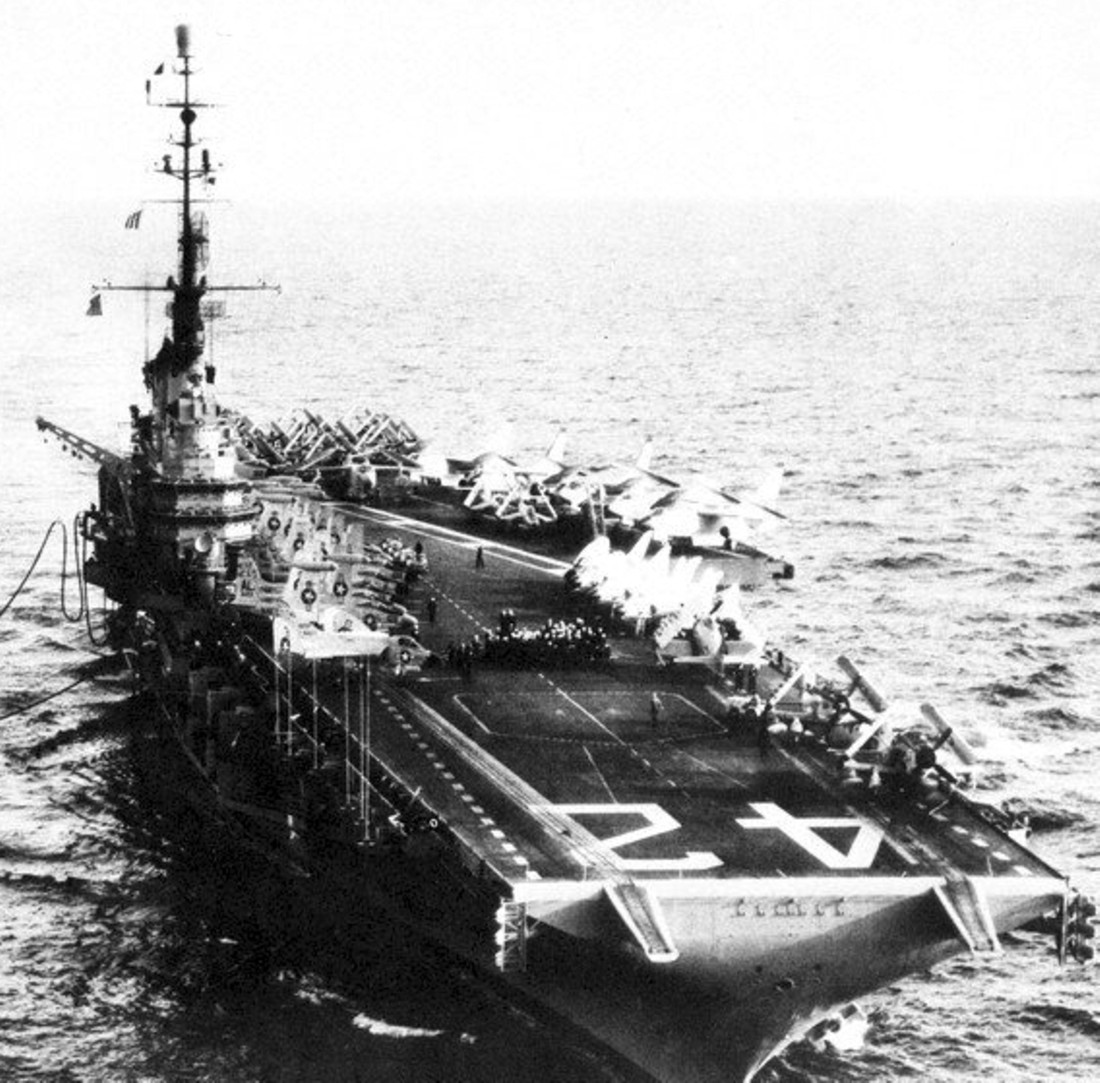  with Carrier Air Group 17 (CVG-17) embarked - circa 1957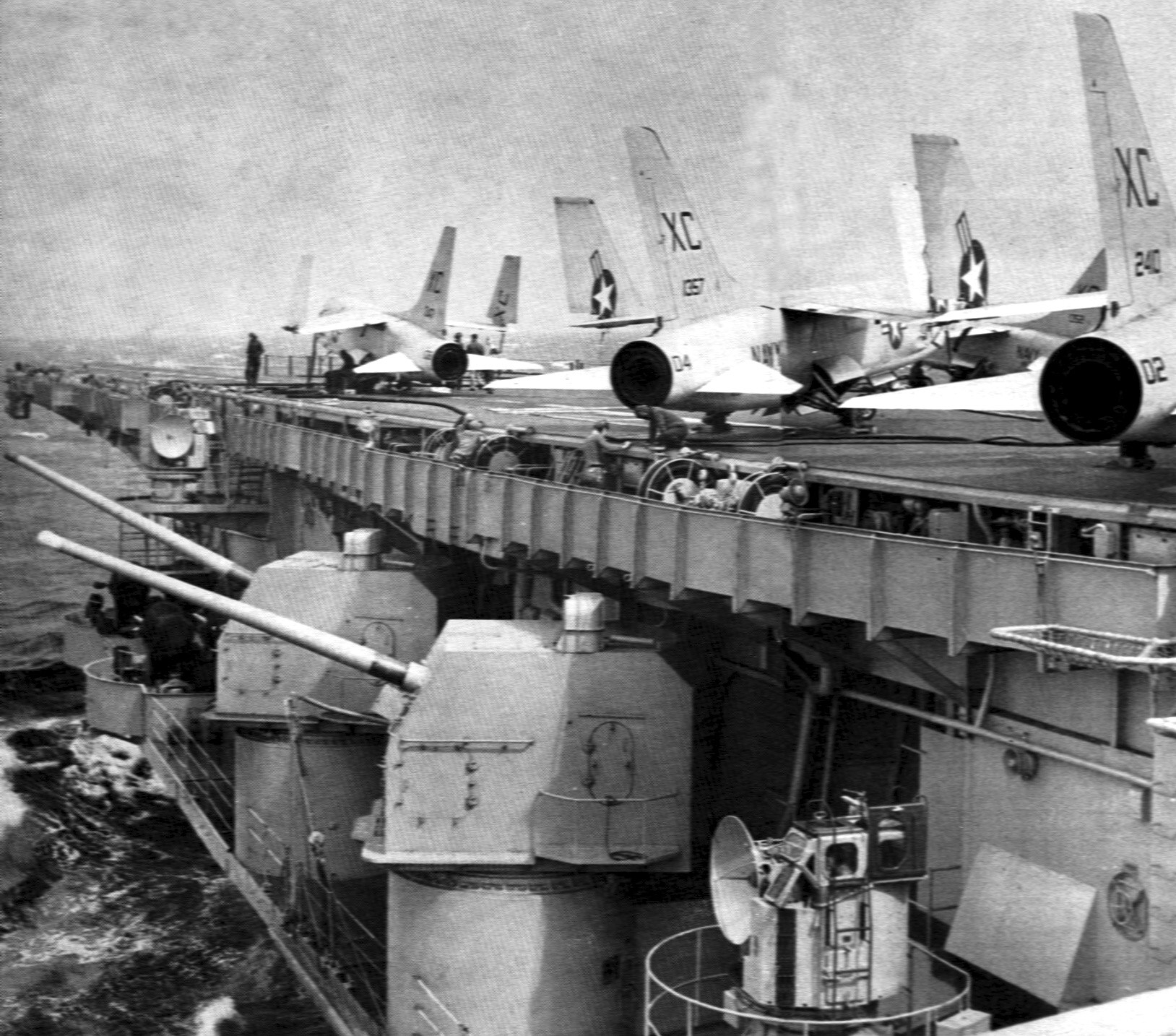  Mark 16 (5"/54-caliber) guns aboard USS Franklin D. Roosevelt - 1957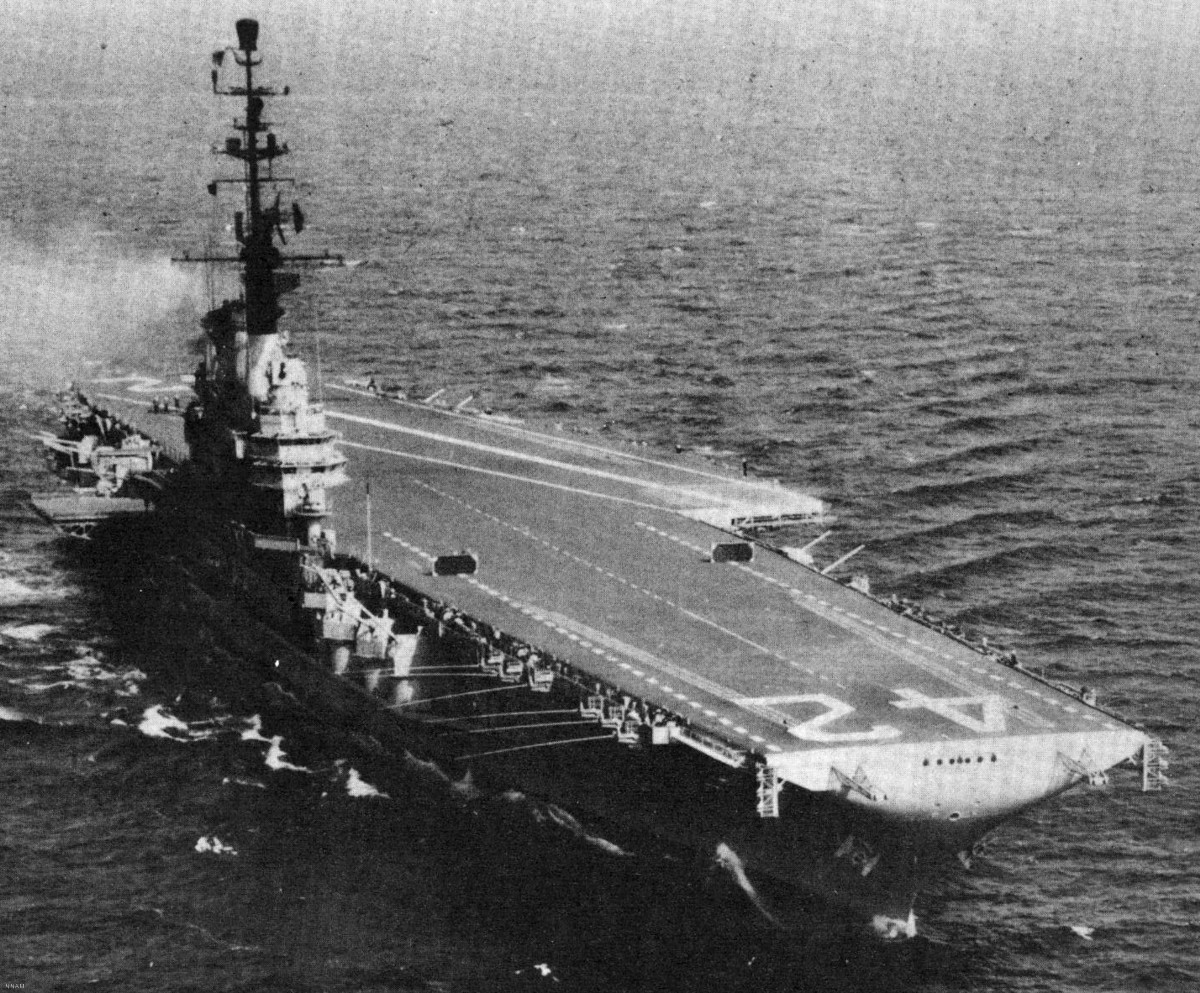  circa 1957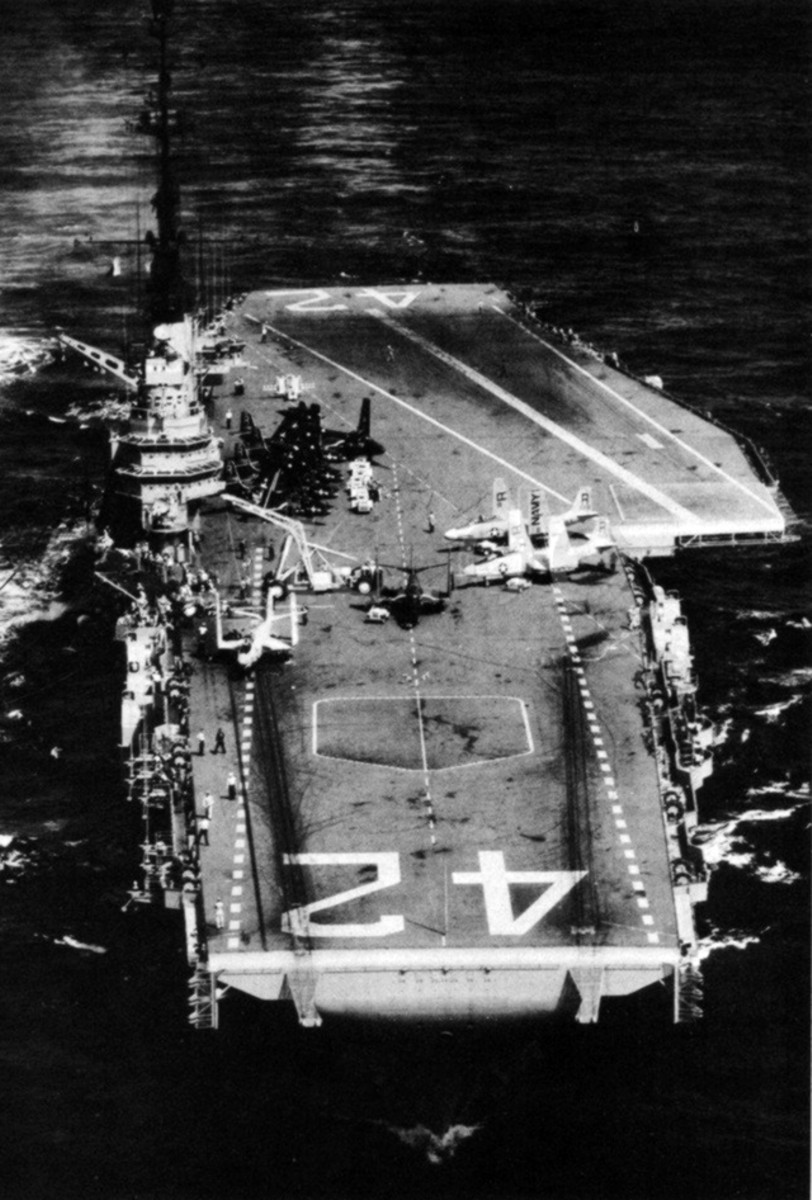  USS Franklin D. Roosevelt, with CVG-17 embarked, during her voyage from the Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington to her new homeport Mayport, Florida, following her SCB-110 modernisation. The FDR circumnavigated South America via Cape Hoorn from 4 June to 8 August 1956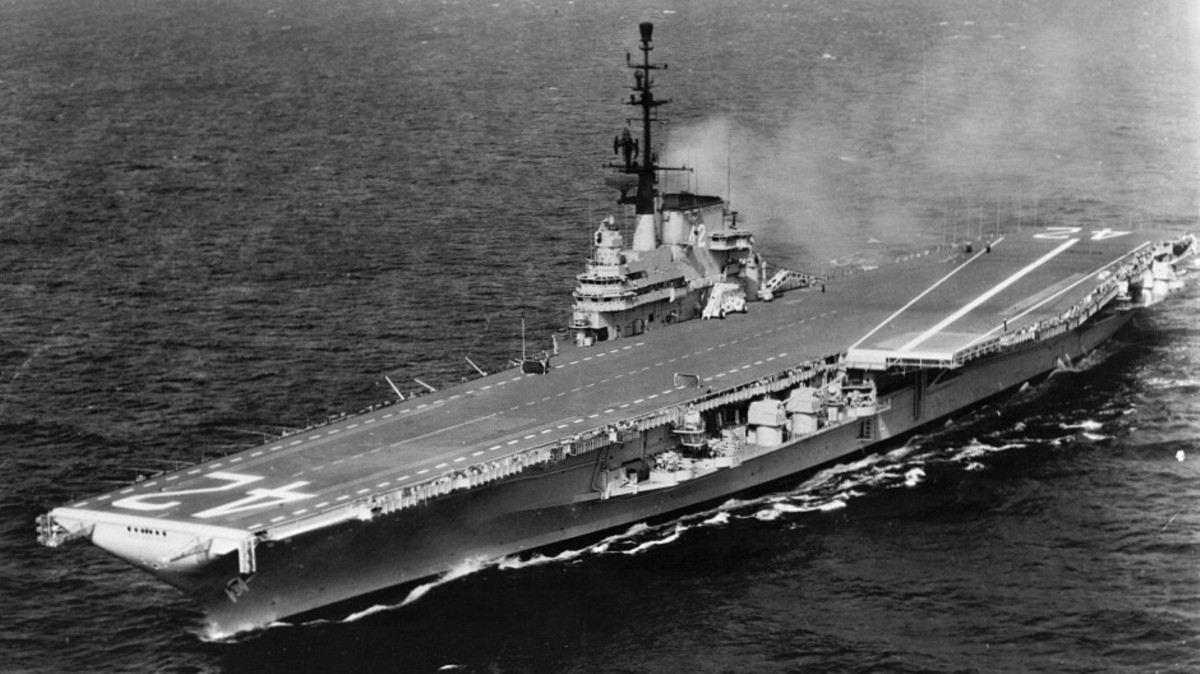  after her SCB-110 conversion - June 1956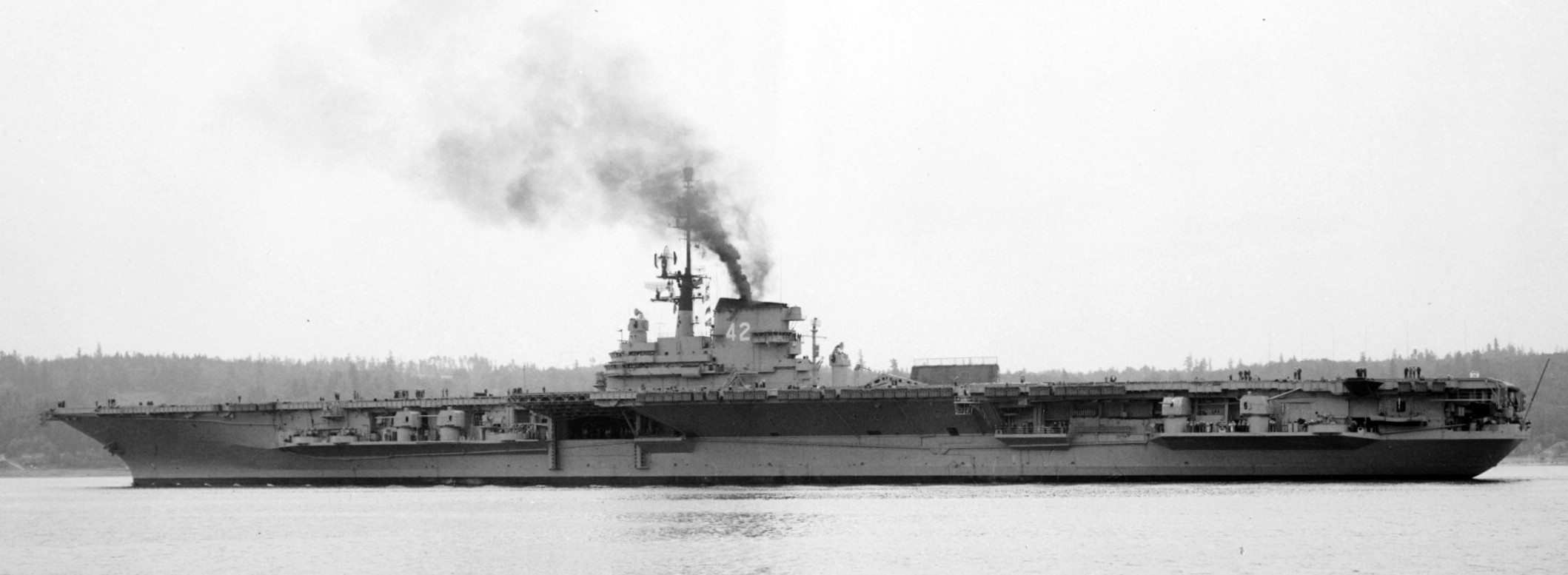  after her SCB-110 conversion - June 1956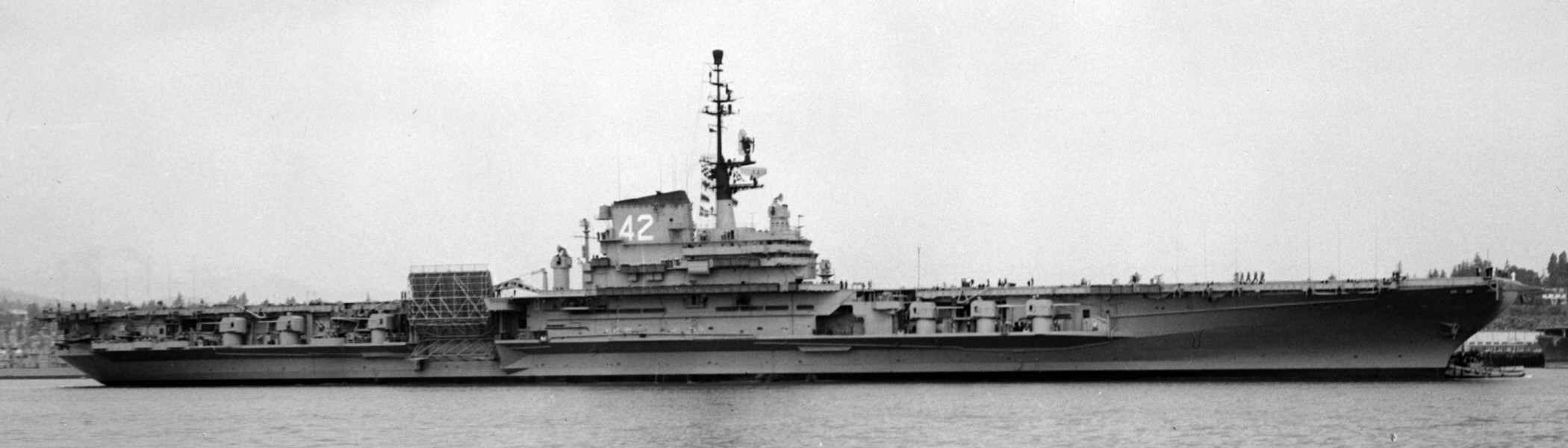  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956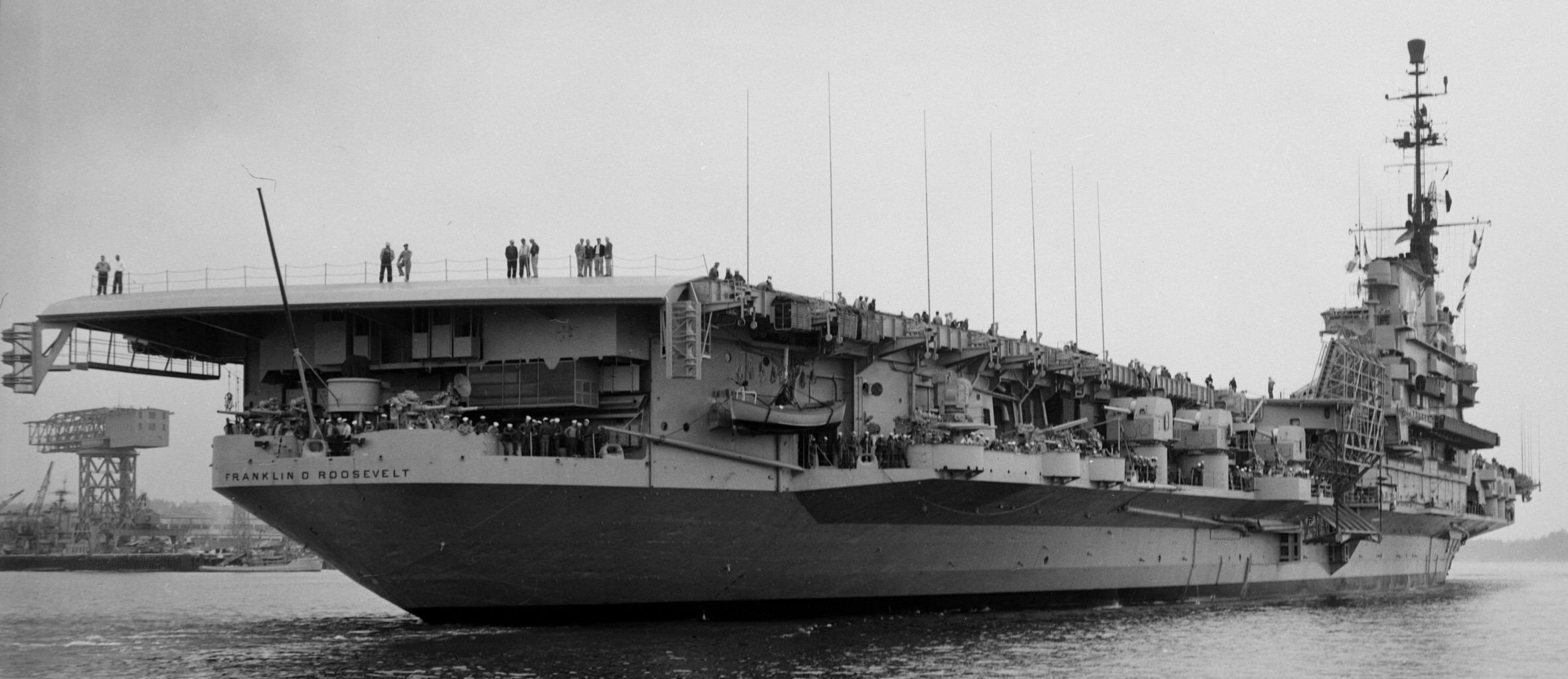  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956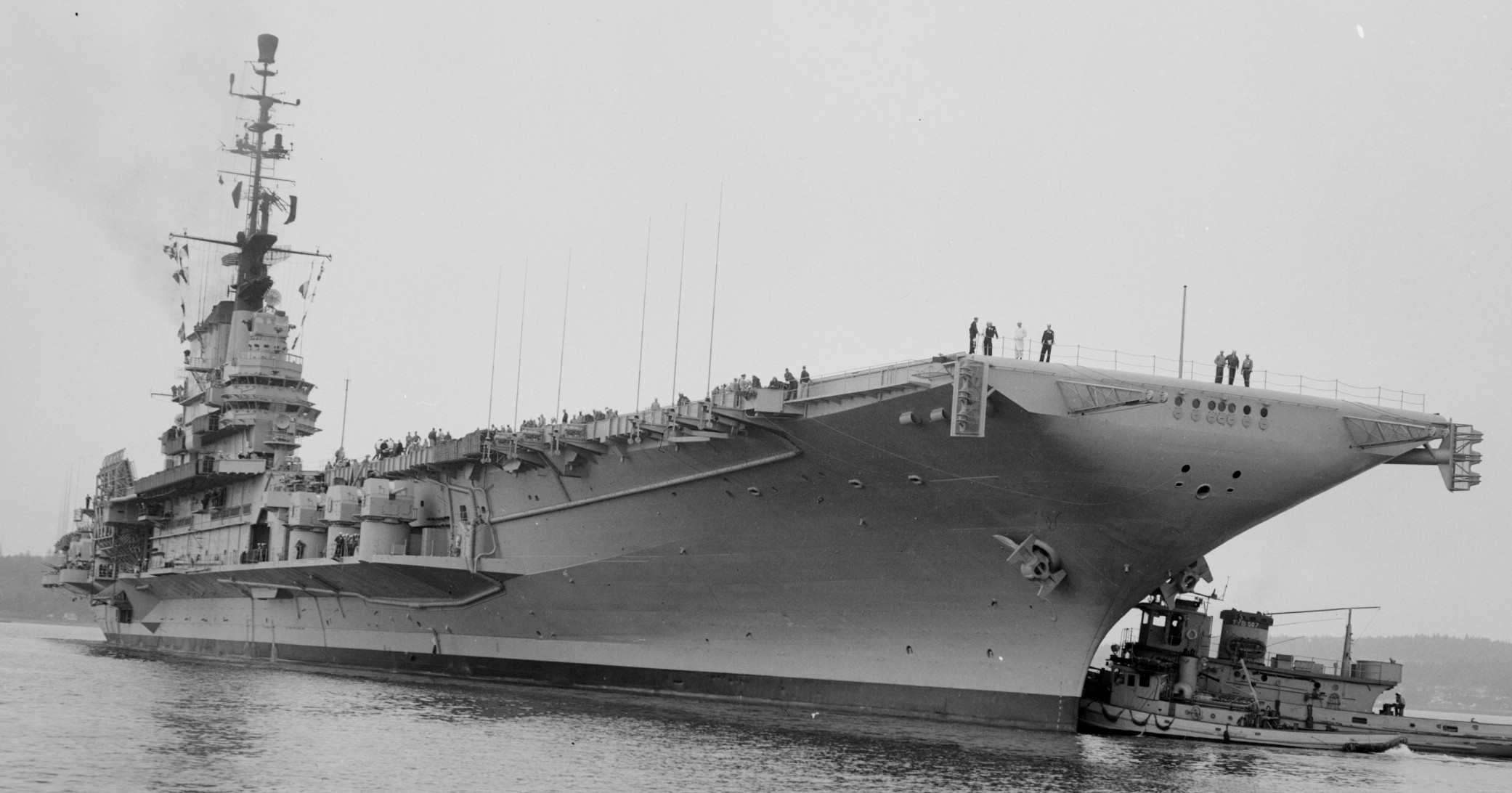  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956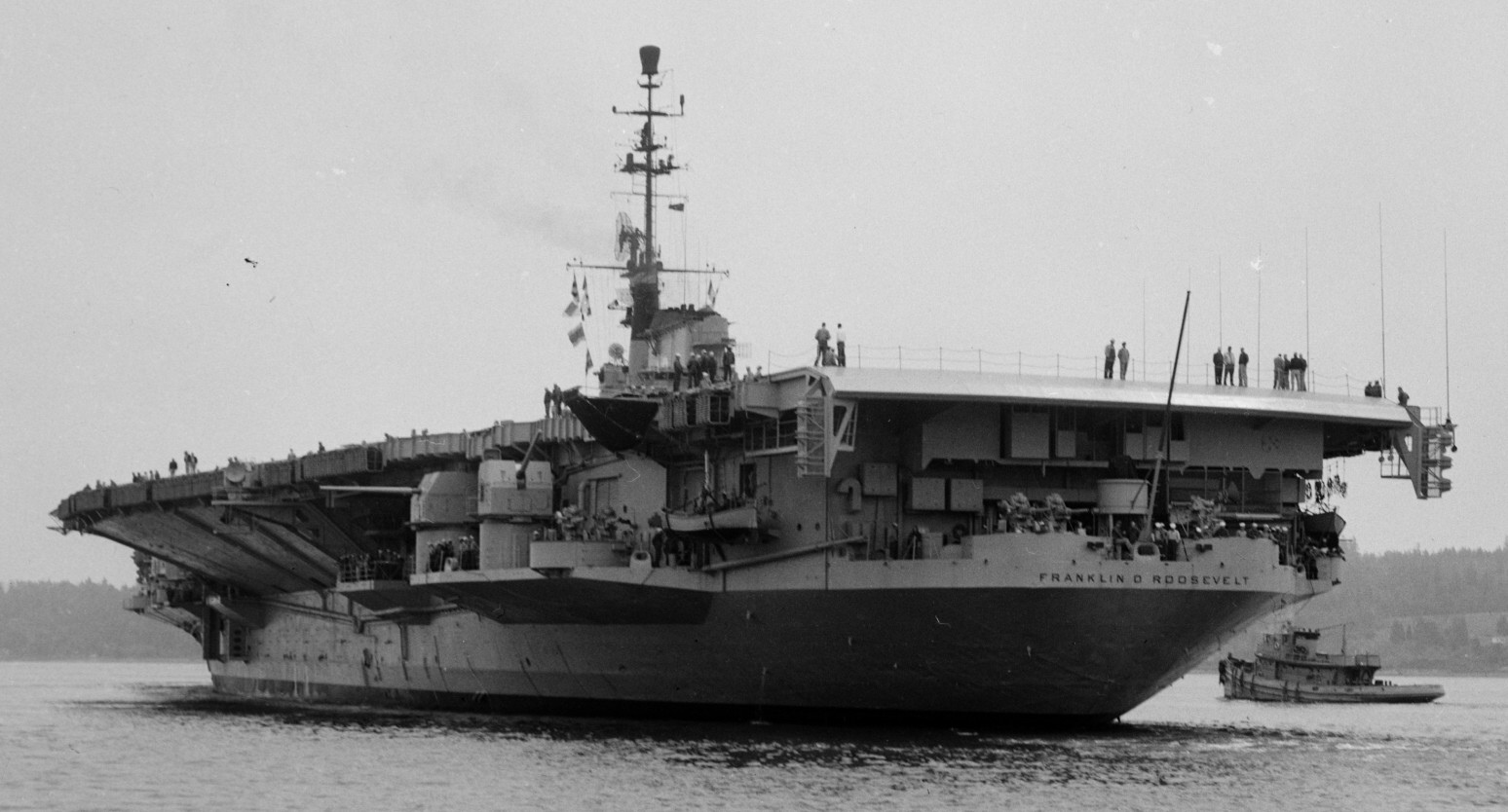  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956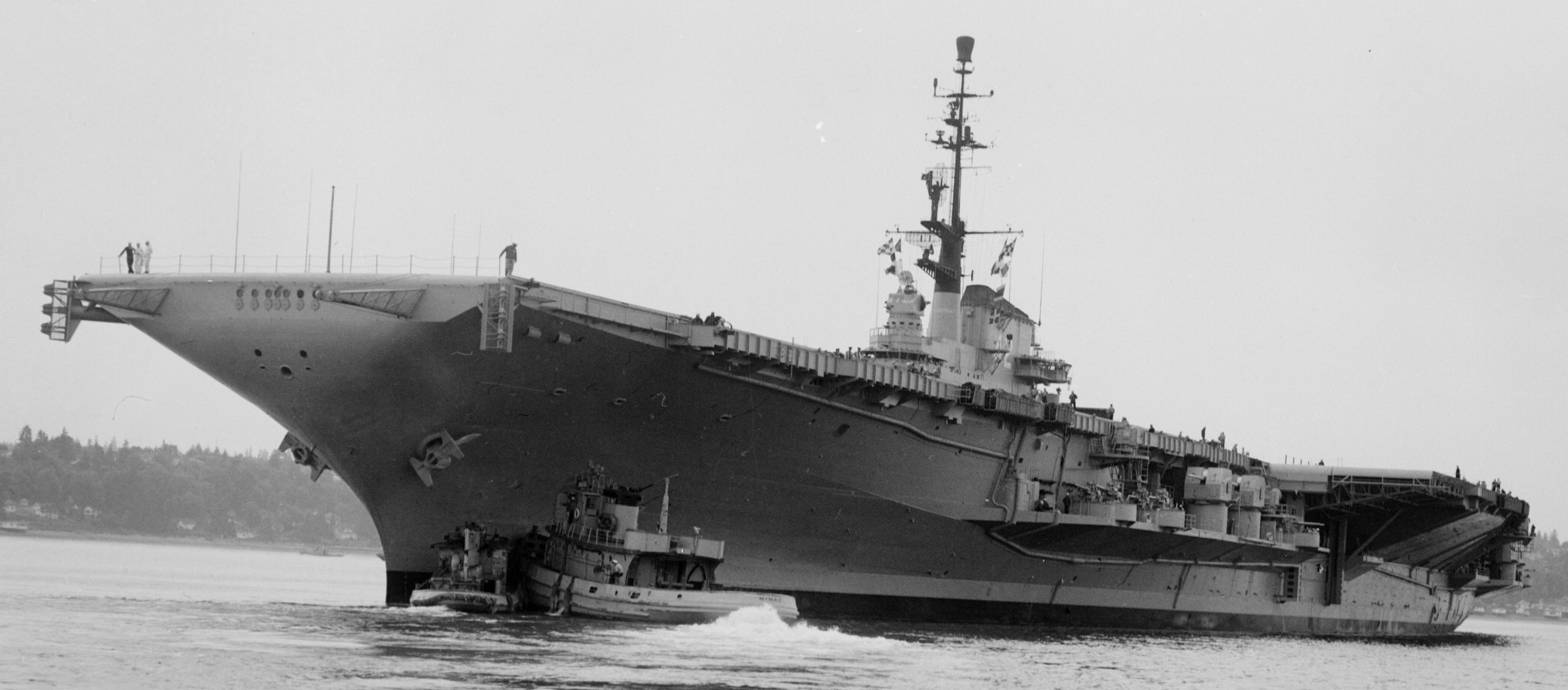  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956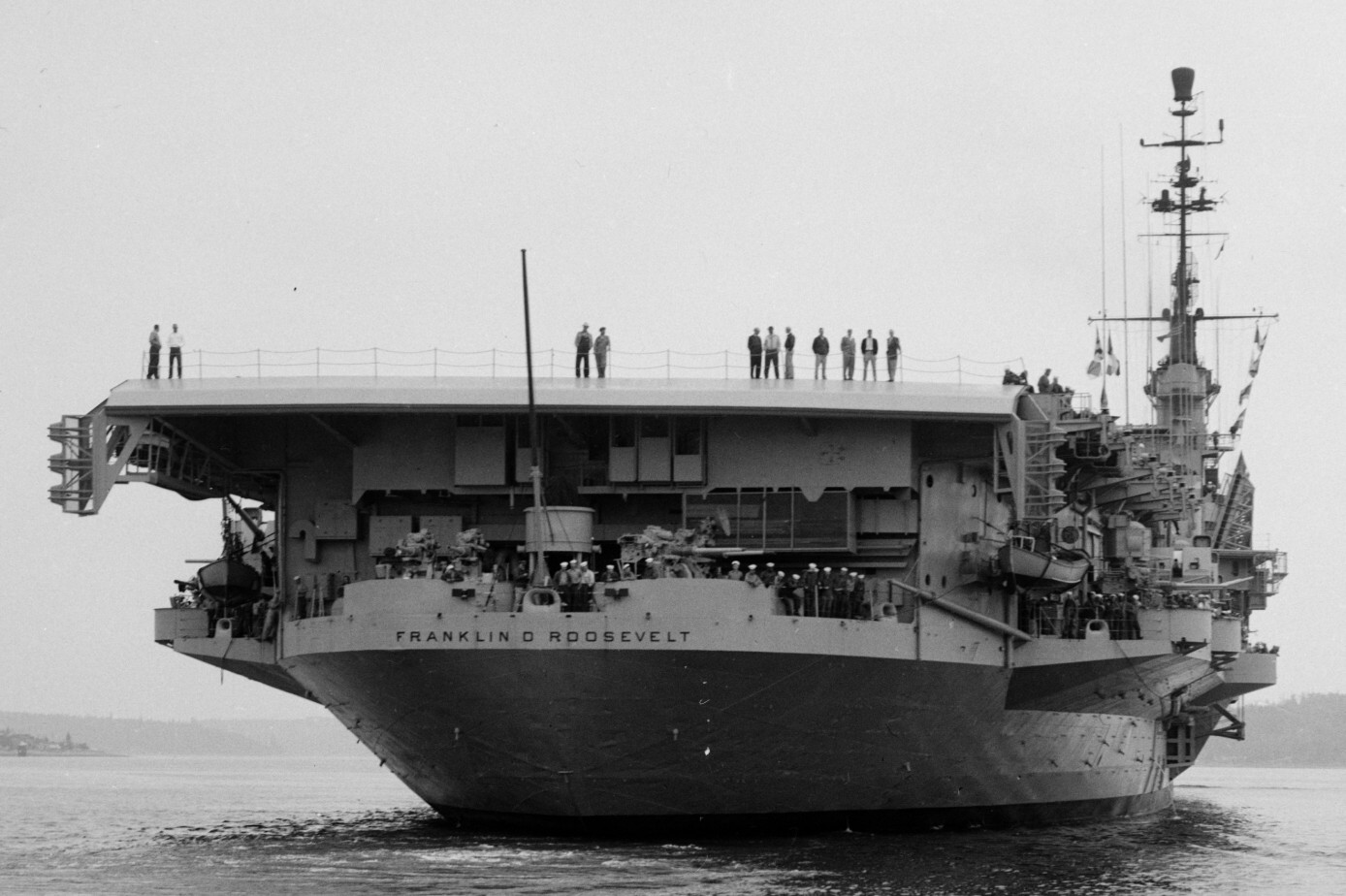  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956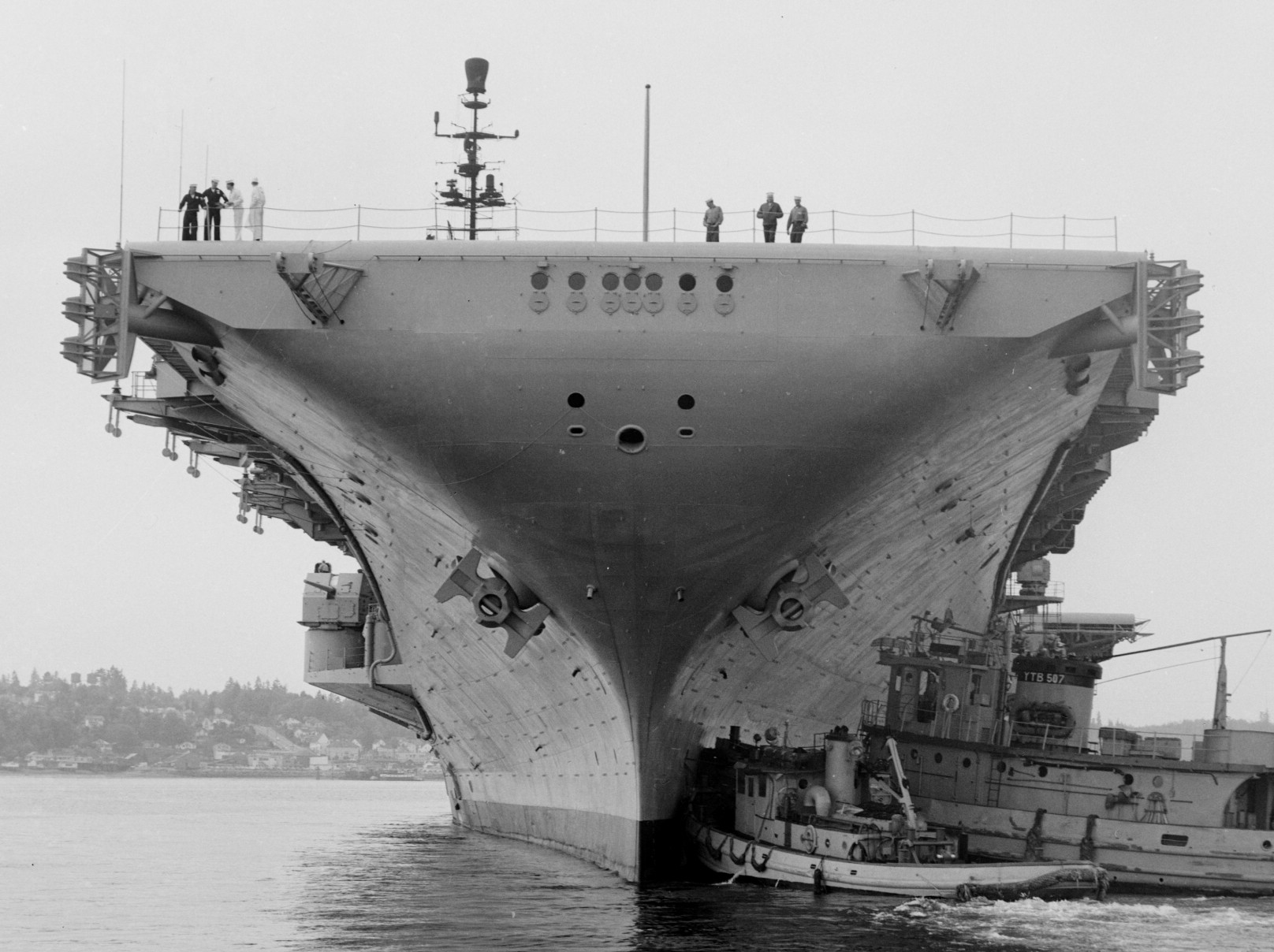  Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington - June 1956  May 1956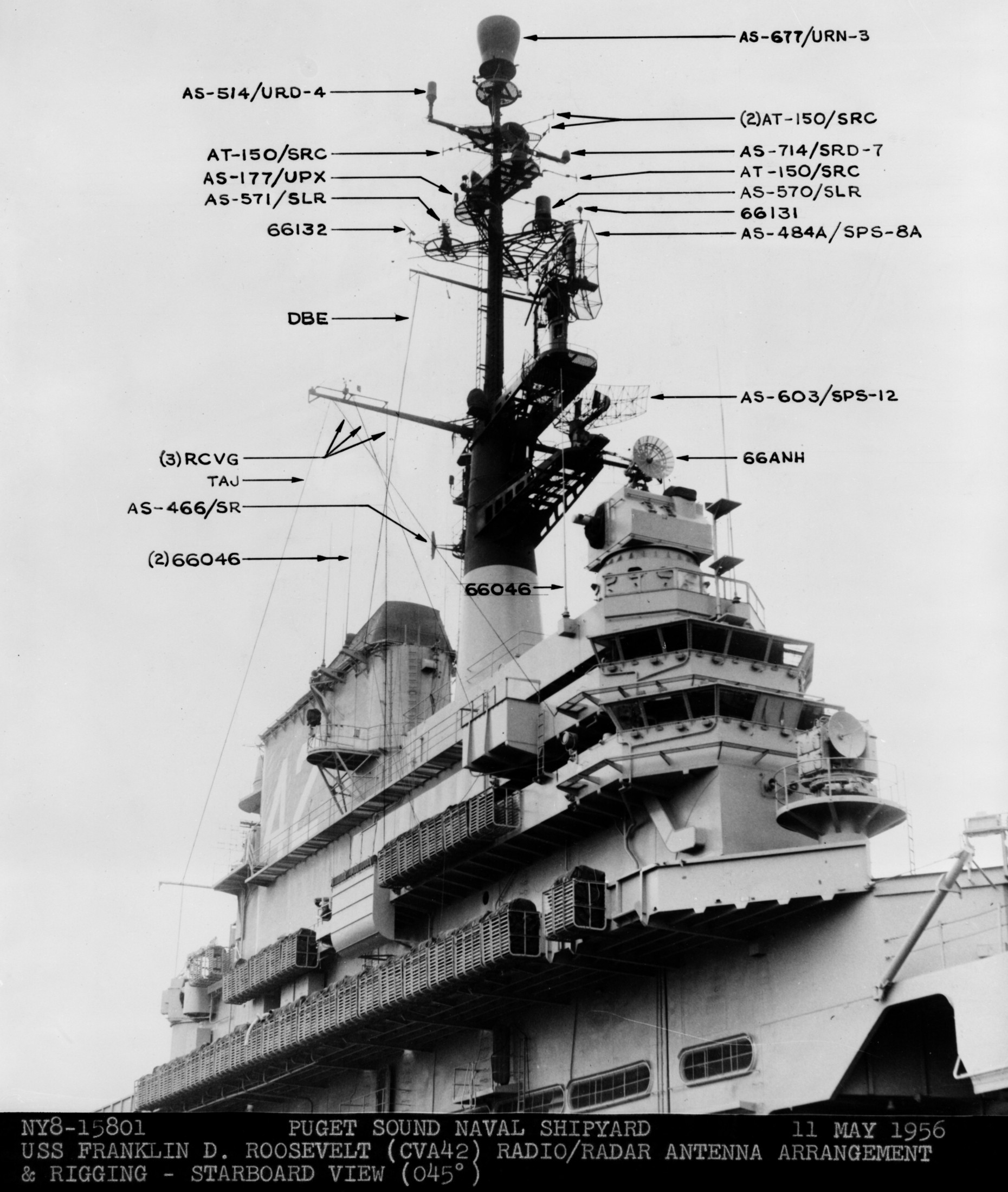  May 1956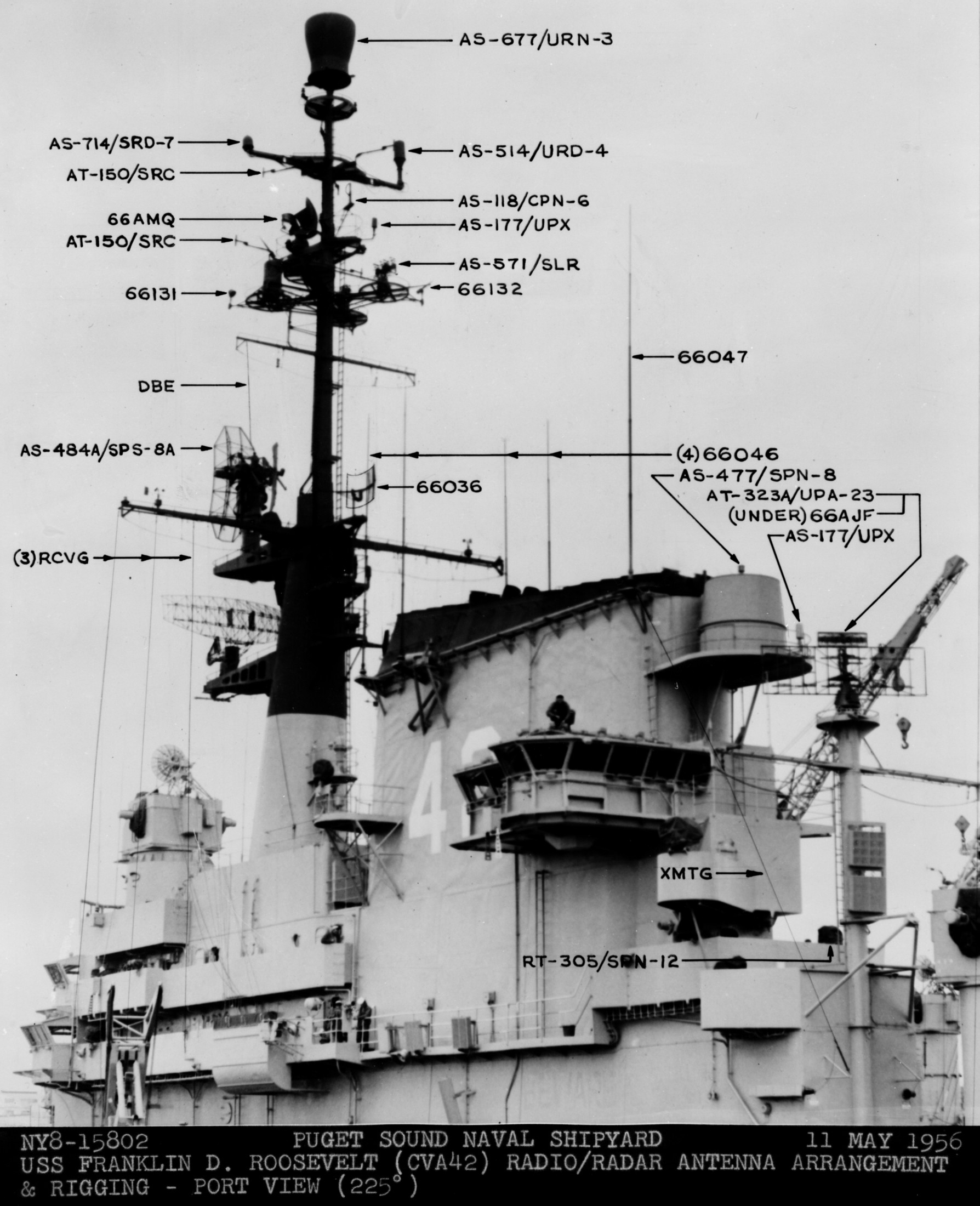  May 1956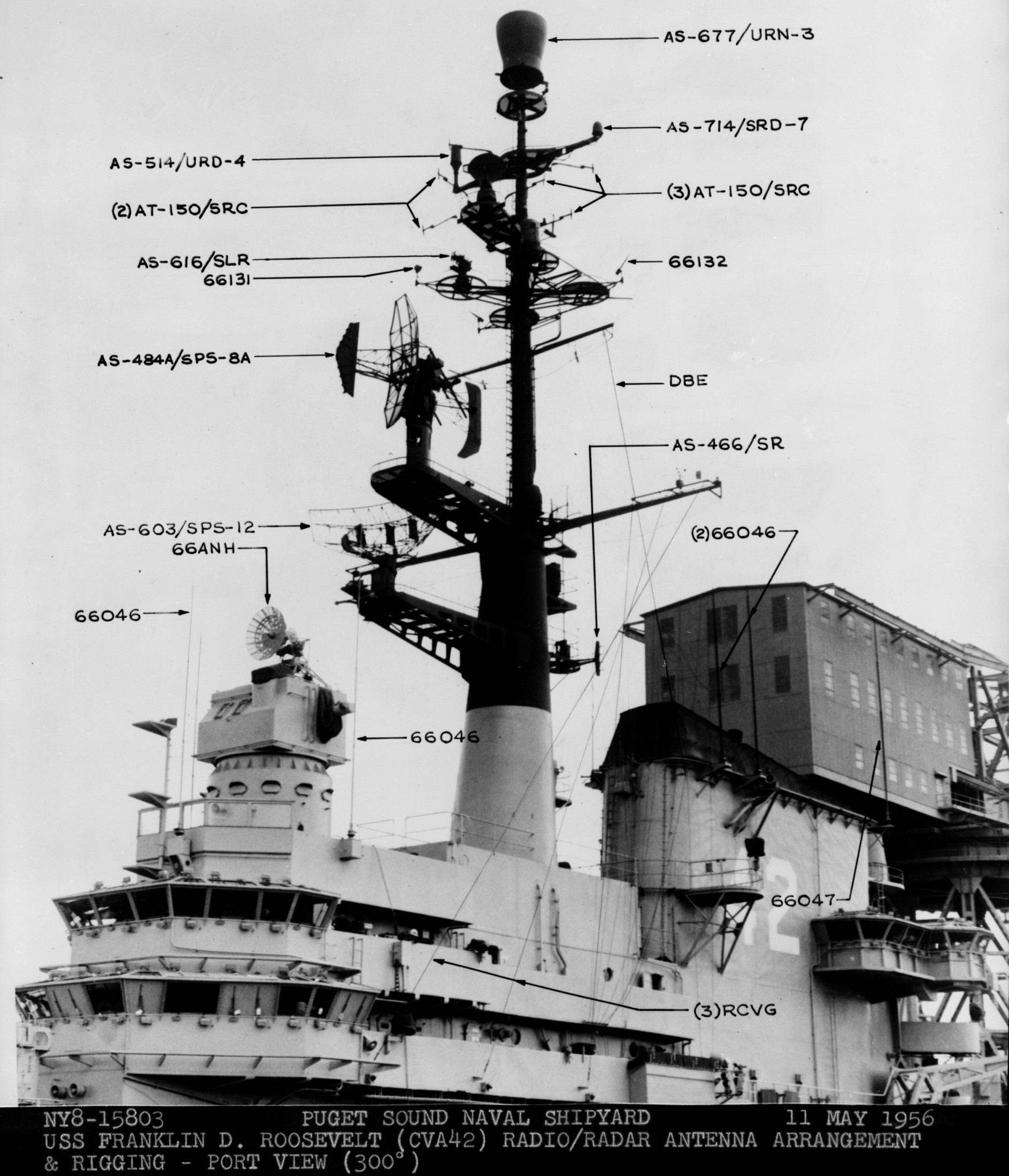  May 1956 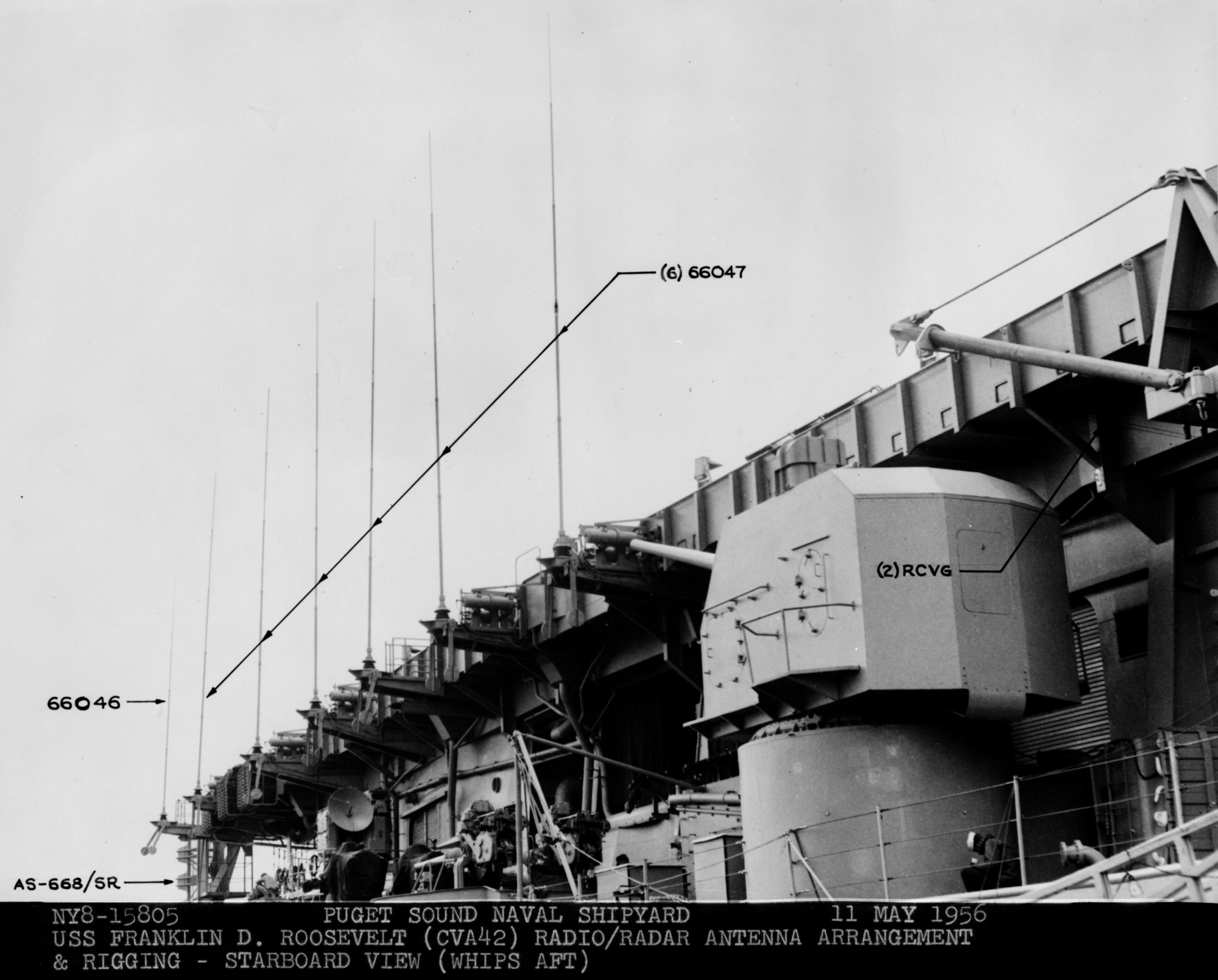 May 1956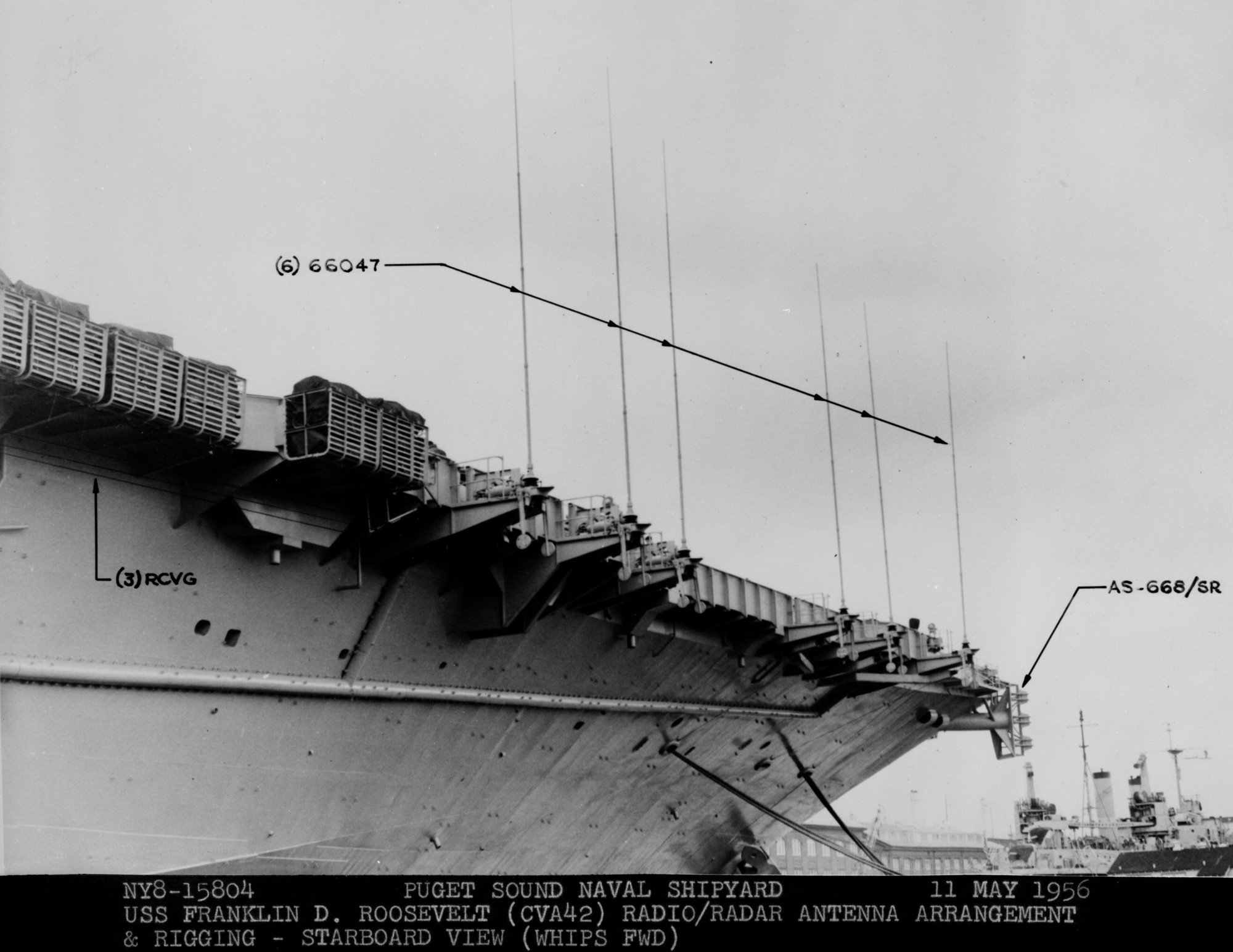  May 1956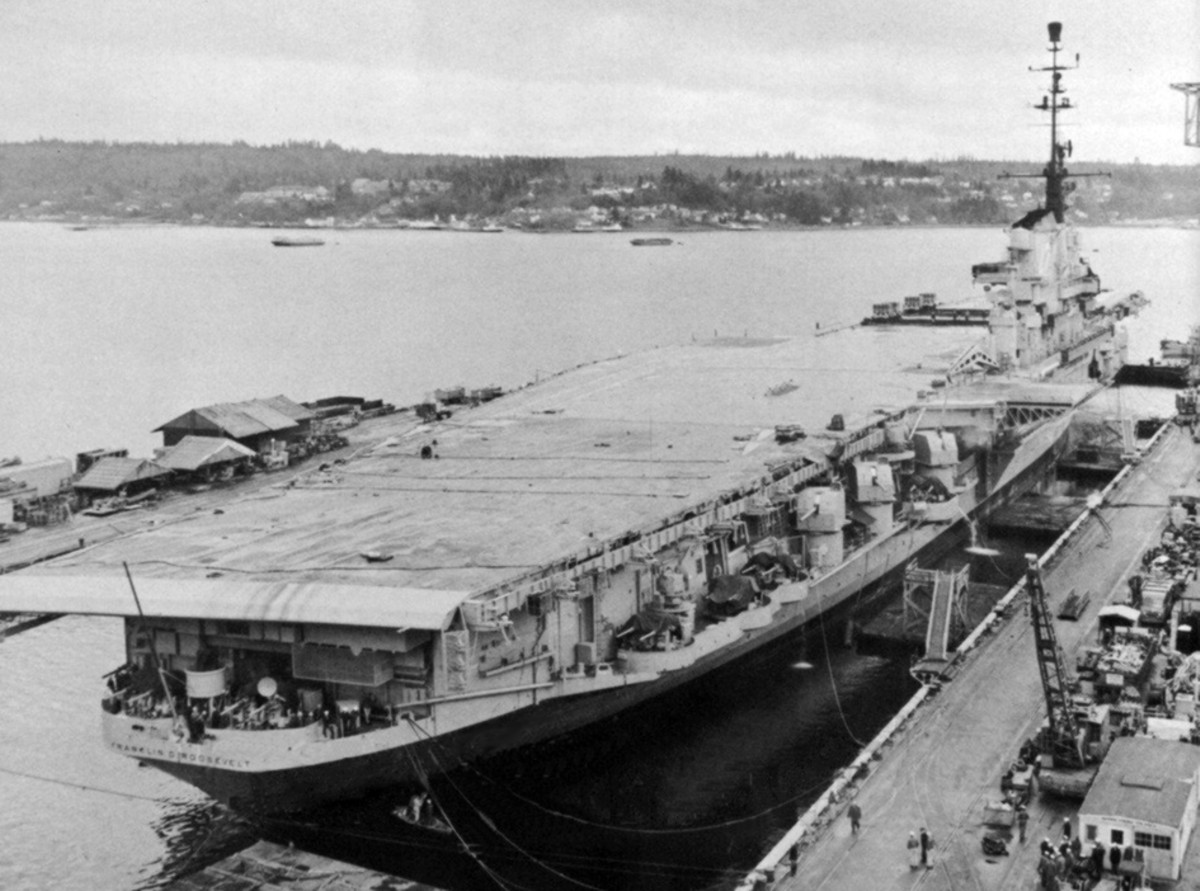  USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVA 42) during her SCB-110 modernisation at the Puget Sound Naval Shipyard which lasted from 5 March 1954 to June 1956SCB-110 modification: March 1954 - June 1956 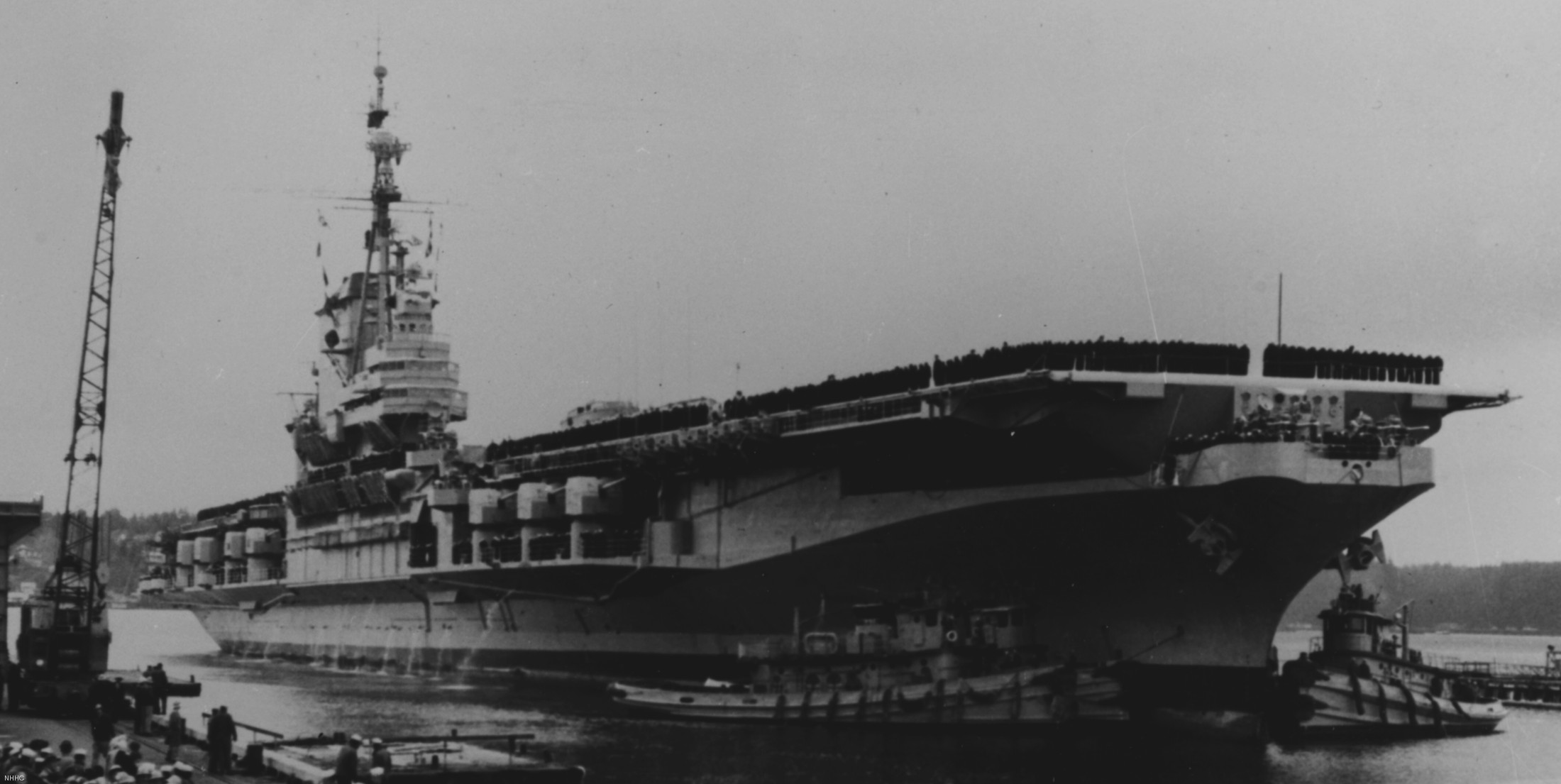 arriving at Puget Sound Naval Shipyard for her upcoming conversion - March 1954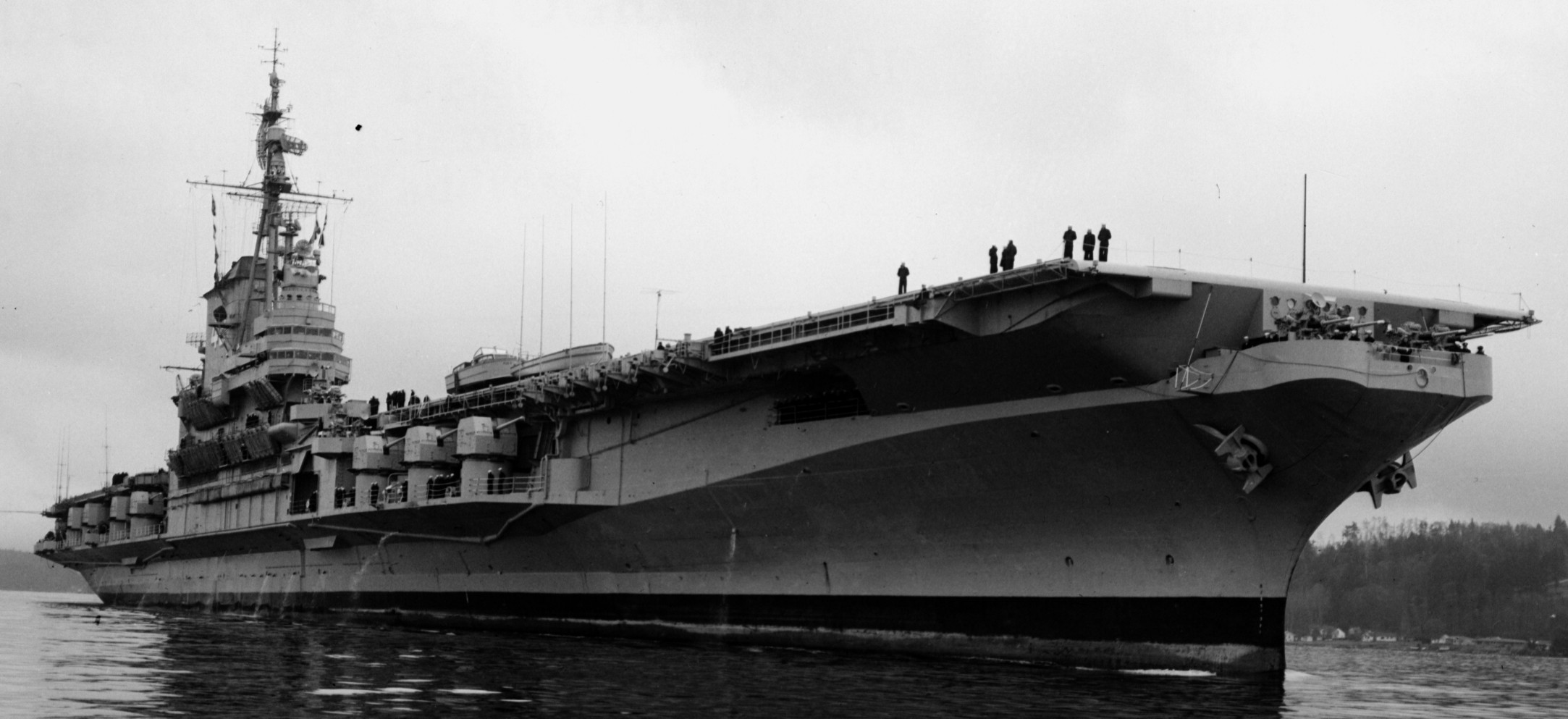  March 1954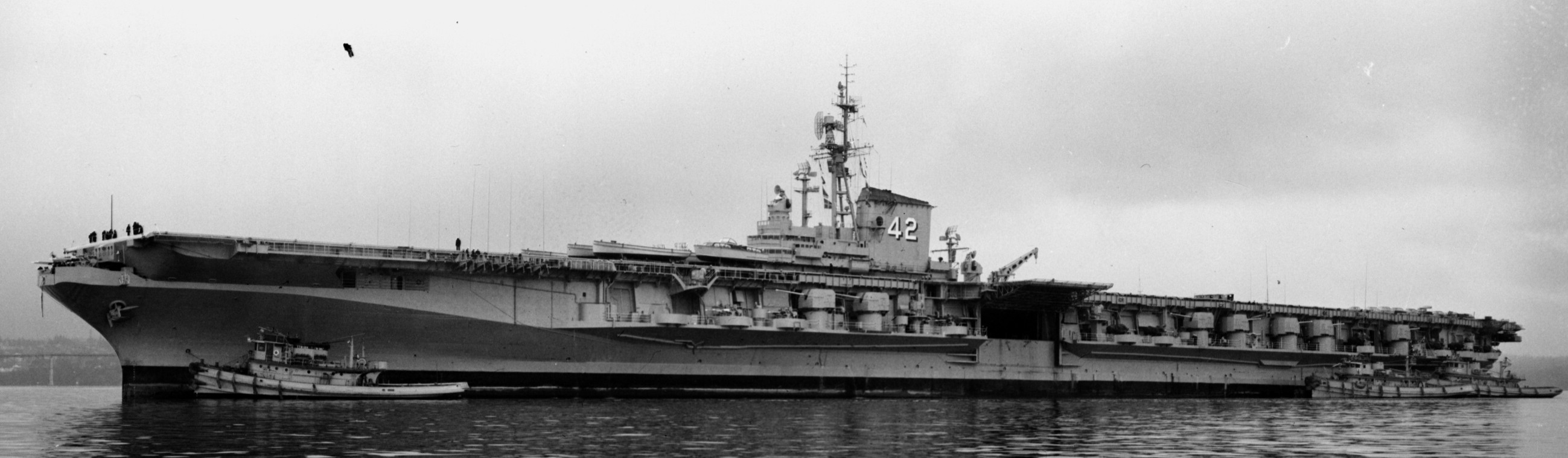  March 1954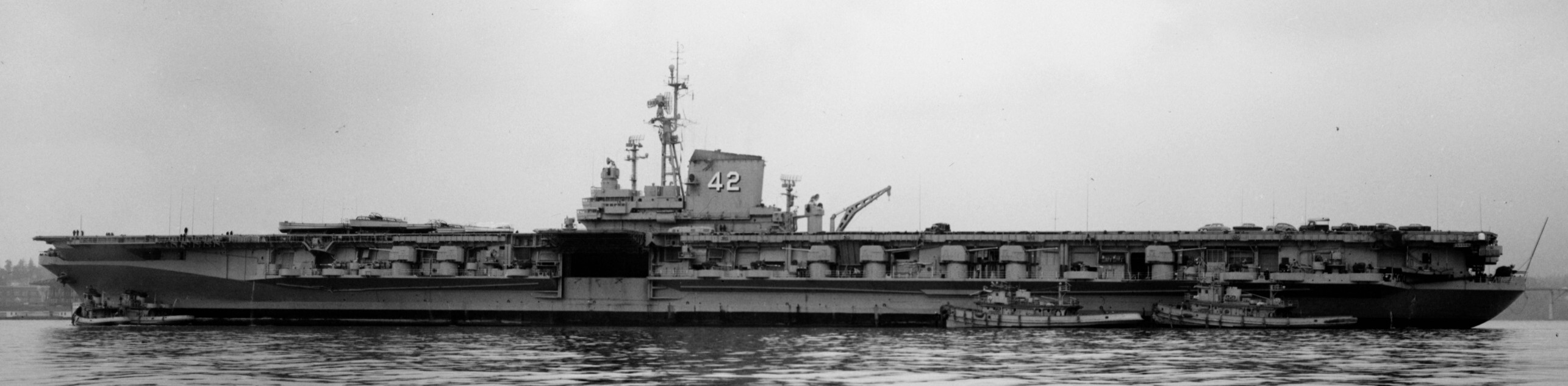  March 1954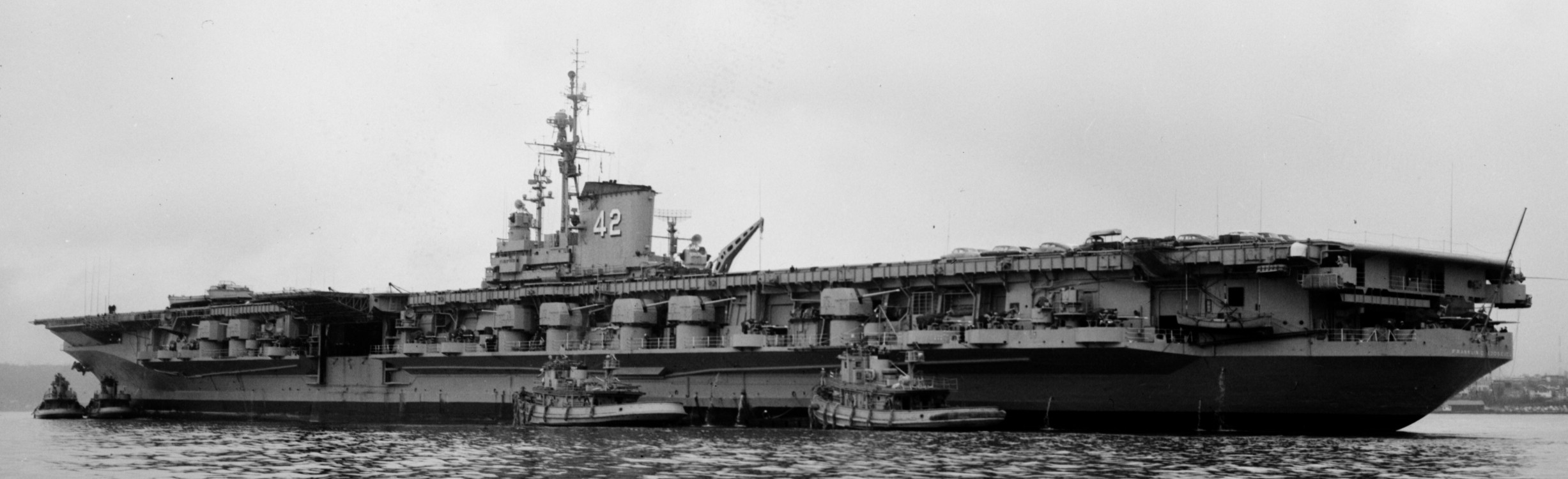  March 1954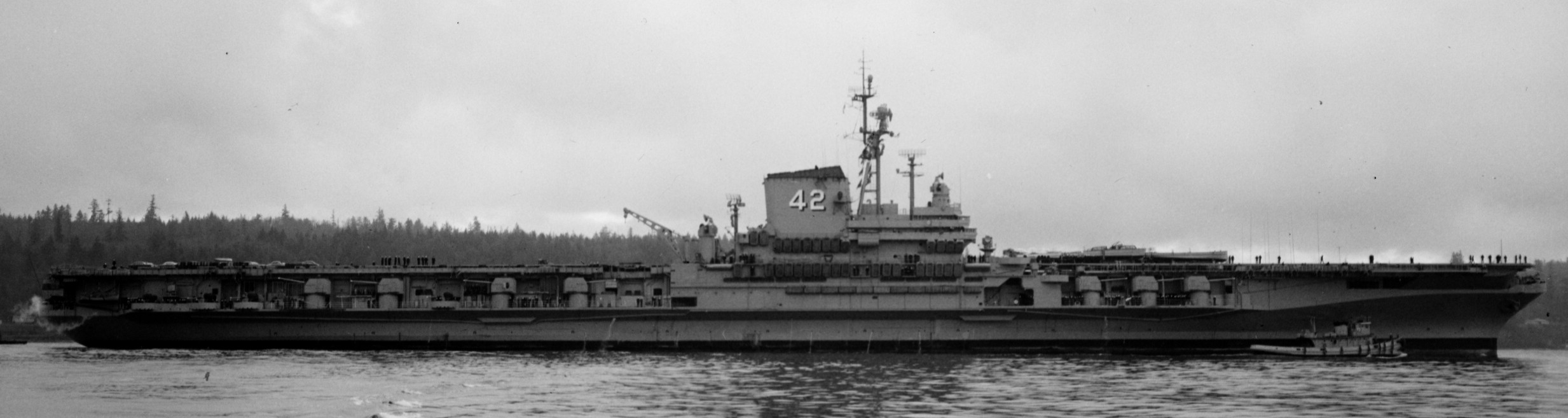  March 1954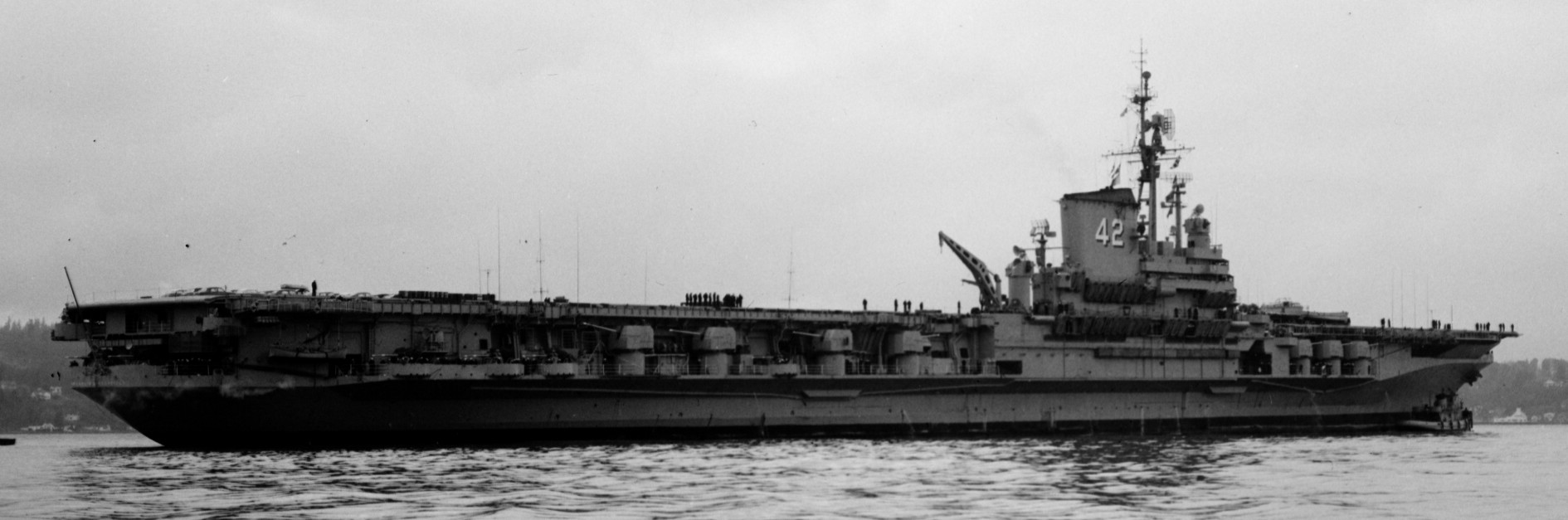  March 1954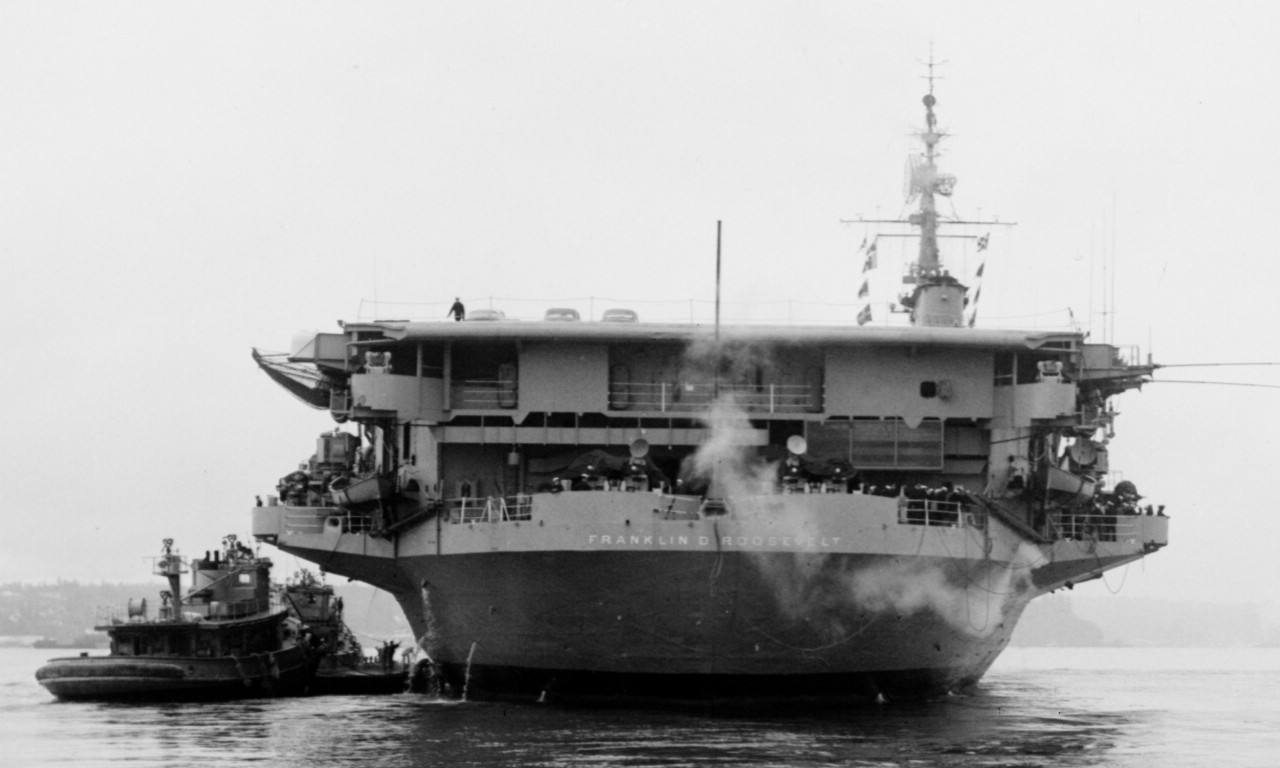  March 1954 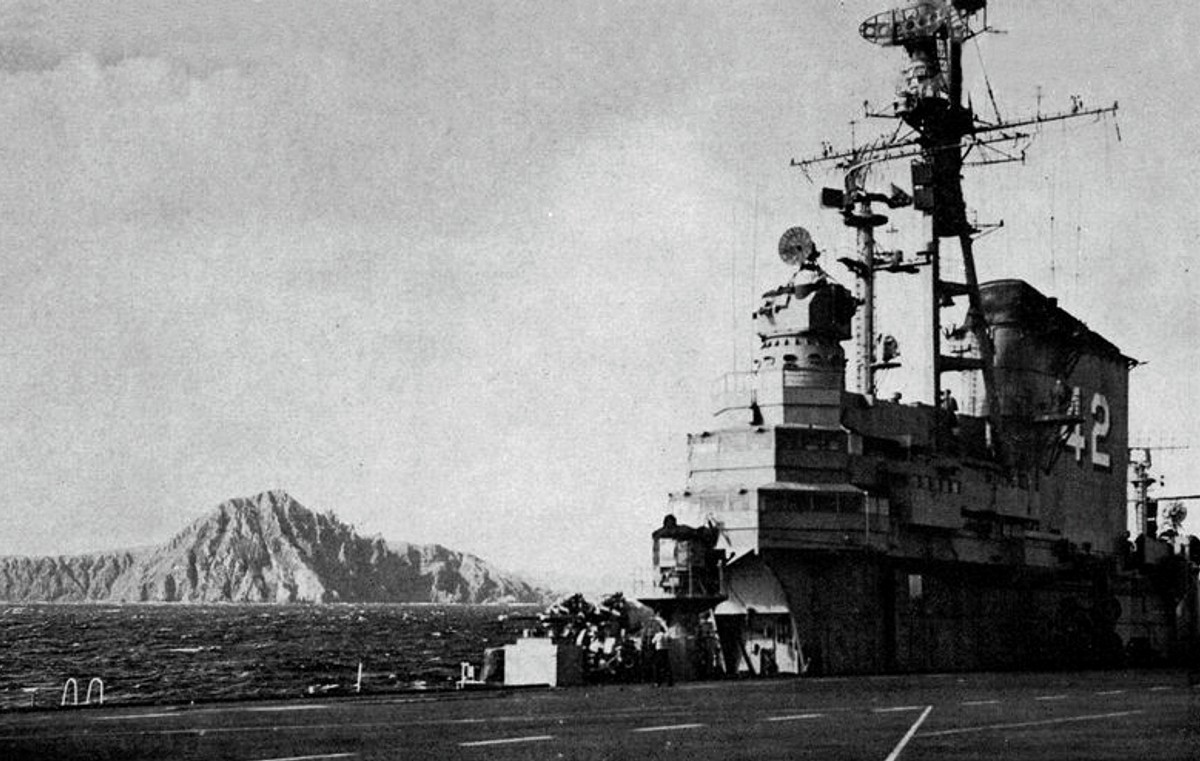 USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVA 42) off Cape Horn on 4 February 1954. FDR, with assigned Carrier Air Group 8 (CVG-8), circumnavigated South America between 7 January and 5 March 1954 to enter the Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, Washington (USA), for her SCB-110 modernization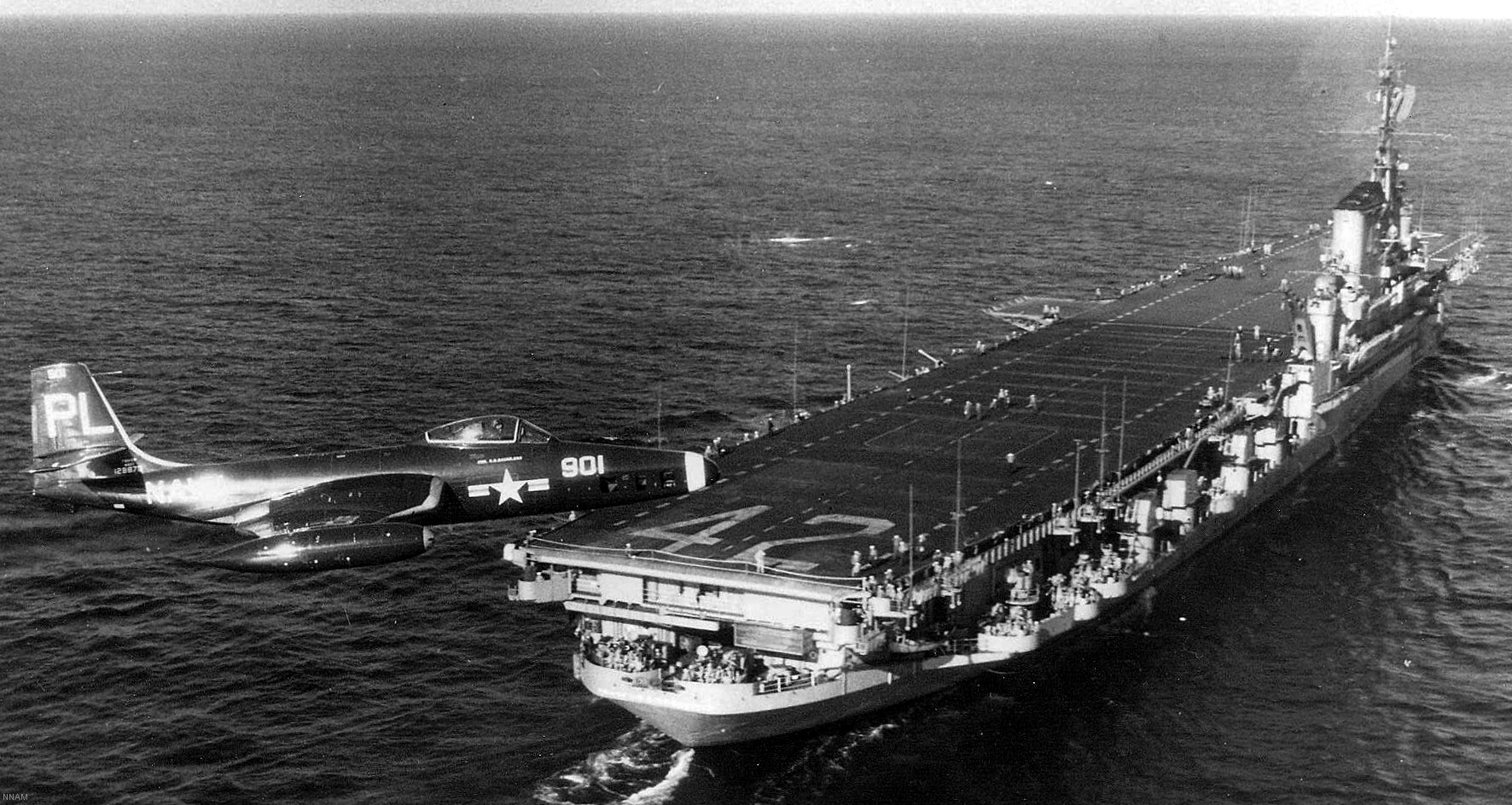  McDonnell F2H-2P Banshee of Composite Squadron 62 (VC-62) "Fighting Photos" in flight over USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVA 42) on 27 January 1953. VC-62 Det.7 was assigned to Carrier Air Group 17 (CVG-17) aboard the Franklin D. Roosevelt for a deployment to the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean Sea from 26 August to 19 December 1952redesignated CVA 42 on October 1, 1952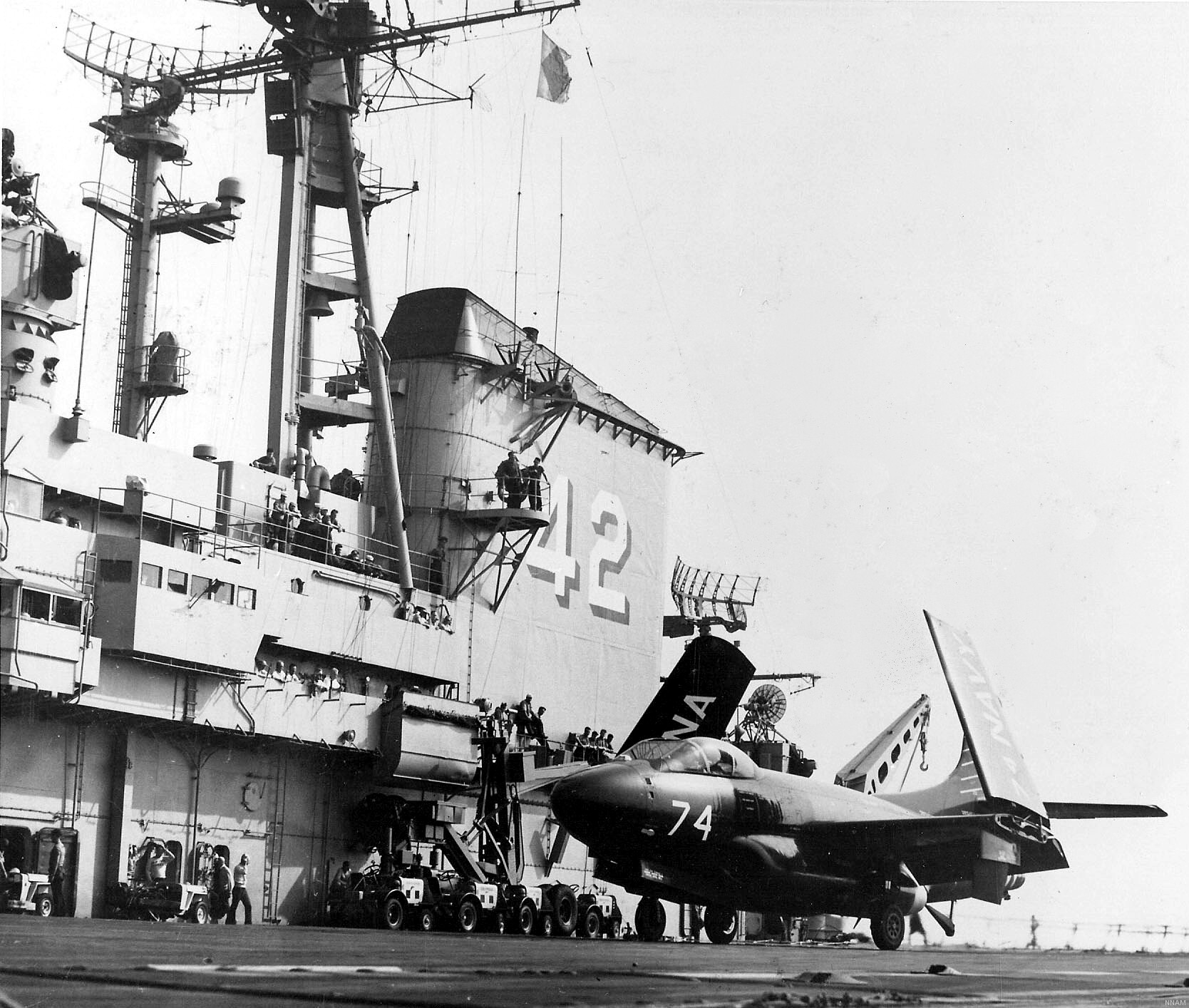  Douglas F3D-2 Skyknight of VC-4 on the flight deck - 1952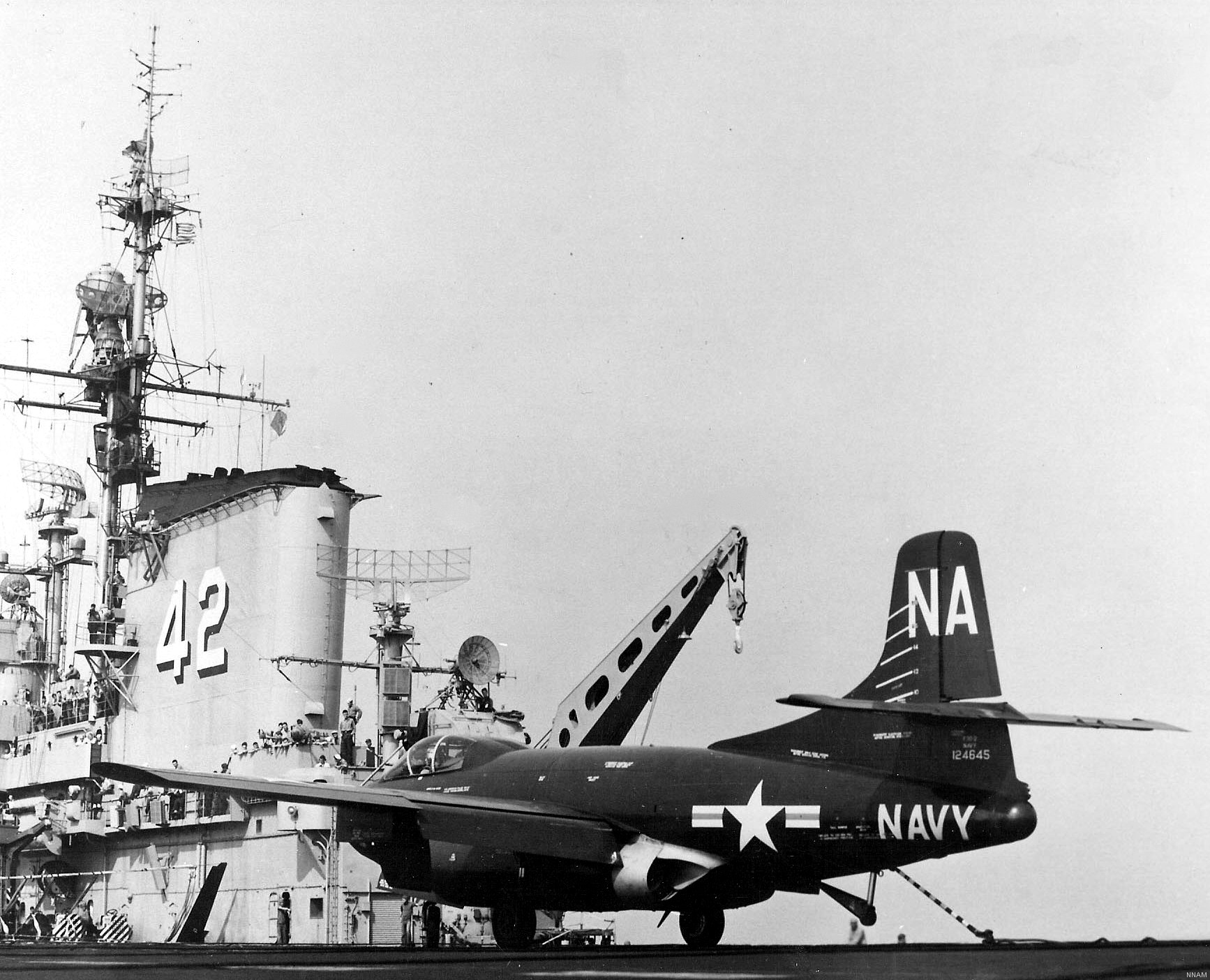  Douglas F3D-2 Skyknight of VC-4 on the flight deck - 1952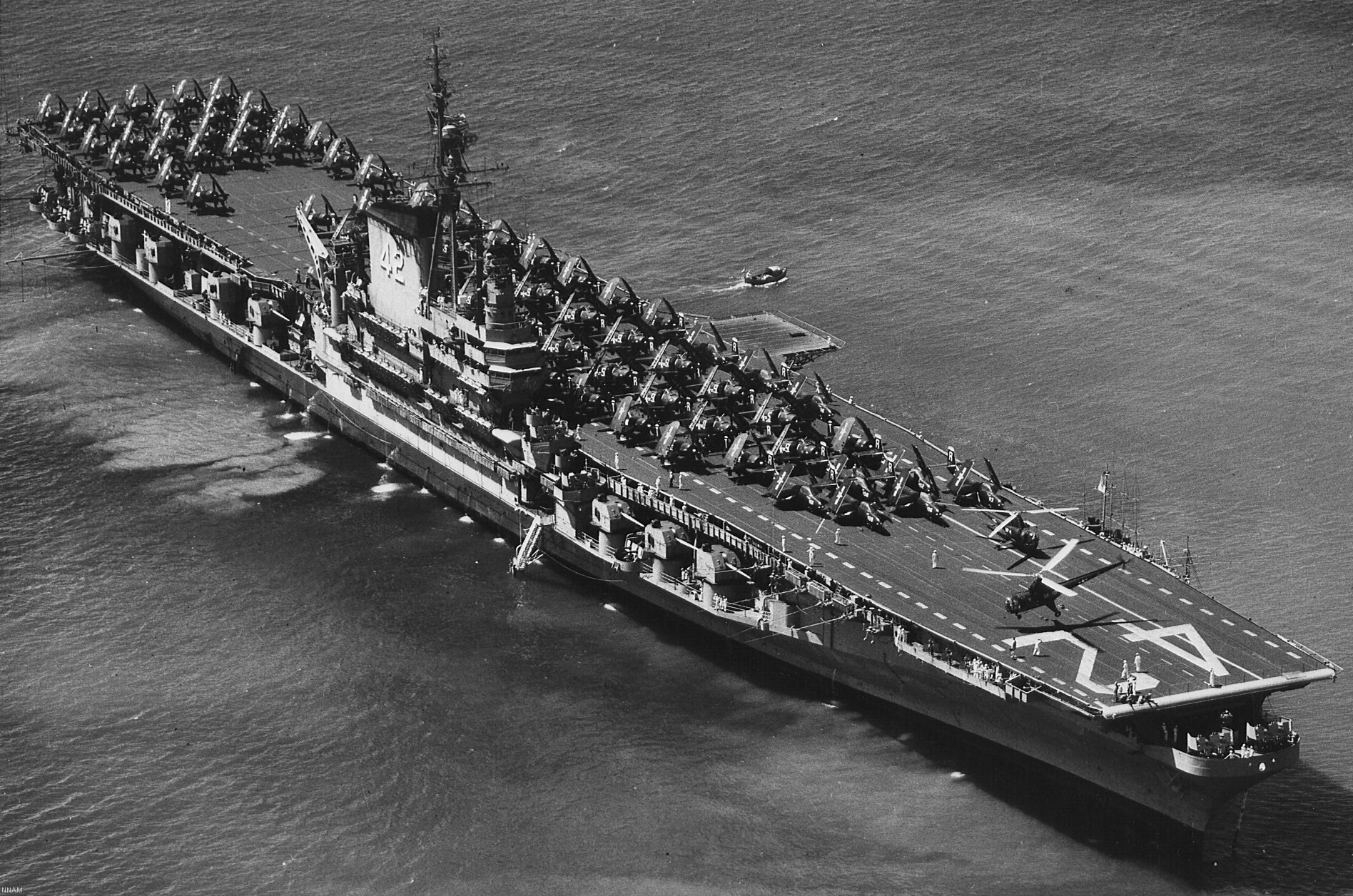  with Carrier Air Group 17 (CVG-17) embarked - early 1950's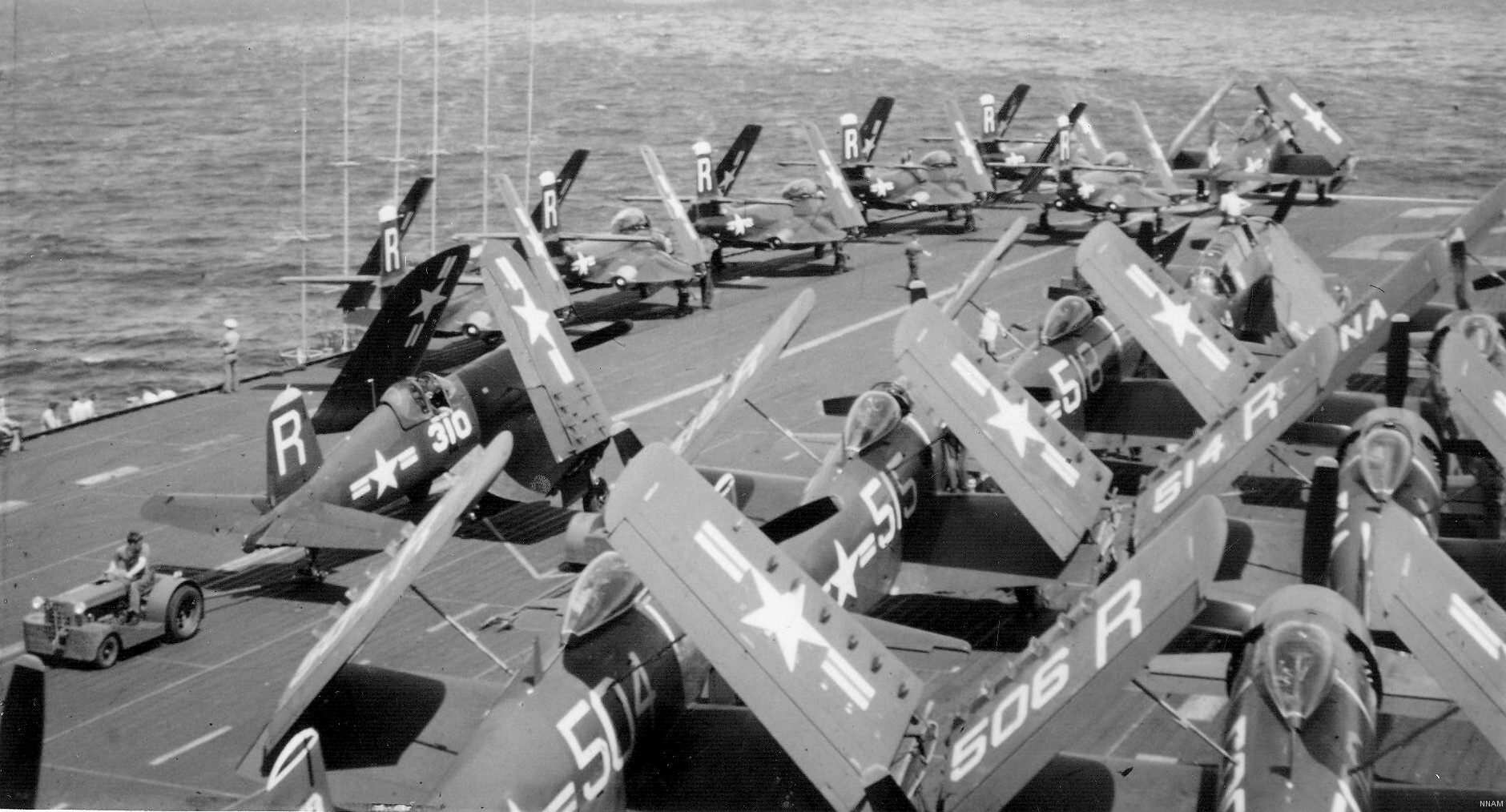  with Carrier Air Group 17 (CVG-17) embarked - early 1950's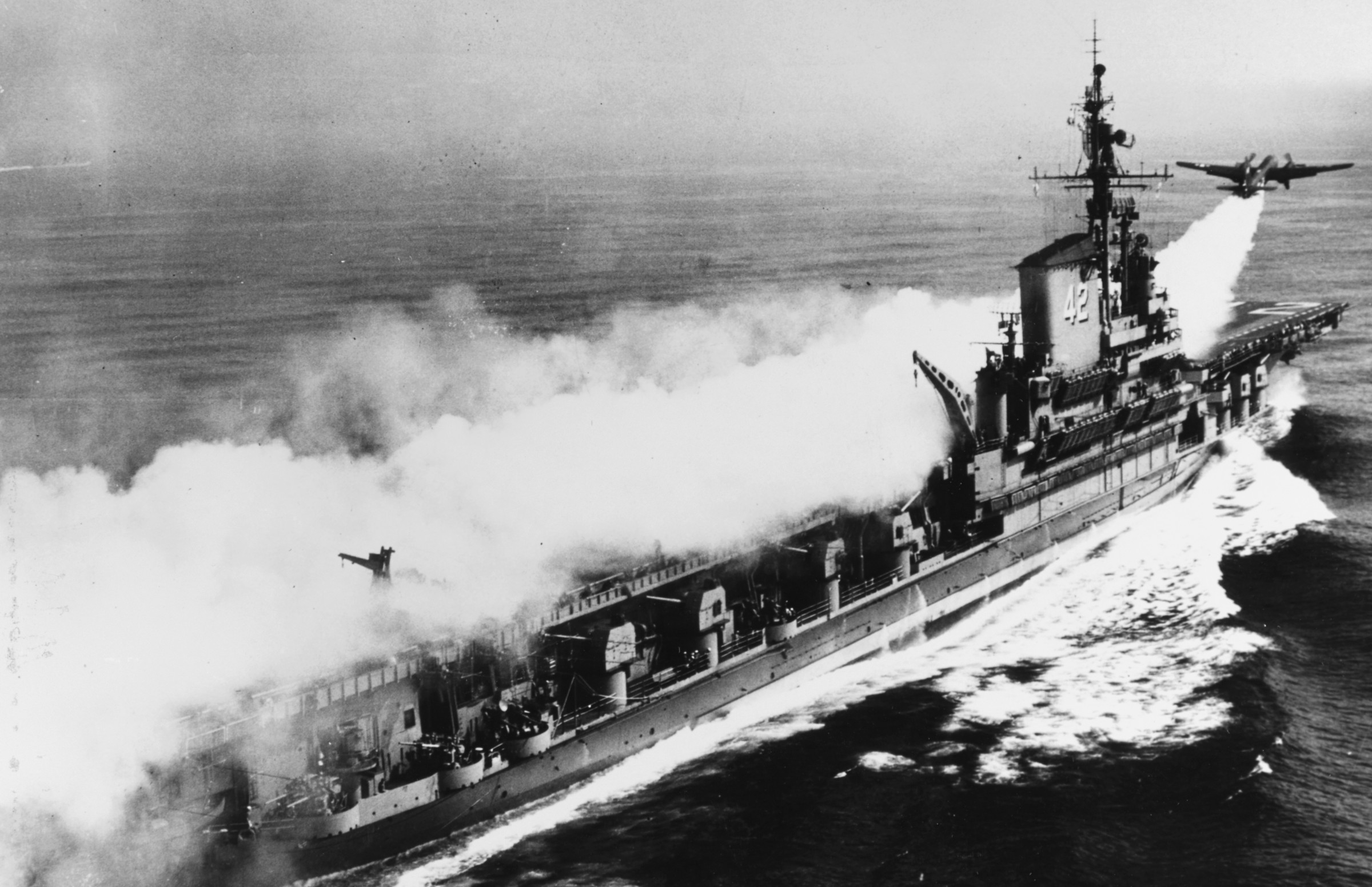  Lockheed P2V-3C Neptune launches with "Jet-assisted take-off (JATO)" from USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVB 42) on 2 July 1951  with CVG-6 embarked - off Nice, France - 1951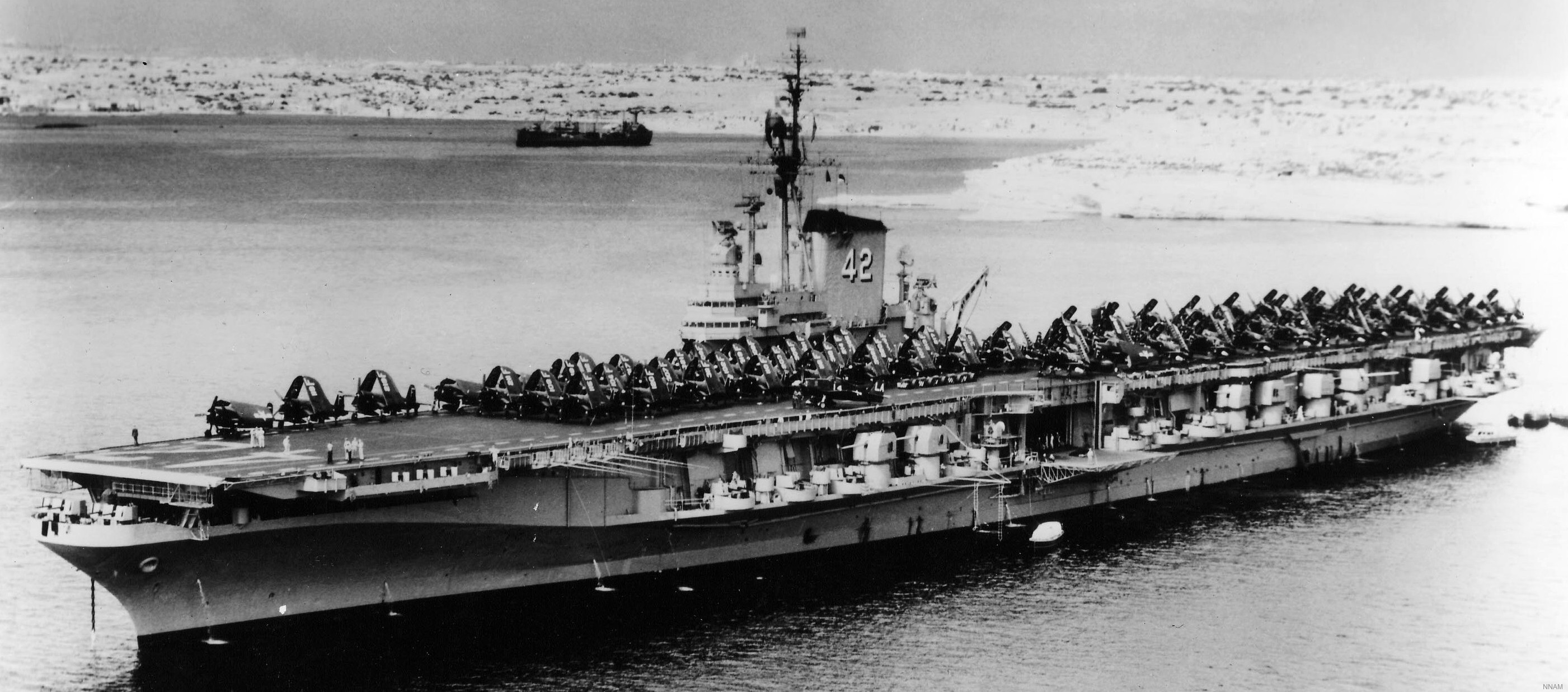  USS Franklin D. Roosevelt anchored at an unknown location in the Mediterranean Sea. On the flight deck are various aircraft of Carrier Air Group 4 (CVG-4) which was deployed aboard the FDR from 13 September 1948 to 23 January 1949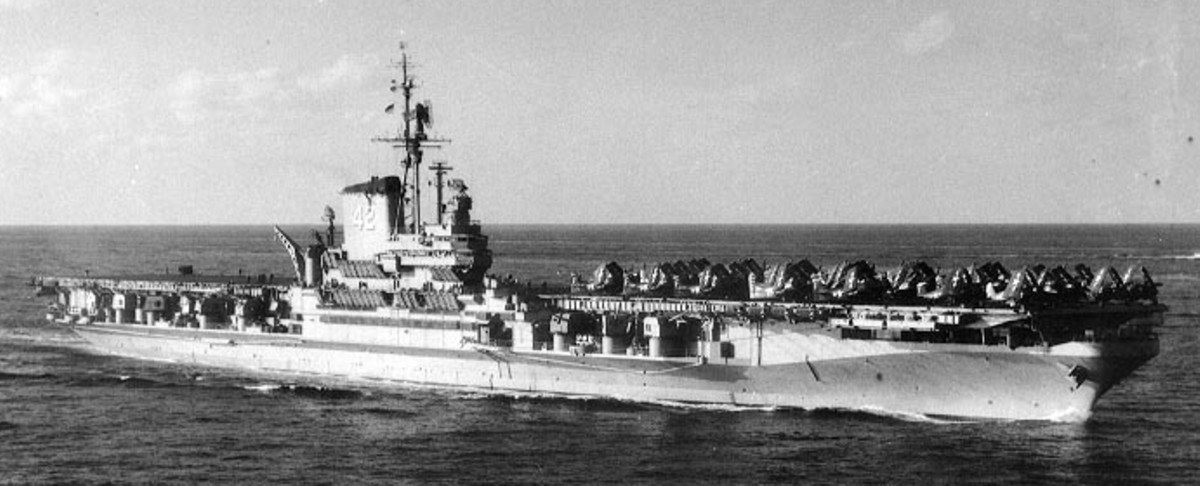  with Carrier Air Group 4 (CVG-4) embarked - November 1948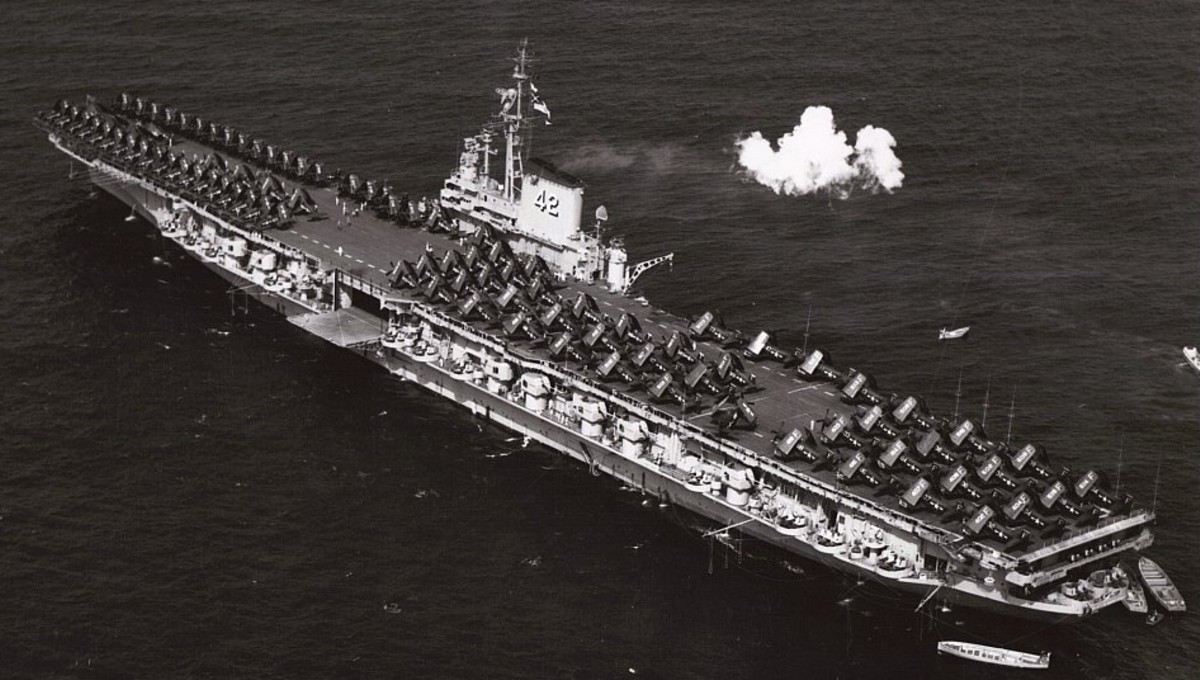  with Carrier Air Group 4 (CVG-4) embarked - late 1948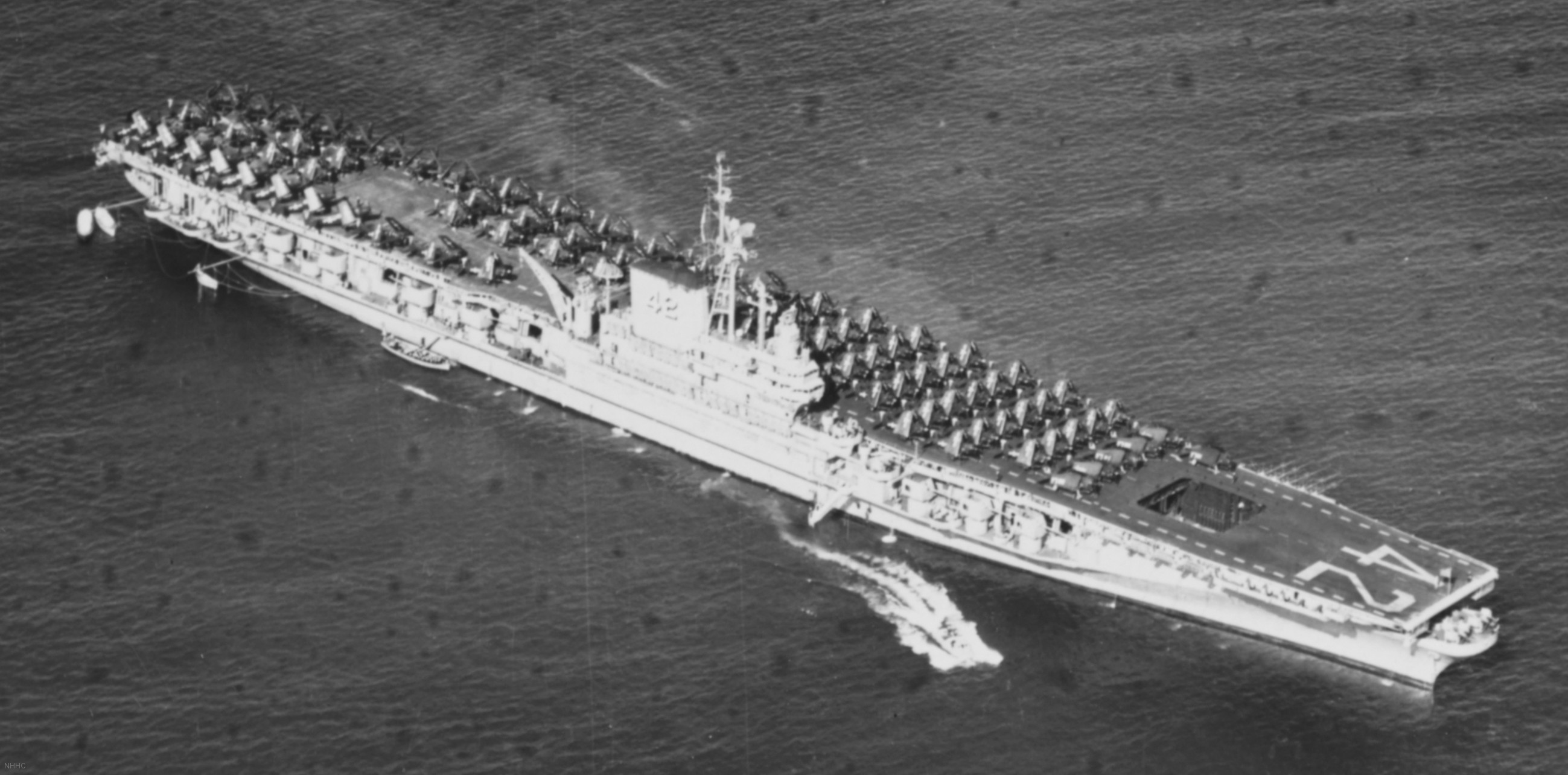  with Carrier Air Group 4 (CVG-4) embarked - off Piraeus, Greece - October 1948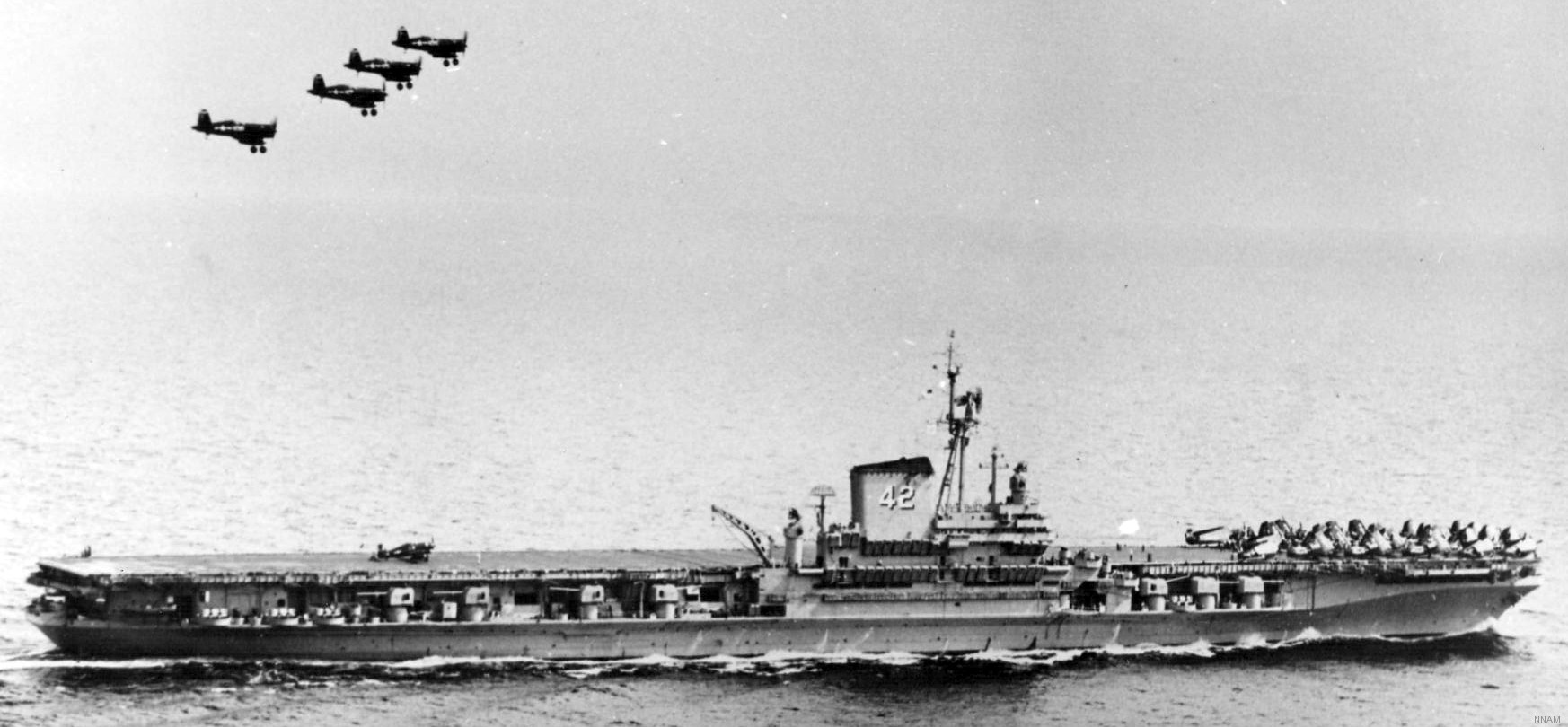  circa 1946-48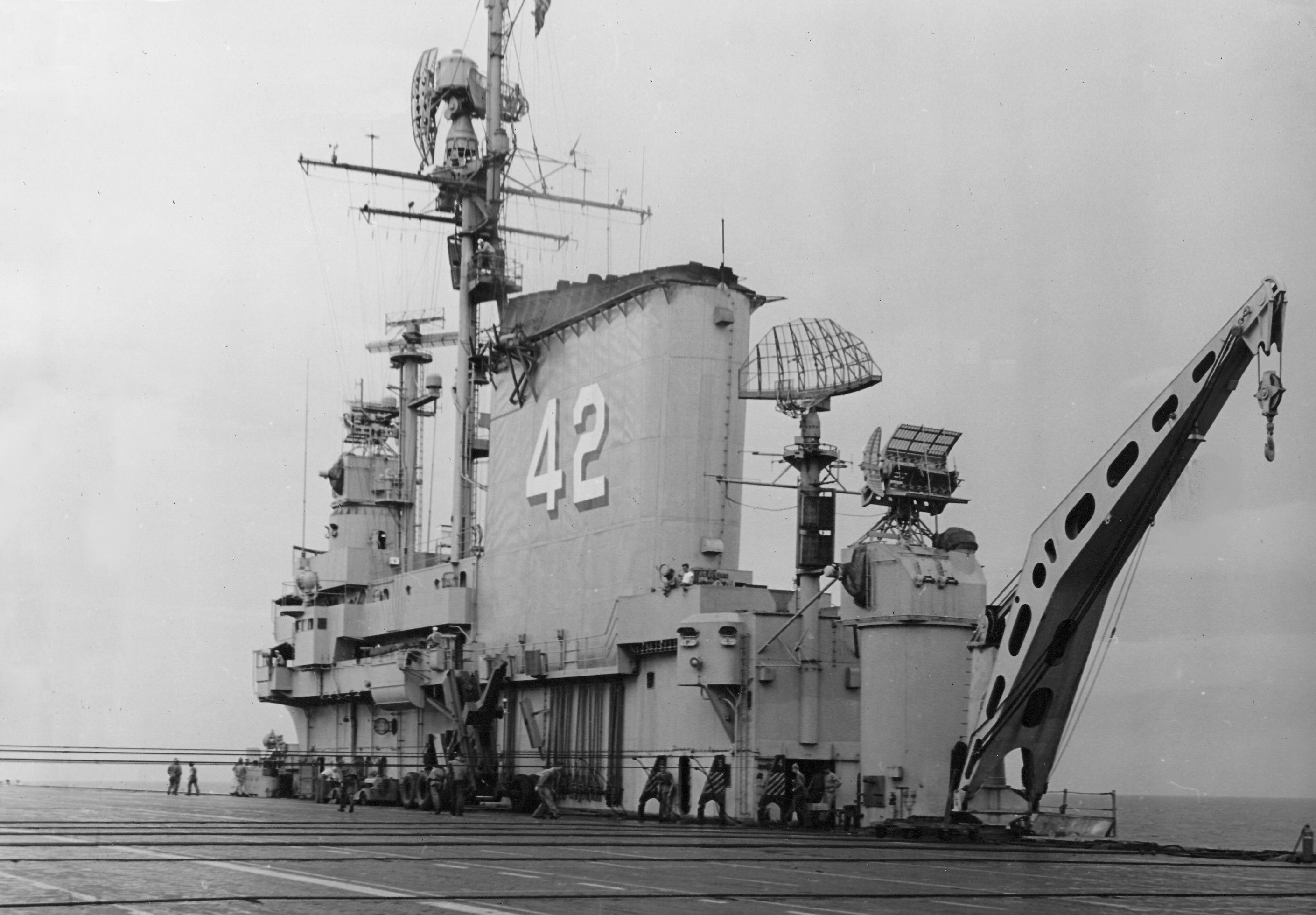  circa 1947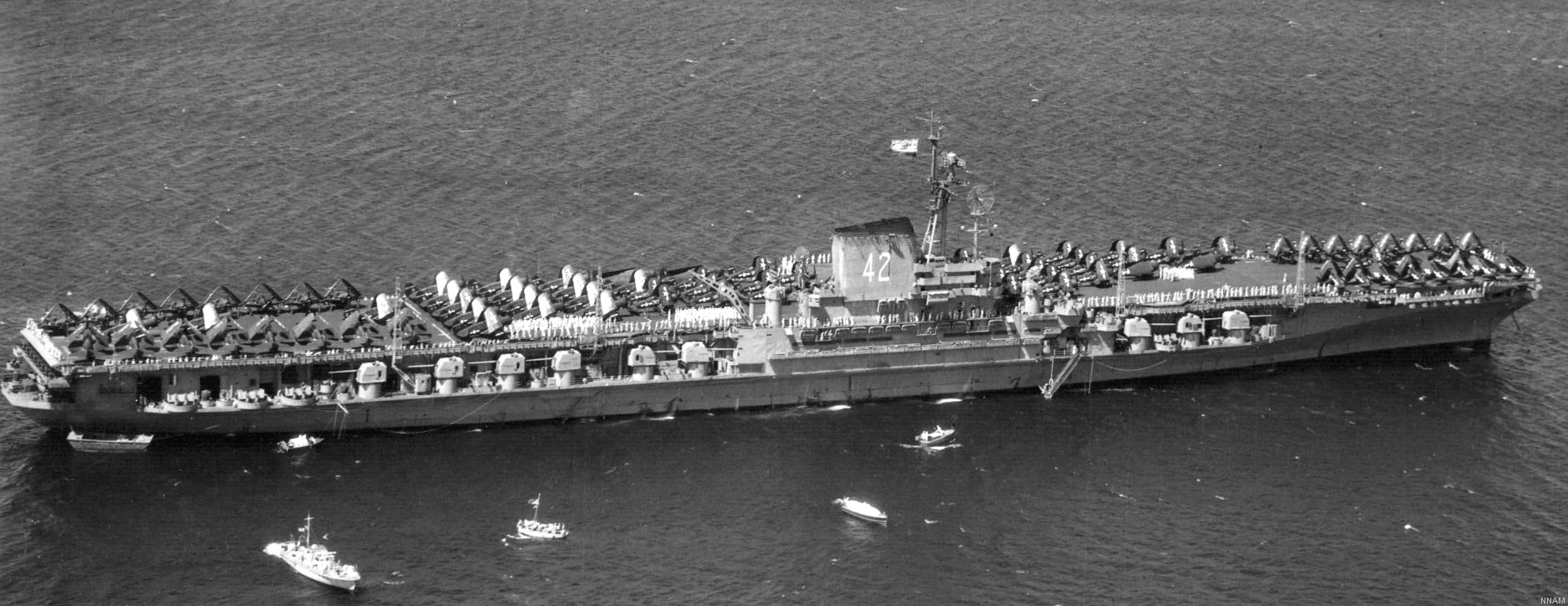  with CVBG-75 embarked - at anchor at Piraeus, Greece - September 1946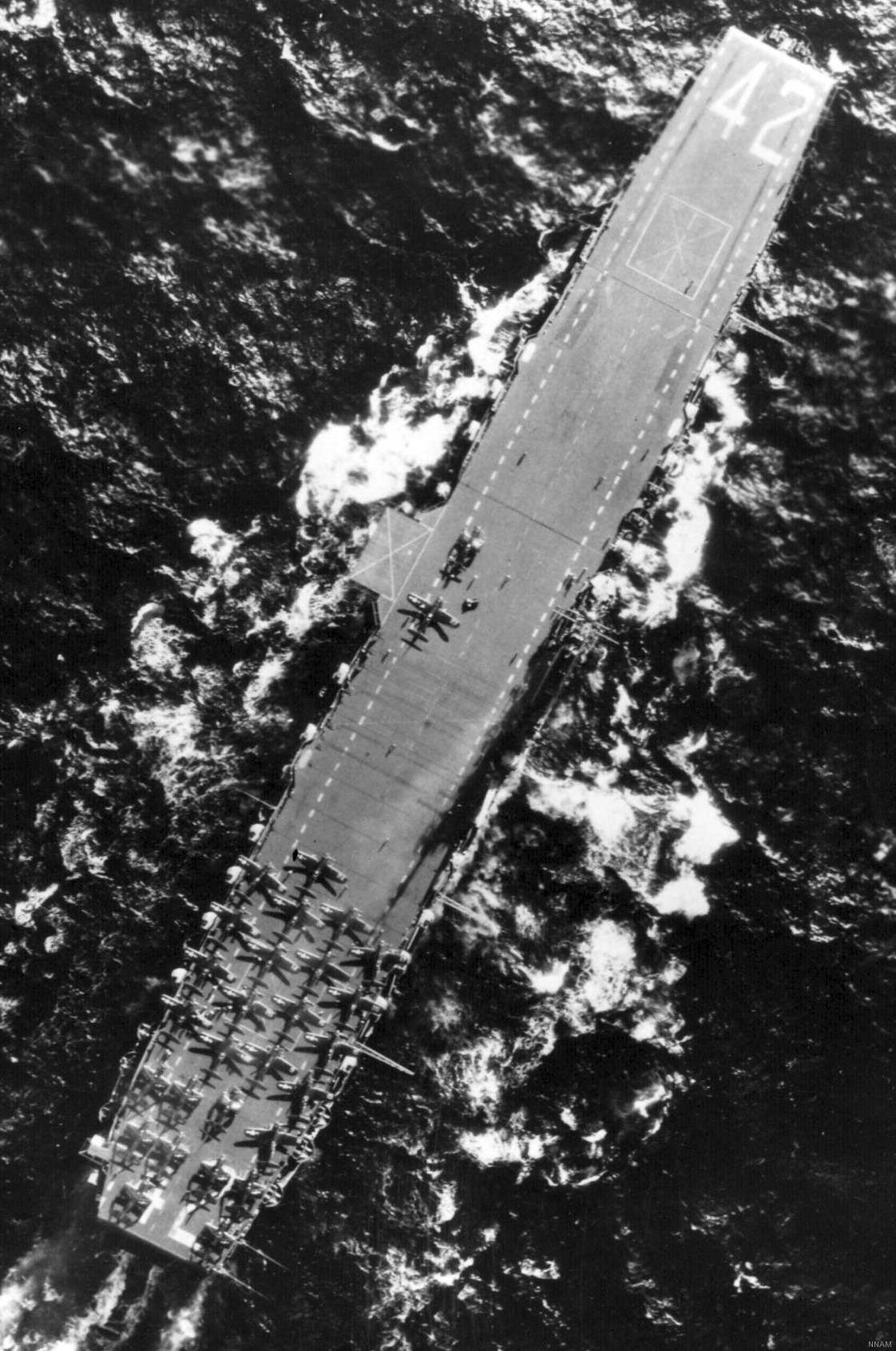  with CVBG-75 embarked - circa May 1946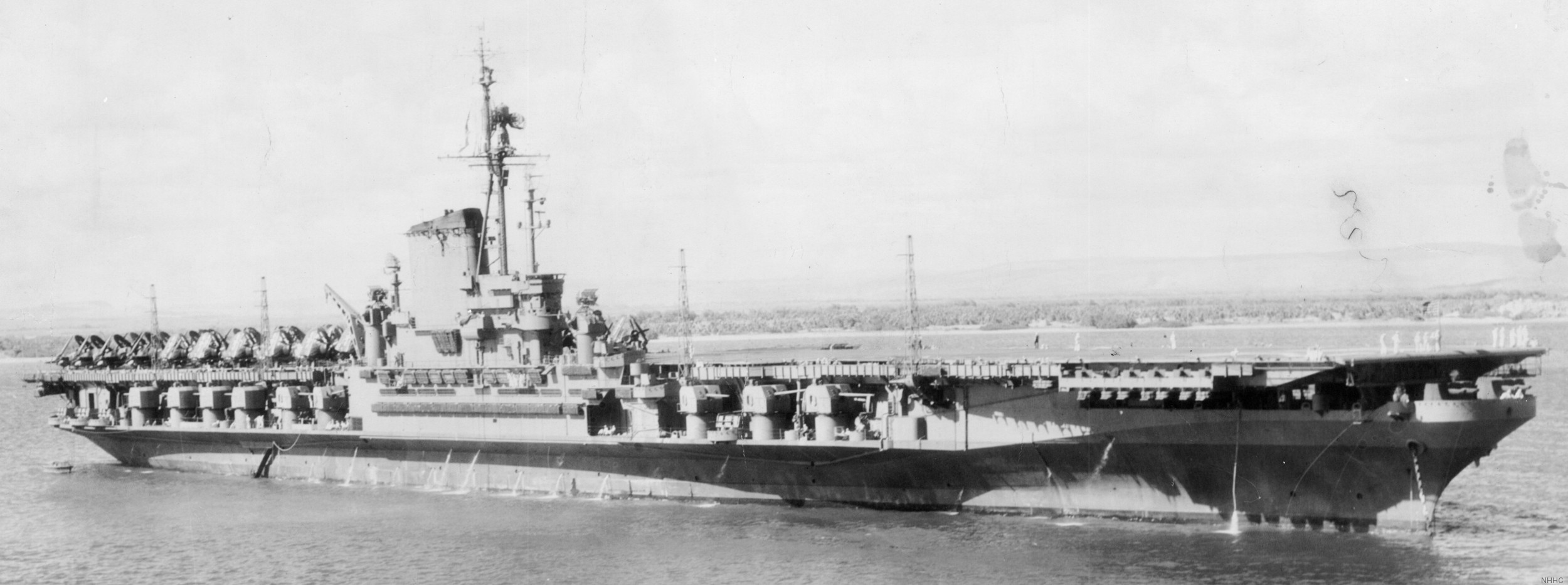  early 1946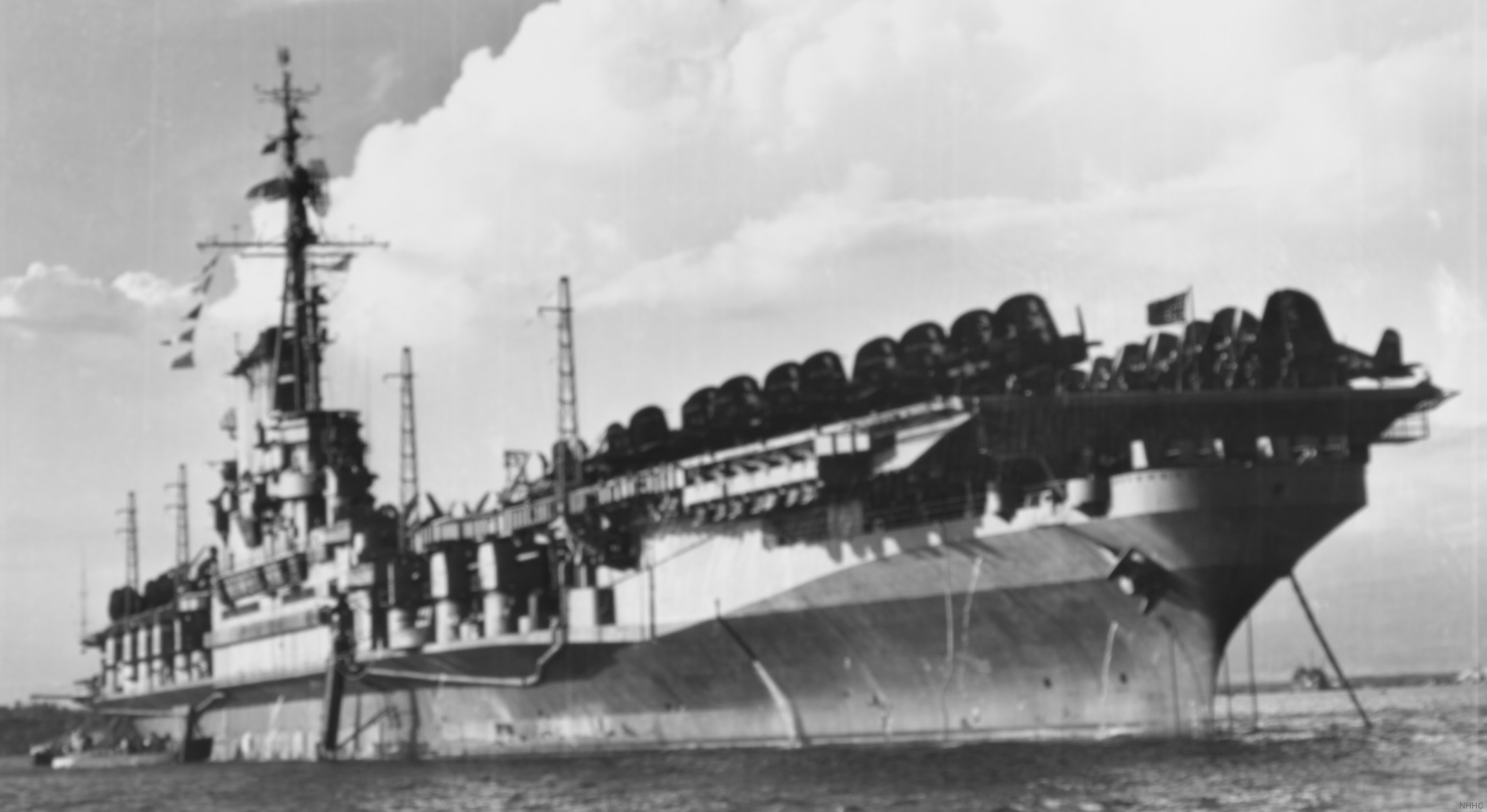  Guantanamo Bay, Cuba - May 1946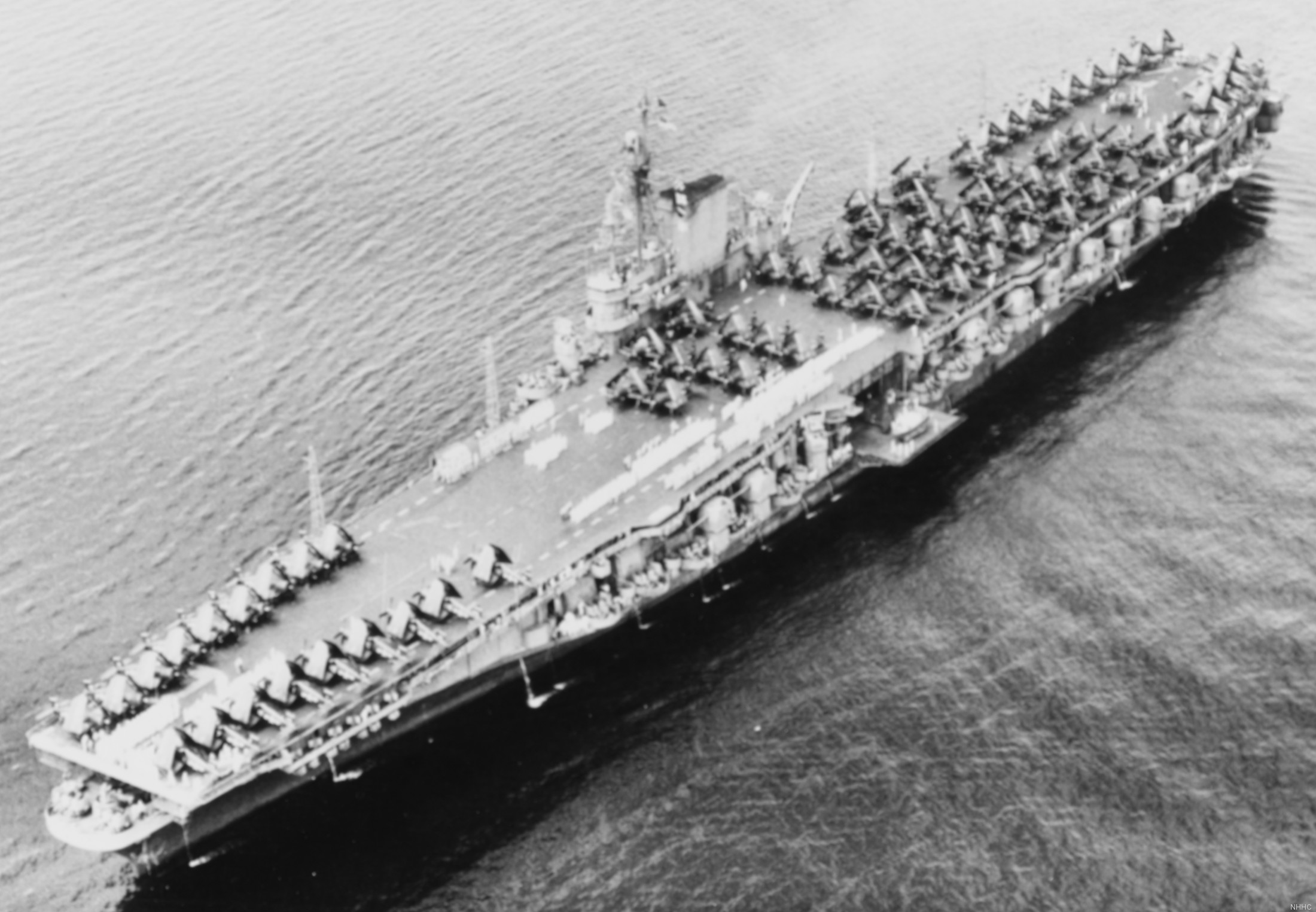  Gulf of Paria, off Trinidad - April 1946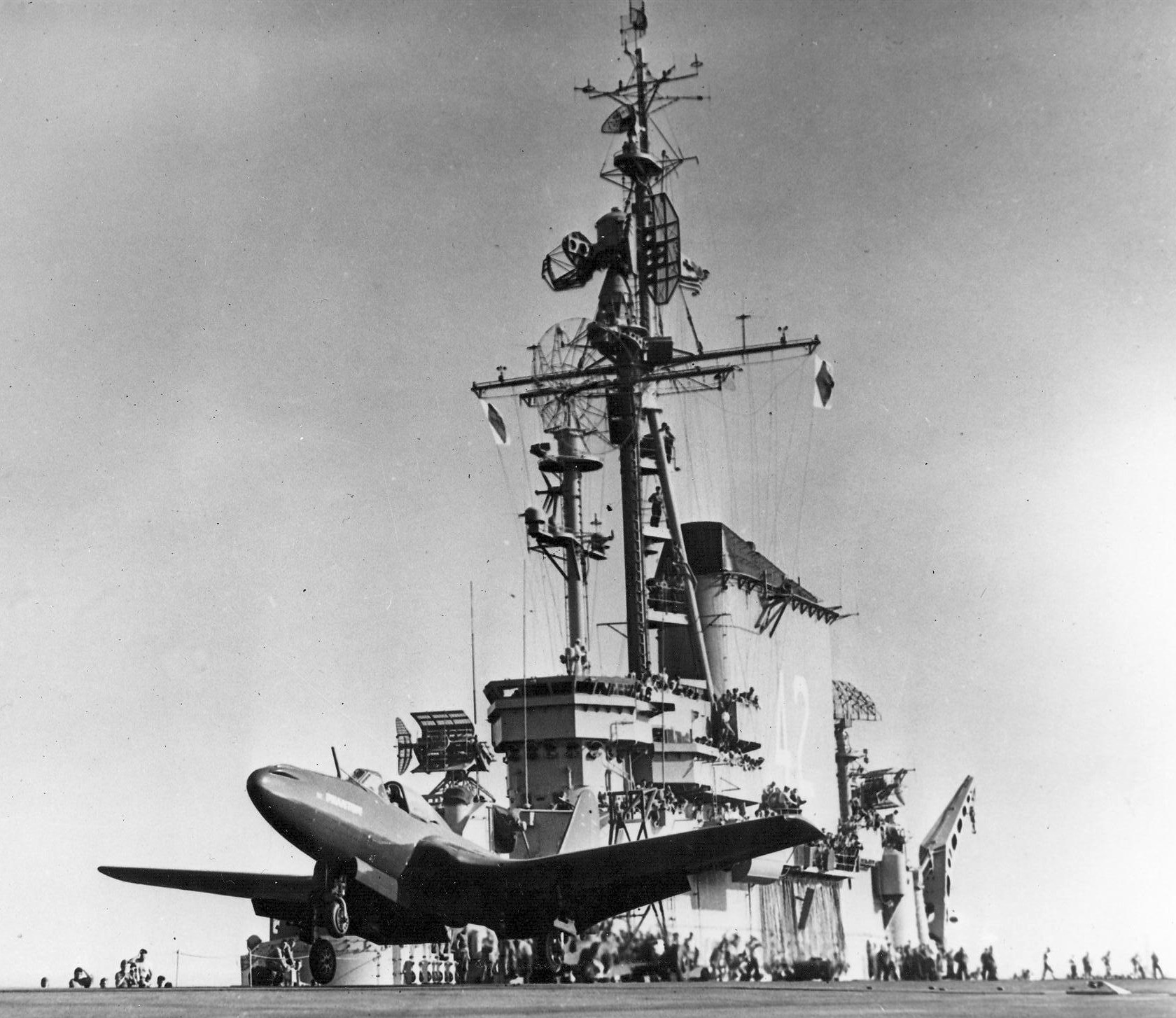  FH-1 Phantom taking off from USS Franklin D. Roosevelt - 1946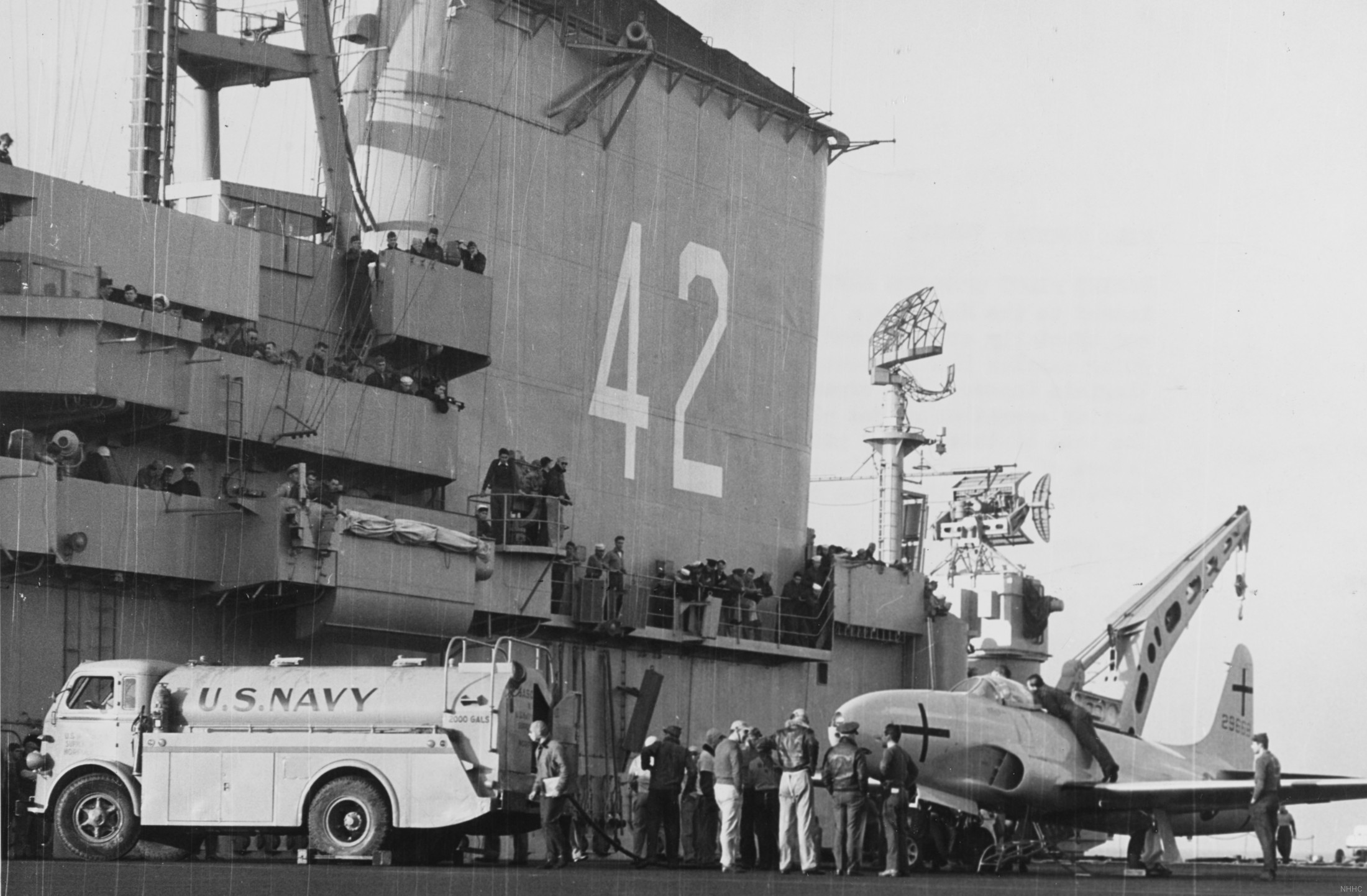  Lockheed P-80A fighter aircraft tests off Virginia - 1946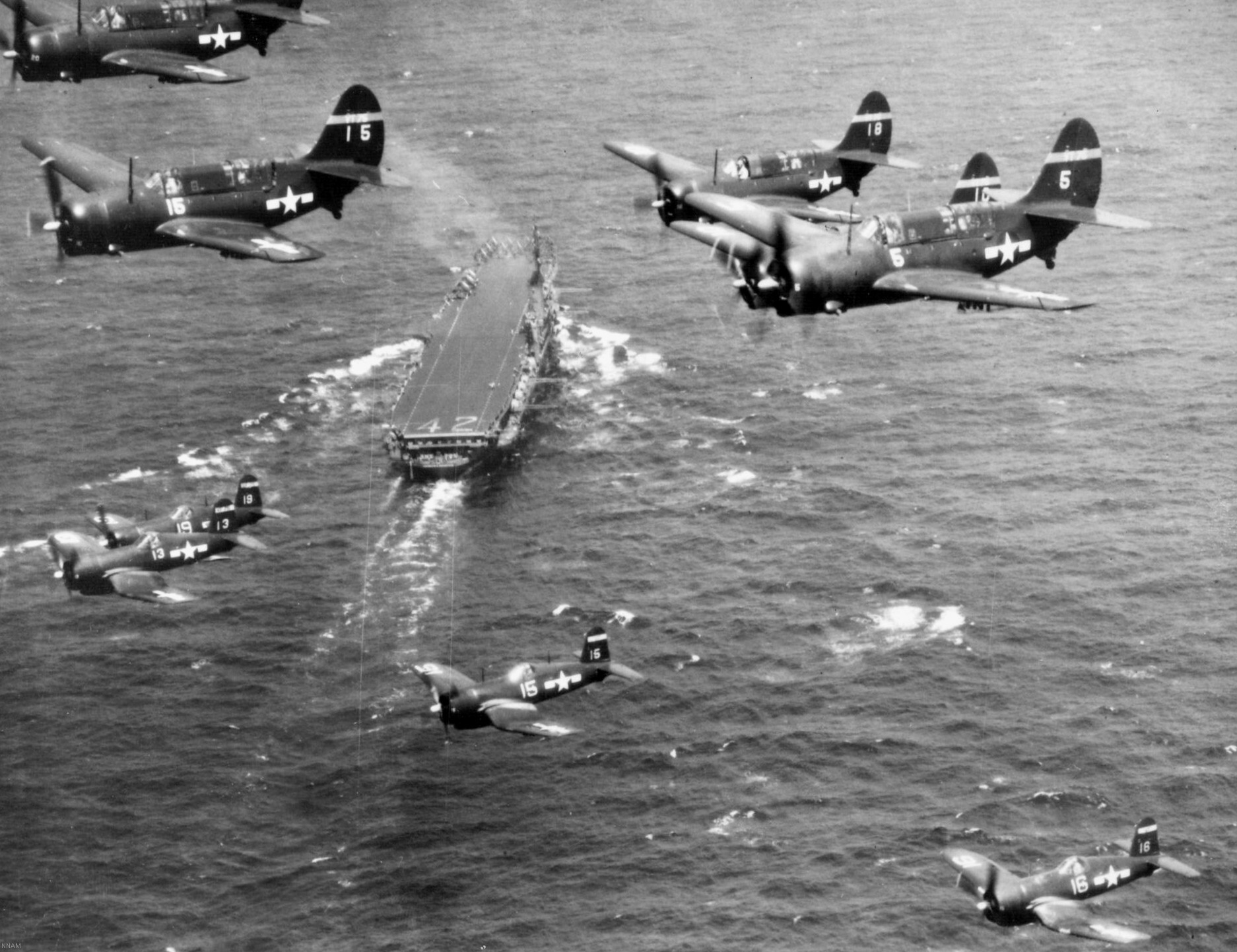  Vought F4U-4 Corsair fighters from Fighting Squadron VF-75 Gay Blades and Curtiss SB2C-4E Helldivers of Torpedo Squadron VT-75 Fish Hawks fly over USS Franklin D. Roosevelt (CVB 42). Both squadrons were assigned to Carrier Air Group 75 (CVBG-75) aboard the FDR for a cruise in the Western Atlantic from 19 April to 25 May 1946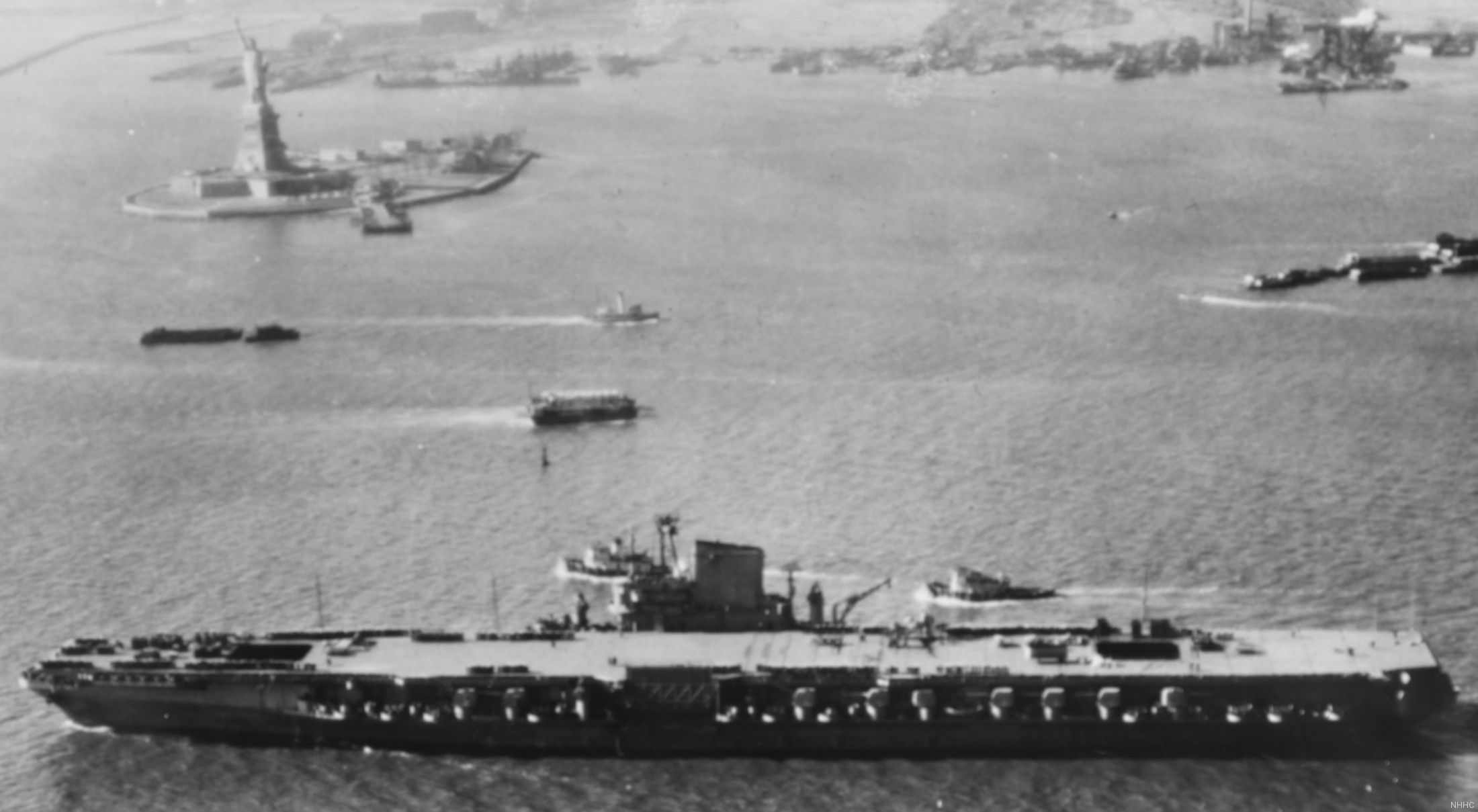  November 1945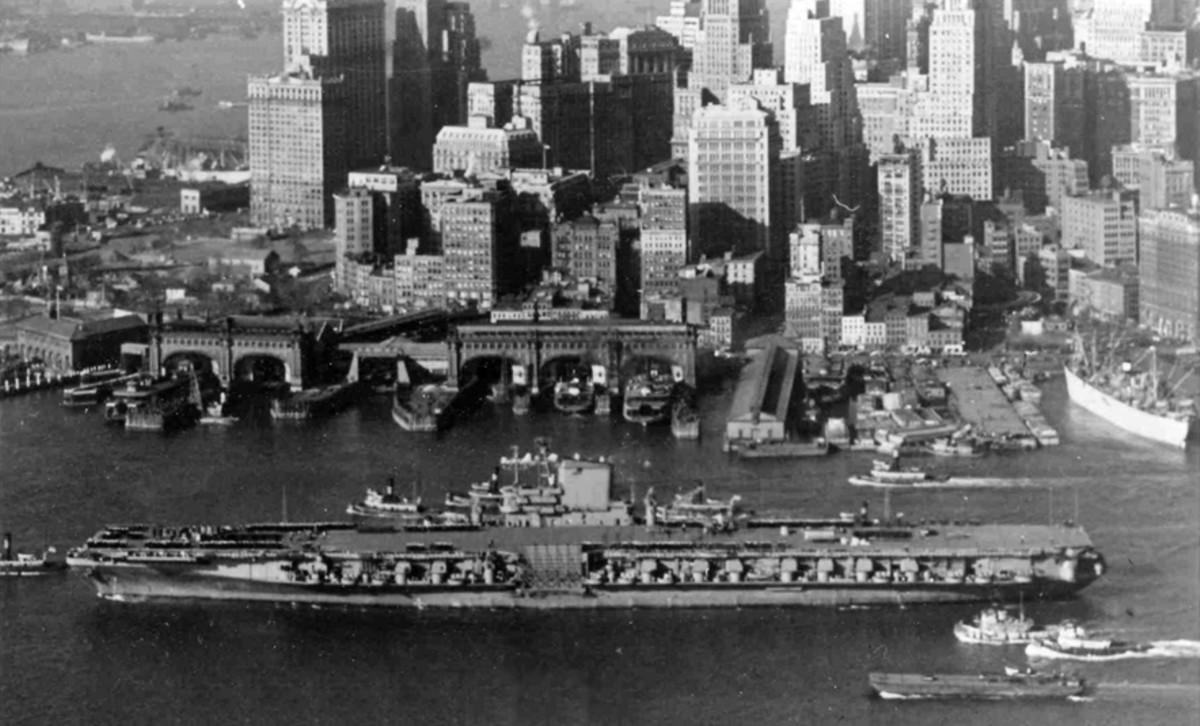  New York City - late 1945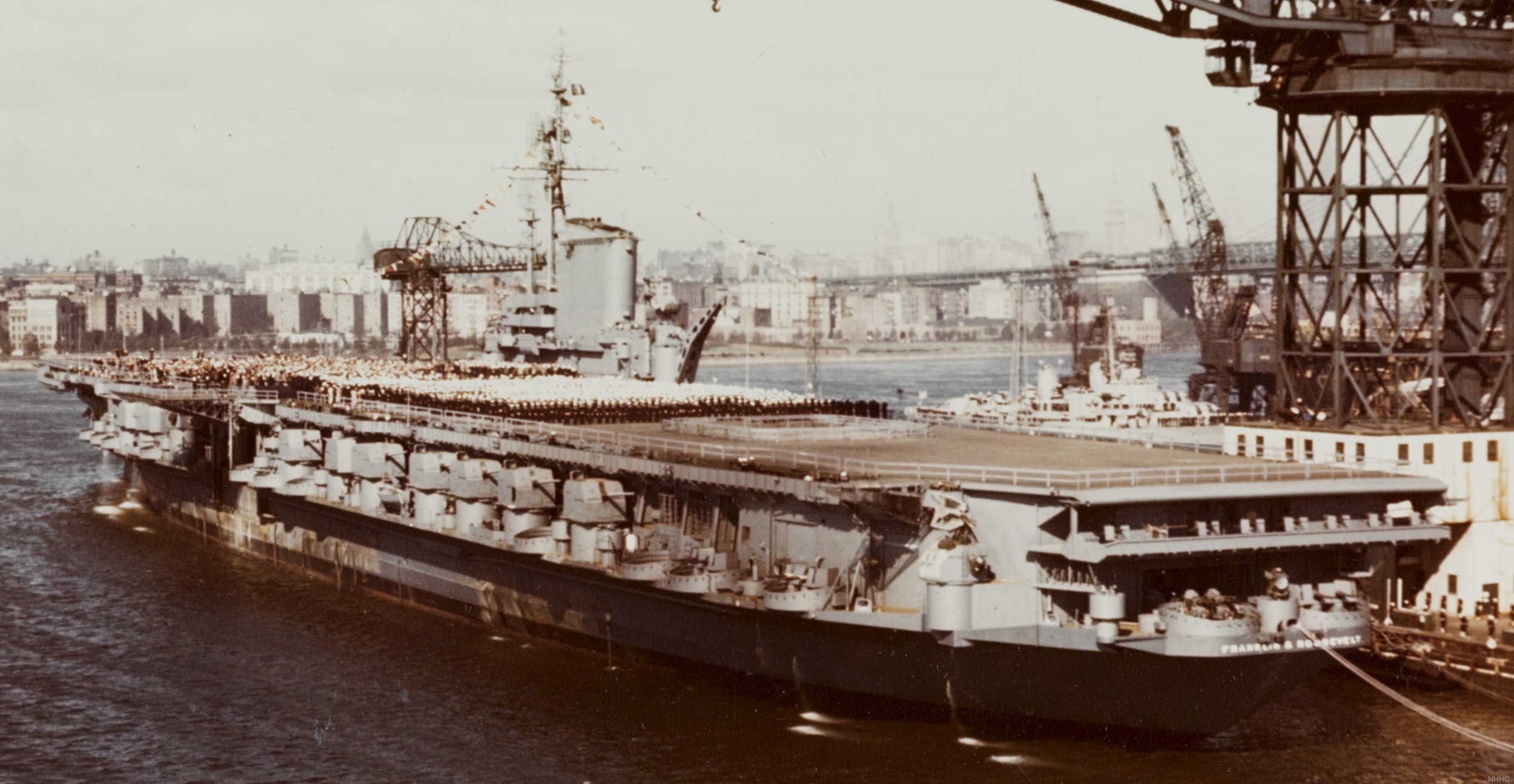  commissioning at the New York Navy Yard, Brooklyn on Navy Day - October 27, 1945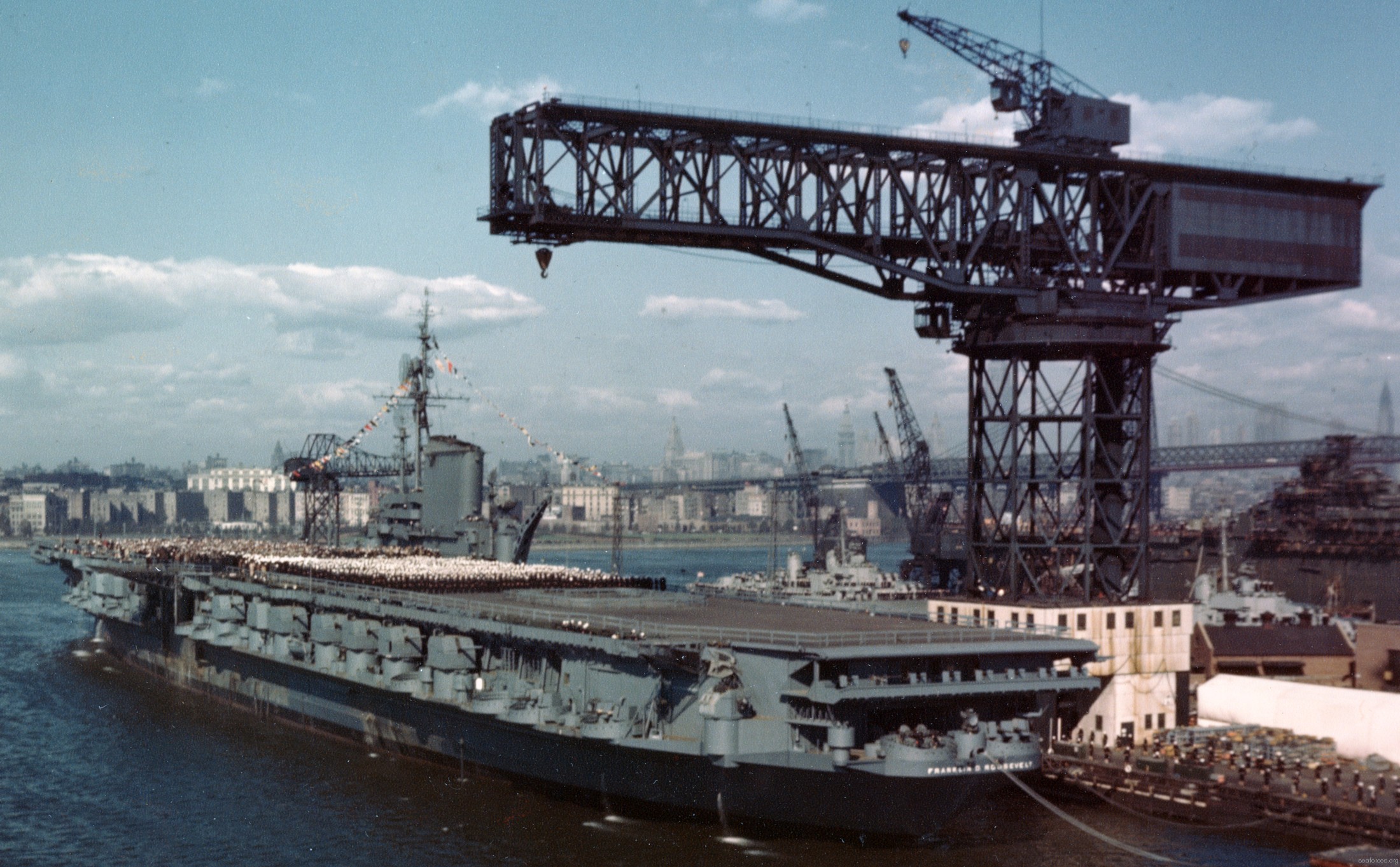  commissioning at the New York Navy Yard, Brooklyn on Navy Day - October 27, 1945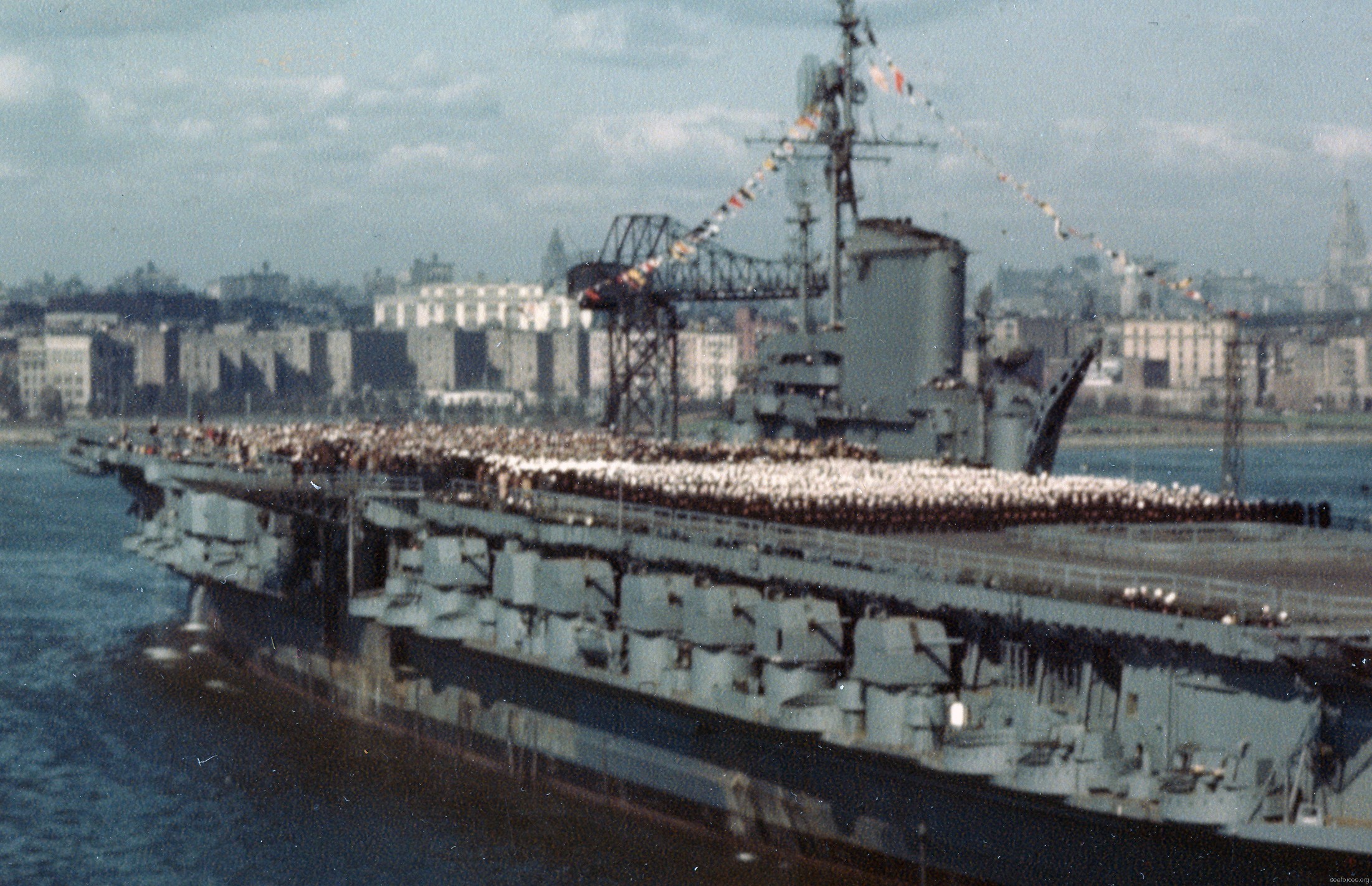  excerpt | |||||
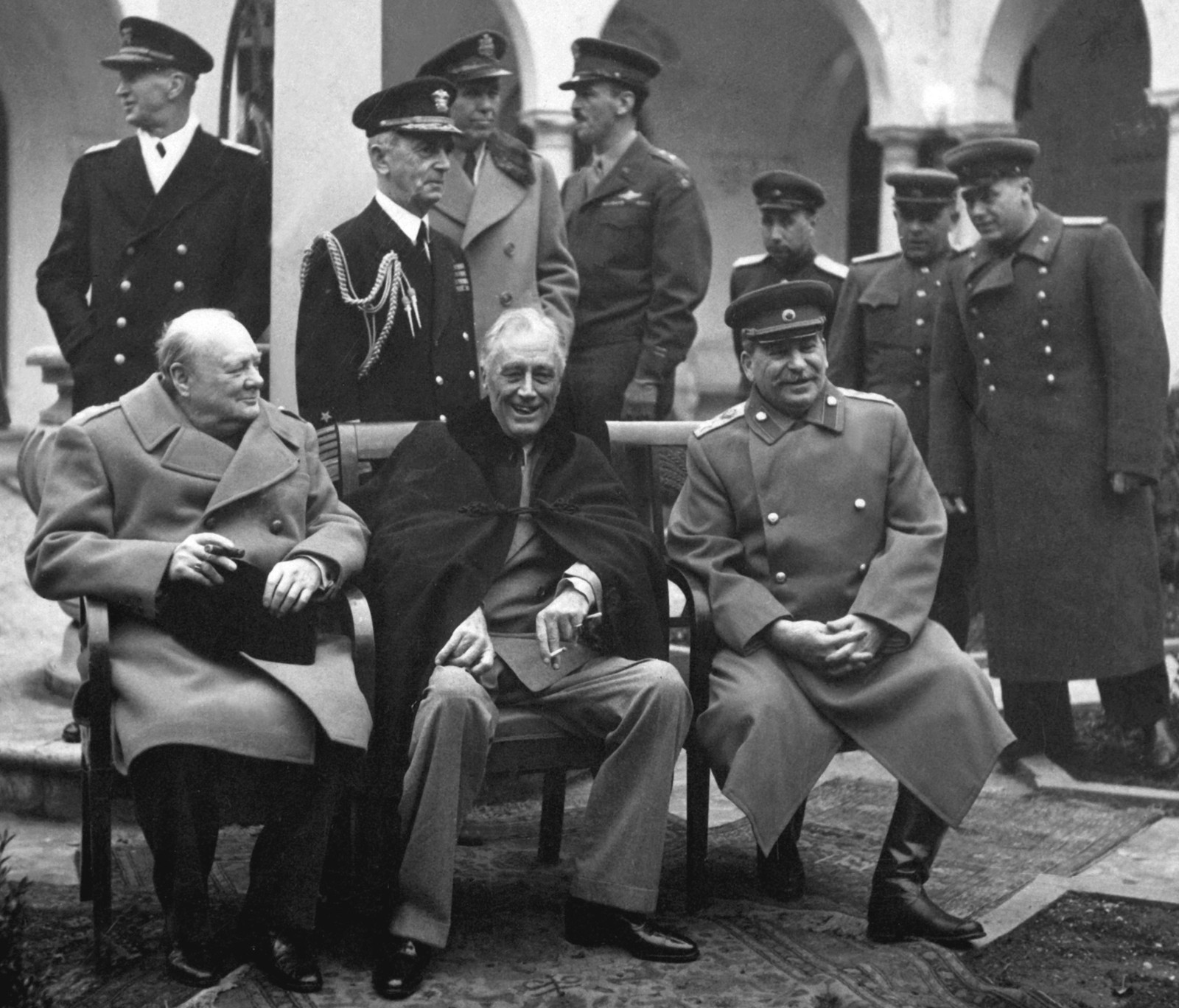
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (January 30, 1882 - April 12, 1945)... often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American statesman and political leader who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. A member of the Democratic party, he won a record four presidential elections and became a central figure in world events during the first half of the 20th century. Roosevelt directed the federal government during most of the Great Depression, implementing his New Deal domestic agenda in response to the worst economic crisis in U.S. history. As a dominant leader of his party, he built the New Deal Coalition, which realigned American politics into the Fifth Party System and defined American liberalism throughout the middle third of the 20th century. His third and fourth terms were dominated by World War II. Roosevelt is widely considered to be one of the most important figures in American history, as well as among the most influential figures of the 20th century. Though he has been subject to substantial criticism, he is generally rated by scholars as one of the three greatest U.S. presidents, along with George Washington and Abraham Lincoln.Roosevelt was born in Hyde Park, New York, to a Dutch American family made well known by Theodore Roosevelt, the 26th president of the United States, and William Henry Aspinwall. FDR attended Groton School, Harvard College, and Columbia Law School, and went on to practice law in New York City. In 1905, he married his fifth cousin once removed, Eleanor Roosevelt. They had six children, of whom five survived into adulthood. He won election to the New York State Senate in 1910, and then served as Assistant Secretary of the Navy under President Woodrow Wilson during World War I. Roosevelt was James M. Cox's running mate on the Democratic Party's 1920 national ticket, but Cox was defeated by Warren G. Harding. In 1921, Roosevelt contracted a paralytic illness, believed at the time to be polio, and his legs became permanently paralyzed. While attempting to recover from his condition, Roosevelt founded the treatment center in Warm Springs, Georgia, for people with poliomyelitis. In spite of being unable to walk unaided, Roosevelt returned to public office by winning election as Governor of New York in 1928. He was in office from 1929 to 1933 and served as a reform Governor, promoting programs to combat the economic crisis besetting the United States at the time.In the 1932 presidential election, Roosevelt defeated Republican President Herbert Hoover in a landslide. Roosevelt took office while the United States was in the midst of the Great Depression, the worst economic crisis in the country's history. During the first 100 days of the 73rd United States Congress, Roosevelt spearheaded unprecedented federal legislation and issued a profusion of executive orders that instituted the New Deal - a variety of programs designed to produce relief, recovery, and reform. He created numerous programs to provide relief to the unemployed and farmers while seeking economic recovery with the National Recovery Administration and other programs. He also instituted major regulatory reforms related to finance, communications, and labor, and presided over the end of Prohibition. He harnessed radio to speak directly to the American people, giving 30 "fireside chat" radio addresses during his presidency and becoming the first American president to be televised. The economy having improved rapidly from 1933 to 1936, Roosevelt won a landslide reelection in 1936. However, the economy then relapsed into a deep recession in 1937 and 1938. After the 1936 election, Roosevelt sought passage of the Judiciary Reorganization Bill of 1937 (the "court packing plan"), which would have expanded the size of the Supreme Court of the United States. The bipartisan Conservative Coalition that formed in 1937 prevented passage of the bill and blocked the implementation of further New Deal programs and reforms. Major surviving programs and legislation implemented under Roosevelt include the Securities and Exchange Commission, the National Labor Relations Act, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, and Social Security.Roosevelt ran successfully for reelection in 1940. His victory made him the only U.S. President to serve for more than two terms. With World War II looming after 1938, Roosevelt gave strong diplomatic and financial support to China, the United Kingdom and eventually the Soviet Union while the U.S. remained officially neutral. Following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, an event he famously called "a date which will live in infamy", Roosevelt obtained a declaration of war on Japan the next day, and a few days later, on Germany and Italy; all three declarations were very soon approved by Congress. Assisted by his top aide Harry Hopkins and with very strong national support, he worked closely with British Prime Minister Winston Churchill, Soviet leader Joseph Stalin and Chinese Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek in leading the Allied Powers against the Axis Powers. Roosevelt supervised the mobilization of the U.S. economy to support the war effort, and implemented a Europe first strategy, making the defeat of Germany a priority over that of Japan. He also initiated the development of the world's first atomic bomb, and worked with the other Allied leaders to lay the groundwork for the United Nations and other post-war institutions. Roosevelt won reelection in 1944 but with his physical health declining during the war years, he died in April 1945, just 11 weeks into his fourth term. The Axis Powers surrendered to the Allies in the months following Roosevelt's death, during the presidency of his successor, Harry S. Truman.source: wikipedia
|
喜欢刀锋朋友的这个贴子的话, 请点这里投票,“赞”助支持!
请点这里投票,“赞”助支持!


内容来自网友分享,若违规或者侵犯您的权益,请联系我们
所有跟帖: ( 主贴楼主有权删除不文明回复,拉黑不受欢迎的用户 )
打开微信,扫一扫[Scan QR Code]
进入内容页点击屏幕右上分享按钮
进入内容页点击屏幕右上分享按钮
楼主前期社区热帖:
- 空中口占:沁园春,答黄小兔 11/09/24
- 🧧超级大红包! 11/07/24
- 古色儿也有可爱的一面…… 11/07/24
- 朝鲜特种部队首战无伤亡,乌防长惊爆内幕 11/07/24
- 碟中谍:1969年美国派王牌女特工刺杀毛主席,反被我方美男计化解 11/07/24
- 江苏金湖:水上森林初冬景如画 11/07/24
- 外军轰炸上海,解放军如何应对? 11/07/24
- 朝鲜士兵炮击乌军!与俄军编成方式及指挥体系曝光了! 11/07/24
- 火爆全网的乡党委书记遭领导性侵事件水落石出,法院审理揭露真相 11/07/24
- 狗子偷了一个大白鹅回家,铲屎官尴尬录像:真不是我教的 11/07/24
- 响应特朗普号召,马斯克对台重拳出击 11/07/24
- 秦城监狱里的刘志军托话给女儿:千万不要从政 11/07/24
- 凌晨突发!美国,降息25个基点!中国资产,暴涨! 11/07/24
- 特朗普胜选后美“起义军”打响第一枪,西雅图开砸 11/07/24
- 特朗普“和平方案”曝光:乌克兰20年内不得加入北约 11/07/24
- 沙特宣布启动中阿大陆桥计划?连接波斯湾与红海,对中东地缘格局有何影响 11/07/24
- 俄罗斯最忠诚的小弟,为何迟迟不愿与俄罗斯合并? 11/07/24
- 立陶宛后悔了?立准总理喊话:想让中国大使回归 11/07/24
- 特朗普行动迅速,酝酿新政府关键职位人选,推翻拜登政府的诸多政策 11/07/24
- 特朗普重返白宫可能会做这七件事,他的第二个任期会有何大不同? 11/07/24
>>>>查看更多楼主社区动态...





